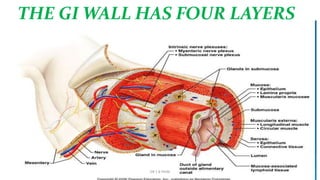
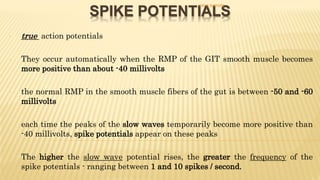
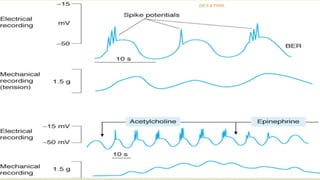
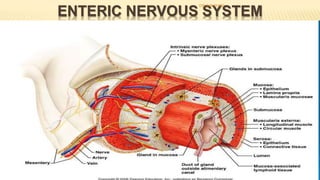
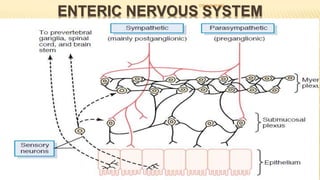
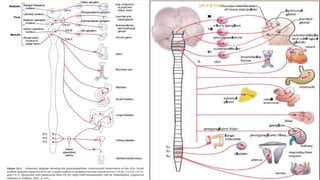
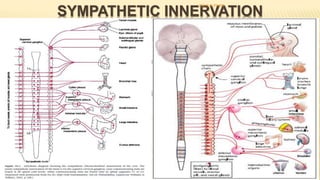
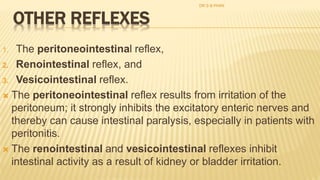
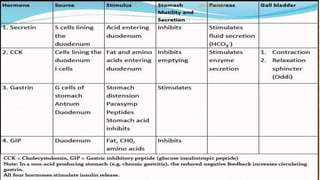
The document discusses the general control of the gastrointestinal tract. It covers the electrical activity of the GI wall generated by slow waves and spikes, the enteric nervous system consisting of the myenteric and submucosal plexuses, autonomic control by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, afferent sensory nerve fibers, gastrointestinal reflexes, and hormonal control by factors like gastrin, cholecystokinin, and secretin. Together, these systems work to coordinate digestion and movement of food through the GI tract.