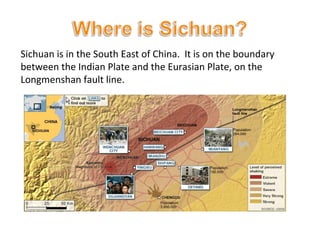
This document provides facts and figures about the 2008 Sichuan earthquake in China. It describes the earthquake having a magnitude of 7.9 and causing approximately 69,000 deaths and 18,000 people missing. It also discusses the effects on infrastructure like collapsed buildings, and the immediate and long-term responses, which included search and rescue efforts as well as rebuilding plans.