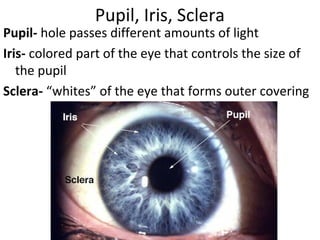
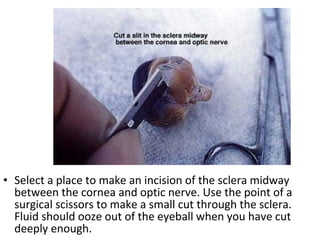
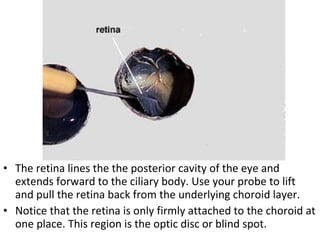
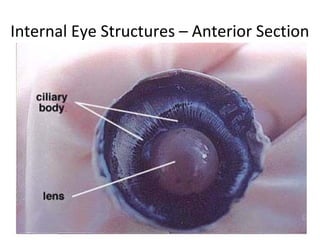
The document summarizes the key parts of the eye that students will learn to identify through a dissection lab. It includes 13 major parts: cornea, iris, pupil, ciliary muscle, sclera, vitreous humor, retina, blind spot, choroid layer, optic nerve, tapetum lucidum, lens, and aqueous humor. The summary provides step-by-step instructions for students to follow during the dissection in order to observe each part and understand its function.