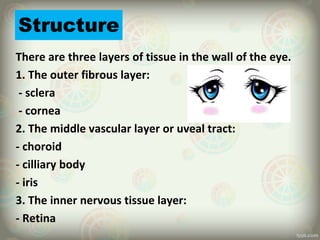
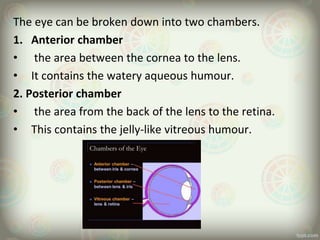
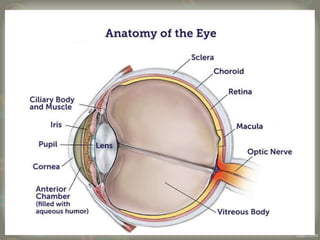
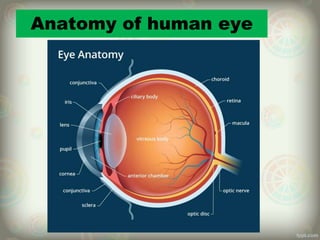
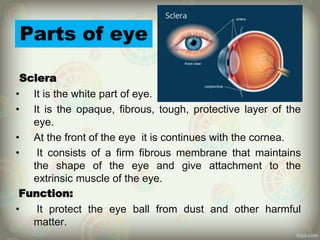
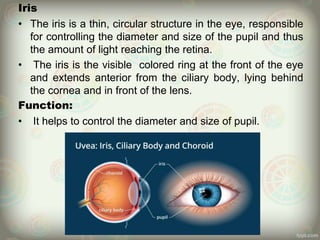
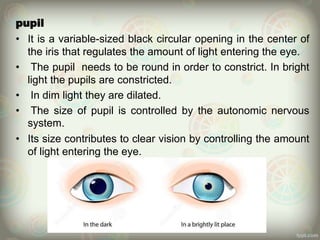
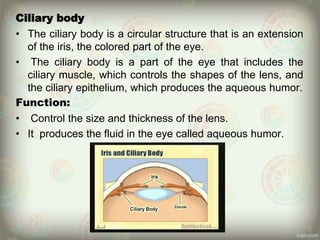
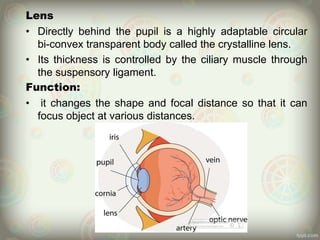
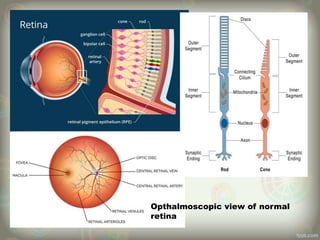
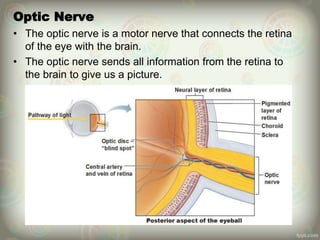
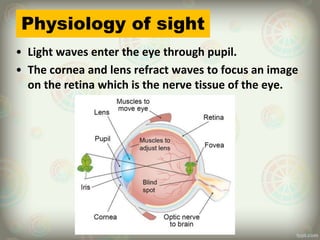
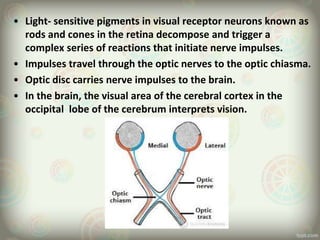
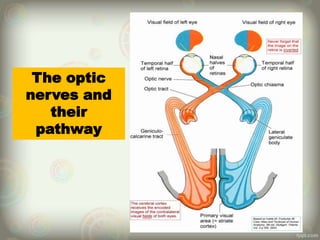
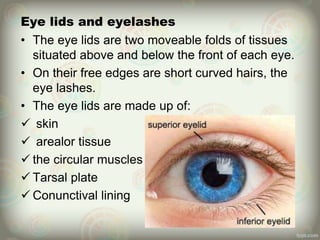
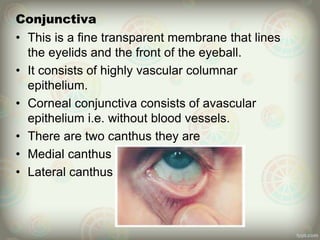
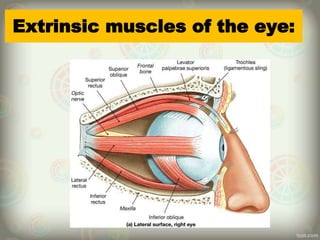
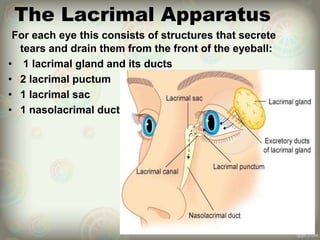
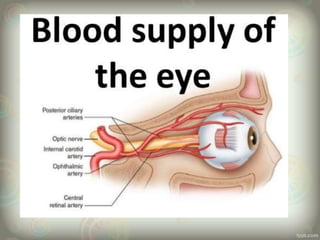
The human eye is roughly spherical and resembles a camera. It has three layers: the outer fibrous layer containing the sclera and cornea, the middle vascular layer containing the choroid, ciliary body and iris, and the inner nervous layer containing the retina. The eye contains two chambers - the anterior chamber between the cornea and lens containing aqueous humor, and the posterior chamber between the lens and retina containing vitreous humor. Key parts include the iris, pupil, choroid, ciliary body, lens, retina and optic nerve. The eye receives nourishment from the choroid and ciliary body and sends signals to the brain via the optic nerve to provide vision.