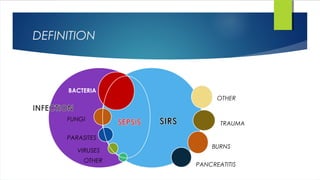
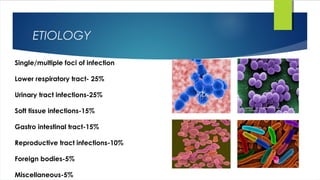
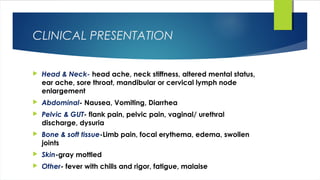
Septic shock is defined as infection combined with systemic inflammatory response syndrome that causes inadequate organ perfusion and progressive organ dysfunction. It is usually caused by bacterial infection spreading from a site of infection into the bloodstream. Diagnosis involves identifying signs of infection and organ dysfunction. Treatment focuses on supporting vital organ functions through respiratory support, circulatory support through fluid resuscitation and vasopressors, administering antibiotics, and treating any underlying infections through drainage or surgery. Prognosis depends on early diagnosis and treatment of infections before organ damage becomes irreversible.