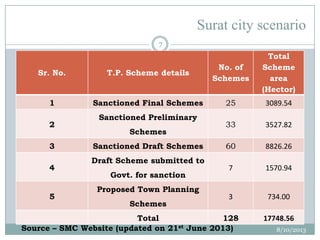
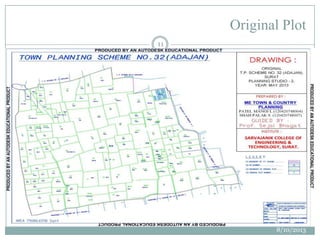
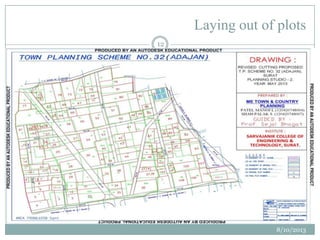
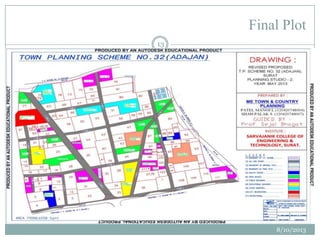
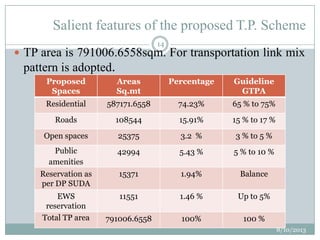
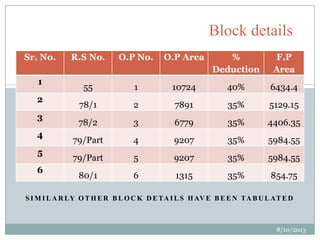
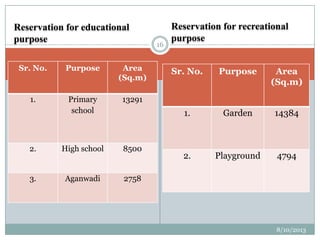
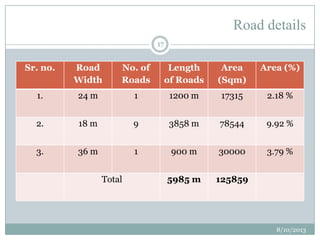
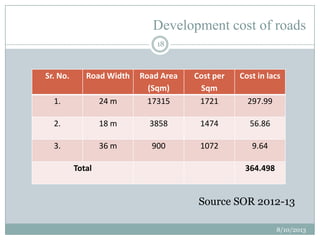
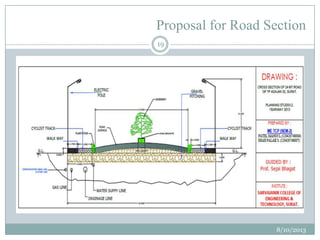
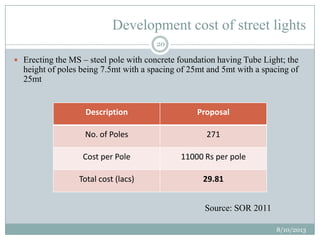
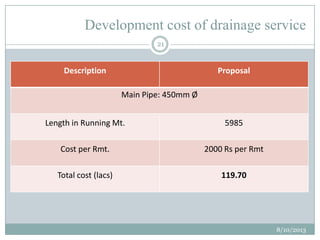
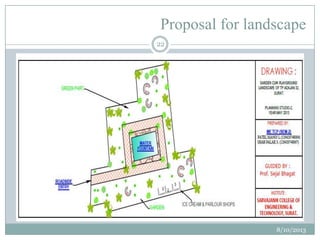
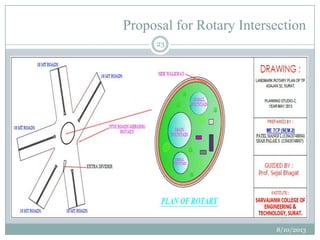
This document summarizes a town planning scheme proposal for an area in Adajan, Surat, Gujarat, India. It includes an analysis of the existing town planning scheme and proposes an alternative scheme. The proposed scheme divides the 79.1 hectare area into residential, road, open space, and public amenity plots. It provides details on the block layout, road widths and costs, reservations for education and recreation, landscape and intersection proposals. The conclusion states that town planning schemes are an effective land management tool that allow for public participation in developing unplanned areas and controlling haphazard urban growth.