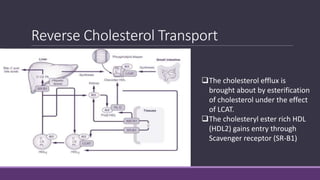
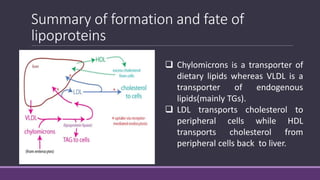
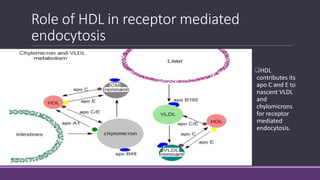
1. HDL is synthesized in the liver and intestine and transports cholesterol from tissues to the liver via reverse cholesterol transport.
2. The enzyme LCAT esterifies free cholesterol on HDL particles, forming a hydrophobic core and spherical HDL structure that can deliver cholesterol to the liver.
3. HDL accepts cholesterol from tissues via SR-B1 and transports it back to the liver for excretion, in a process called reverse cholesterol transport that removes excess cholesterol from the body.