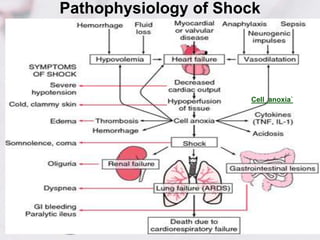
1. Shock is defined as inadequate tissue perfusion and cellular dysfunction due to an imbalance between oxygen delivery and demand.
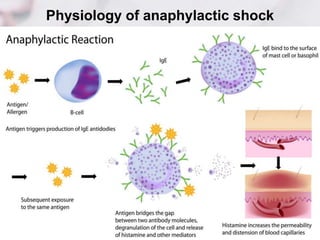
2. There are several types of shock including hypovolemic, cardiogenic, obstructive, anaphylactic, and neurogenic shock.
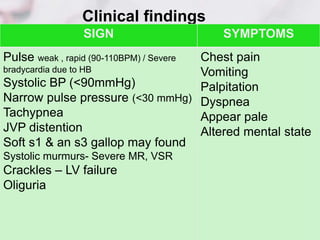
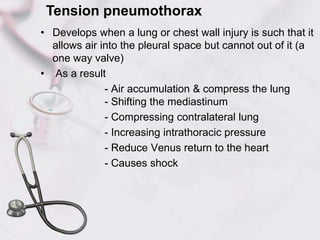
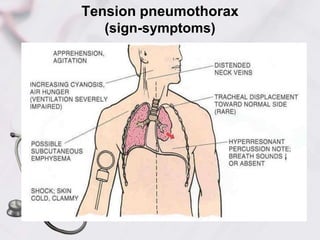
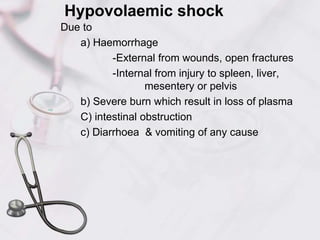
3. Hypovolemic shock occurs due to loss of intravascular volume from hemorrhage, burns, or fluid losses. Cardiogenic shock results from cardiac failure leading to low cardiac output. Obstructive shock involves obstruction of venous return such as from tension pneumothorax.









![Cardiogenic shock /Acute circulatory Failure
• Is a state of end-organ hypoperfusion due to
cardiac failure.
• Cardiogenic shock
-systemic hypoperfusion due to severe
depression of the cardiac index (<2.2 [L/min]/m2)
- sustained systolic arterial hypotension (<90
mmHg) despite an elevated filling pressure
(pulmonary capillary wedge pressure [PCWP]
>18 mmHg)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shock-171013050847/85/Shock-12-320.jpg)