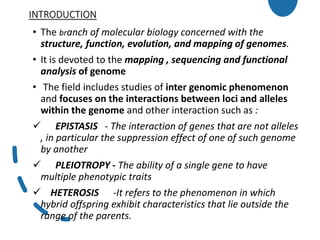
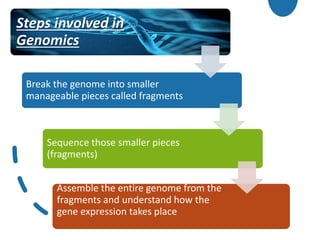
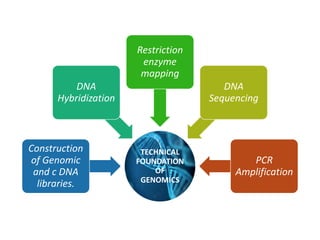
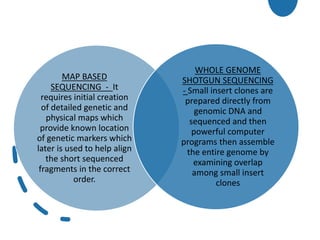
Genomics is the study of genomes through mapping, sequencing, and analysis. It involves sequencing entire genomes and analyzing gene function on a genome-wide scale. There are three main areas of genomics: structural genomics focuses on sequencing and mapping genomes; functional genomics examines gene expression and protein interactions; and comparative genomics compares genomic features between organisms to study evolution and biology. Techniques like DNA sequencing, microarrays, and bioinformatics are used to efficiently analyze entire genomes and understand how the structure and function of genomes relate to biological processes.




![1] Genetic Maps
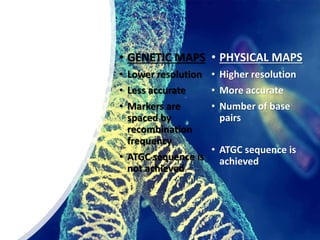
• Also called linkage maps . Provide rough approximation of location of
genes relative to the locations of other known genes.
• These are based on the genetic function of recombination.
• For linked genes, rate of recombination is proportional to physical
distance between loci. It is determined by determining the progeny.
• Distance of genetic maps measures in percent recombination
(centimorgans) or map units.
RECOMBINATION
FREQUENCY BETWEEN LOCI
CONCLUSION
=50% Loci are located on different chromosome
or far apart on same chromosome
<50% Both loci are linked,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genomics-201029132730/85/Genomics-11-320.jpg)
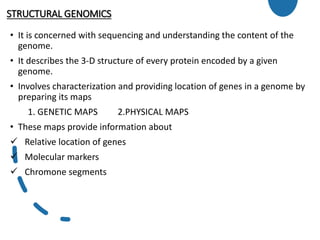
![2] Physical maps
• Based on direct analysis of DNA and place genes in relation
to distances measured in number of base pairs ,kilobase
or mega-base.
• Used to order cloned DNA fragments and to find the order
and physical distance between DNA base pairs by DNA
markers.
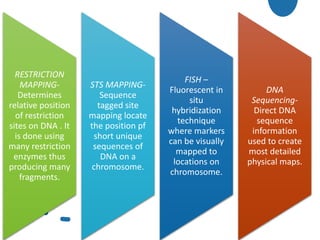
• The techniques used :
Restriction mapping
STS Mapping
FISH
DNA Sequencing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genomics-201029132730/85/Genomics-12-320.jpg)

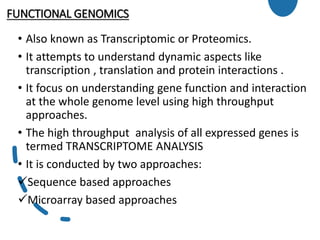
![1] SEQUENCE BASED APPROACHES
Expressed Sequence Tags : ESTs are short
sequences of c DNA typically 200-400
nucleotide in length obtained either from
5’ or 3’ end of c DNA inserts of c DNA
library. They provide a rough estimate of
genes that are actively expressed in a
genome under a particular physiological
condition.
Serial Analysis of Gene Expression-Used
for gene expression profile analysis . It is
more quantitative in determining m RNA
expression in a cell. Short fragments of
DNA excised from c DNA sequences act
as unique markers of gene transcript.
Software tools for SAGE Analysis are
SAGE map , SAGE xprofiler ,SAGE Genie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genomics-201029132730/85/Genomics-18-320.jpg)
![2] MICROARRAY BASED TECHNIQUE
A microarray is a pattern of ss DNA probes which are immobilized
on a surface called chip They use hybridization to detect a specific
DNA or RNA in a sample .It uses a million different probes fixed on
a solid surface .It involved from Southern BlottingIt is used to
analyse the expression of thousands of genes in single reaction and
to understand the genetic causes for abnormal functioning of the
body. Software programs to perform microarray image analysis:
ArrayDB
TIGR Spotfinder
Software programs for microarray data normalization are:
Arrayplot
SNOMAD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genomics-201029132730/85/Genomics-19-320.jpg)