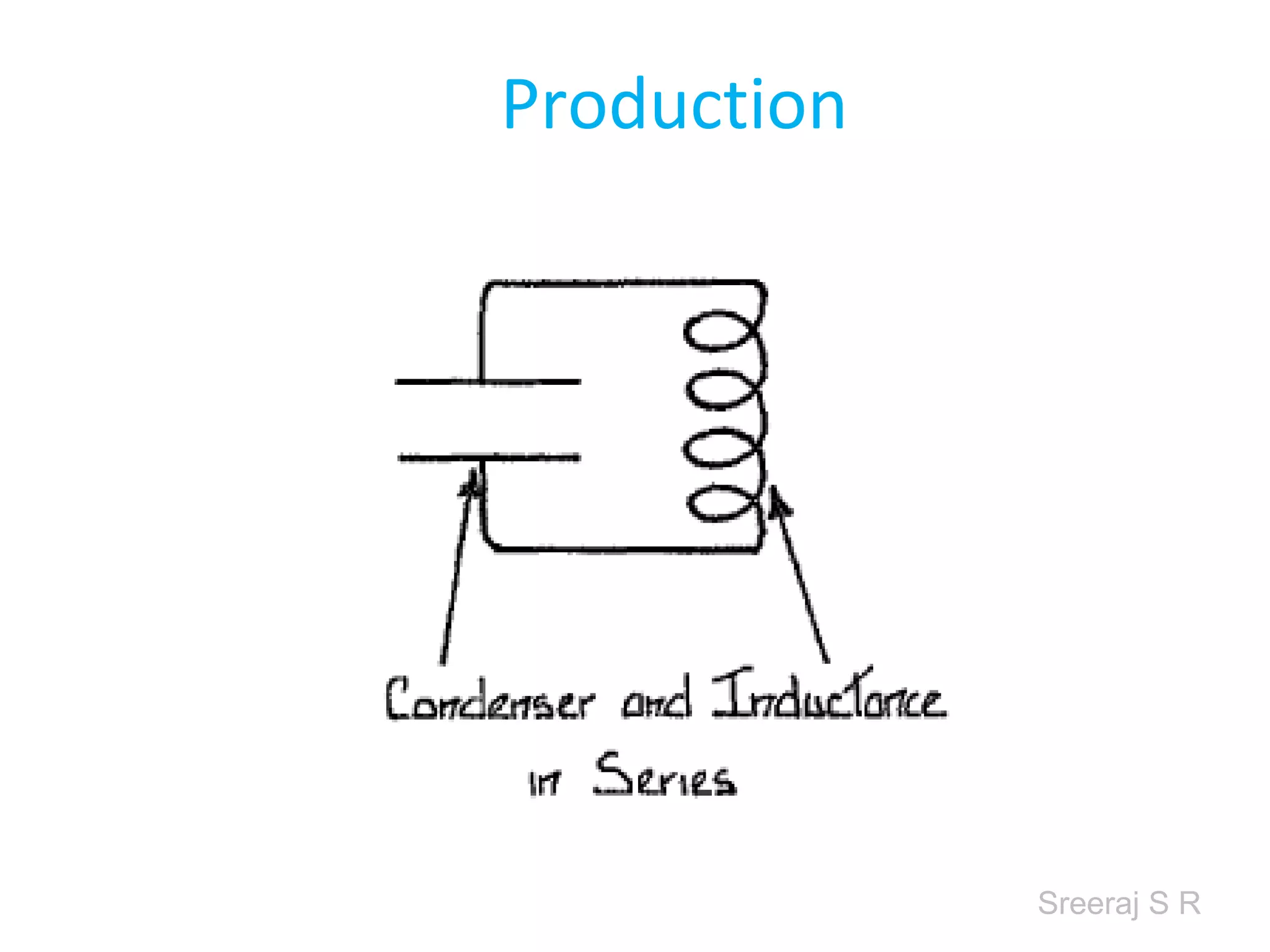
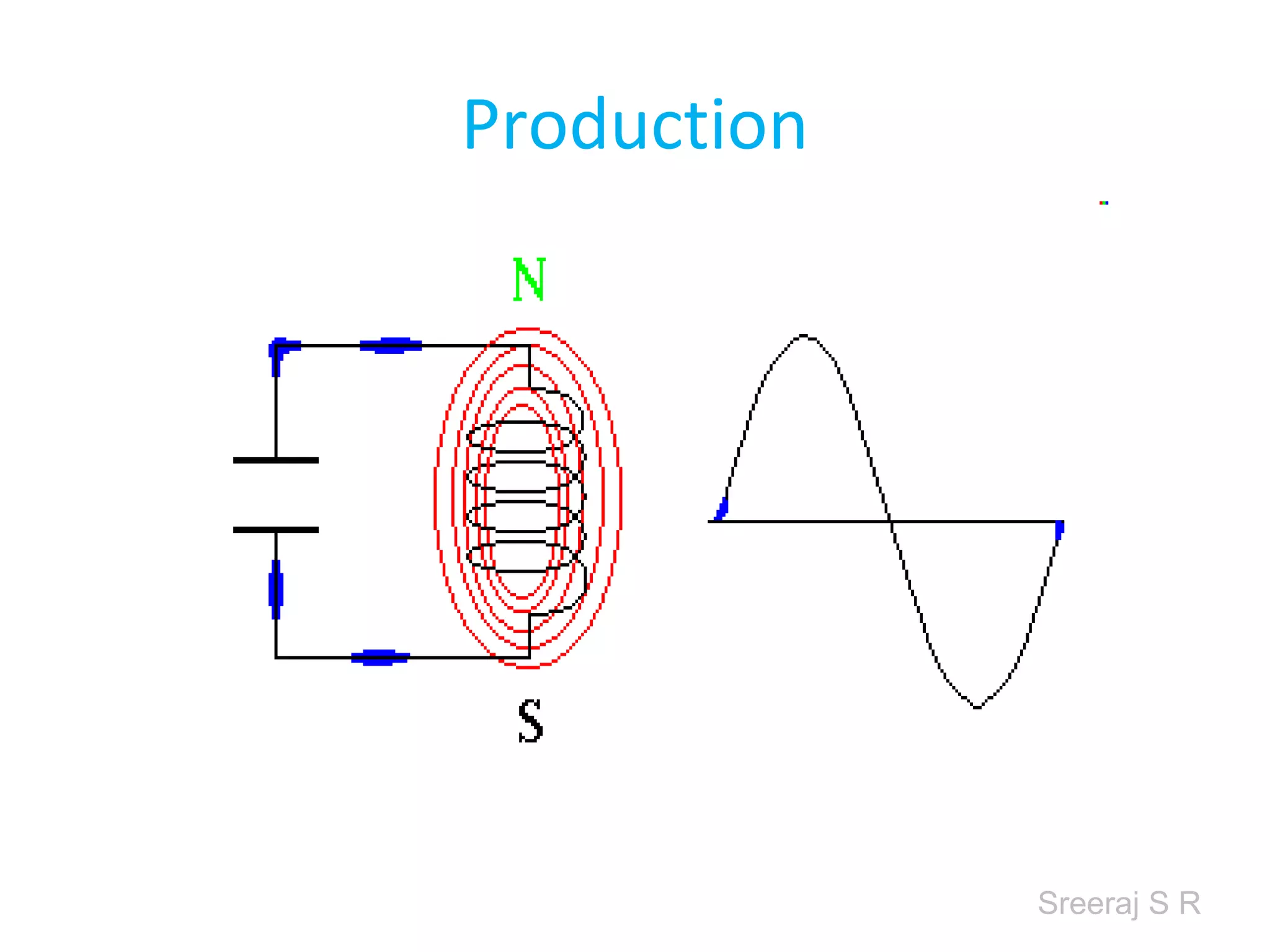
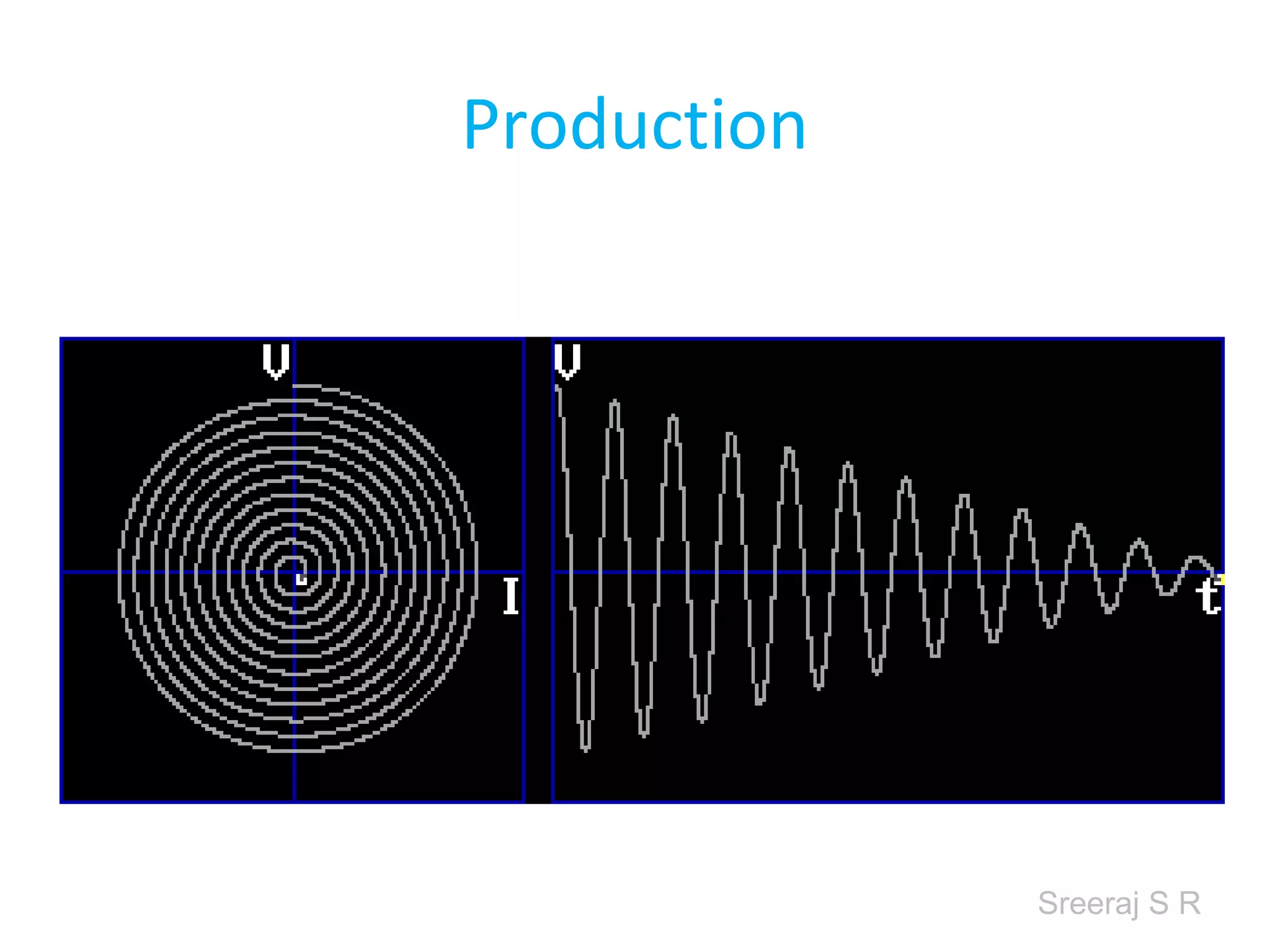
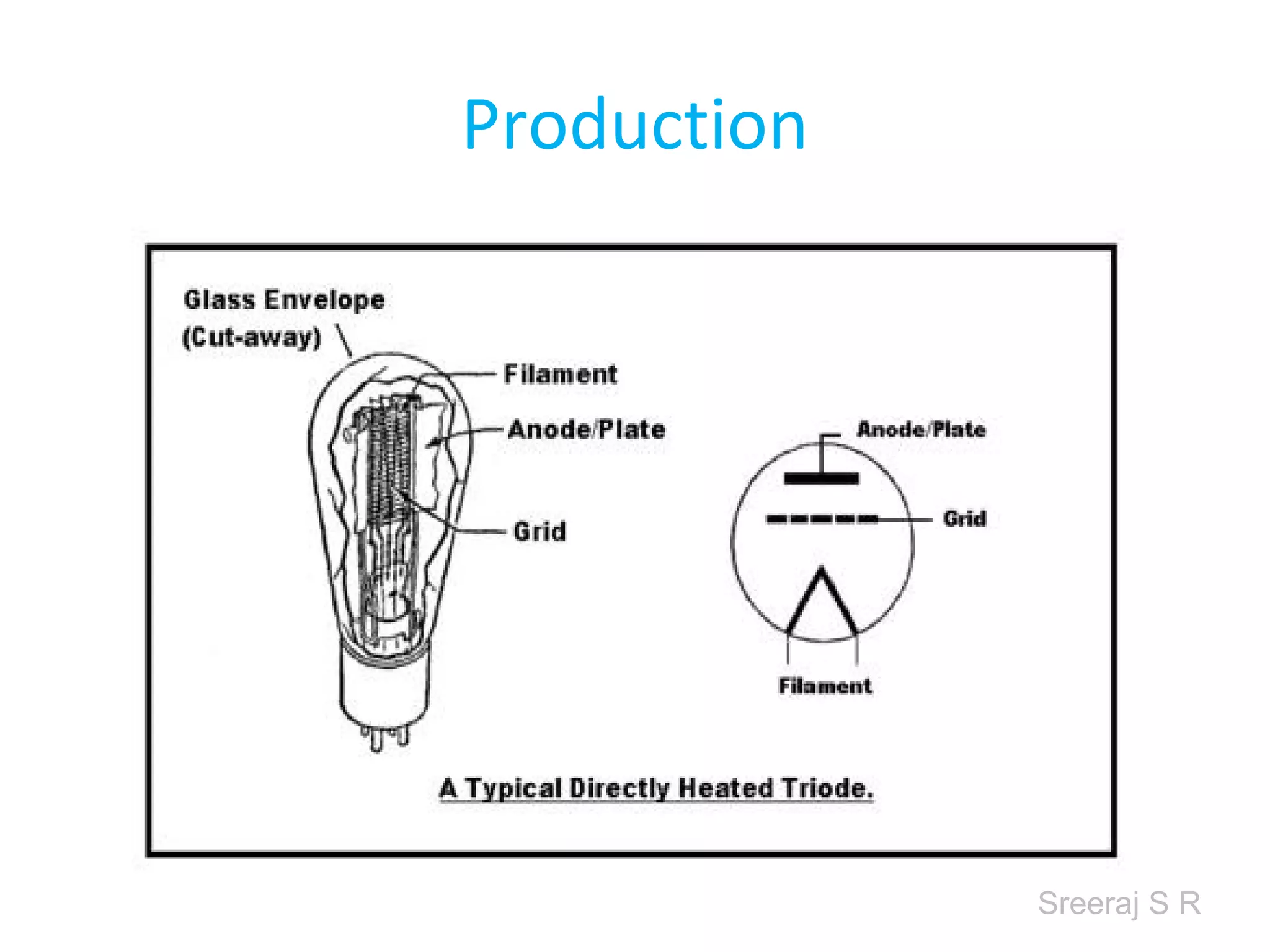
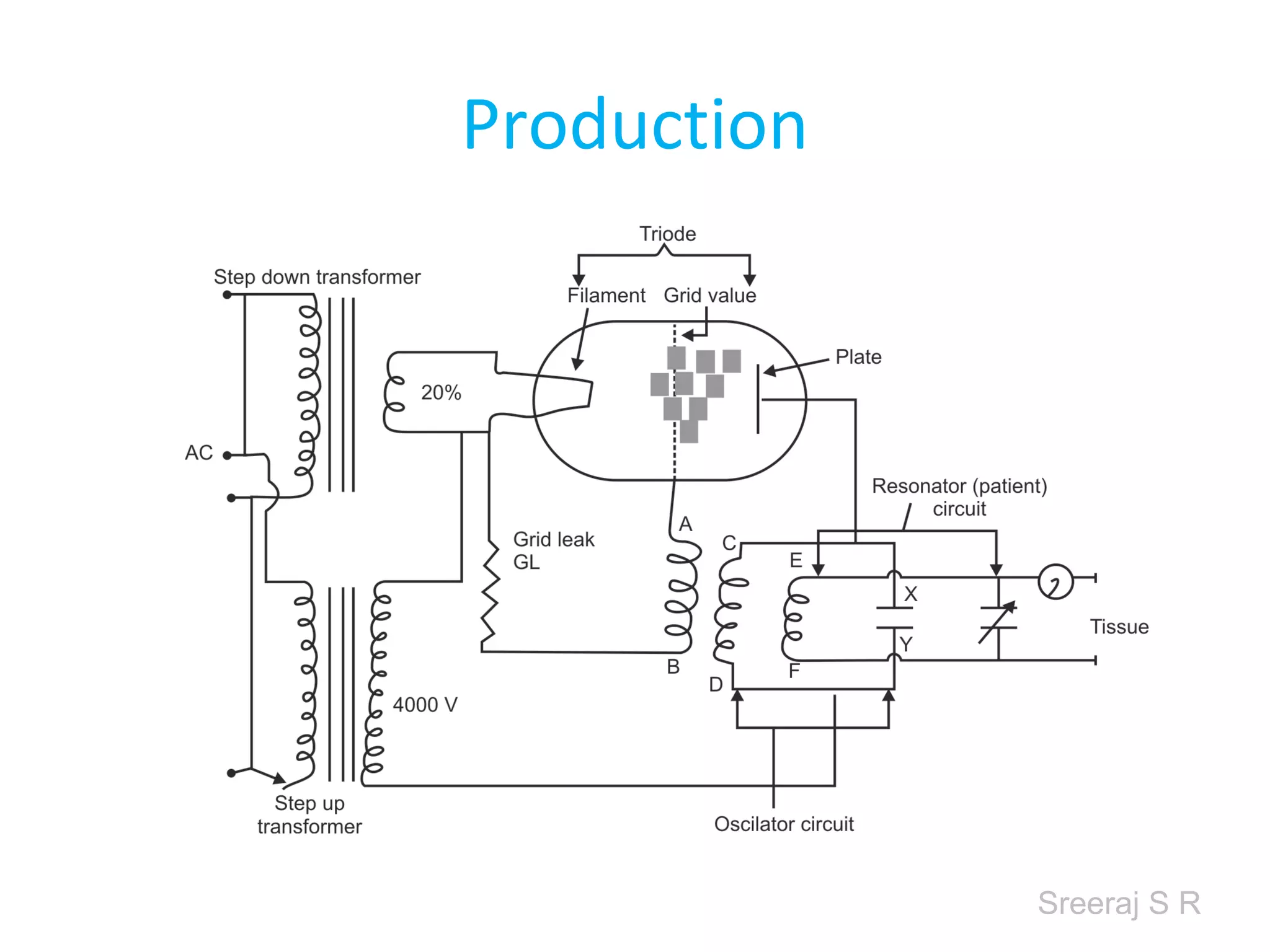
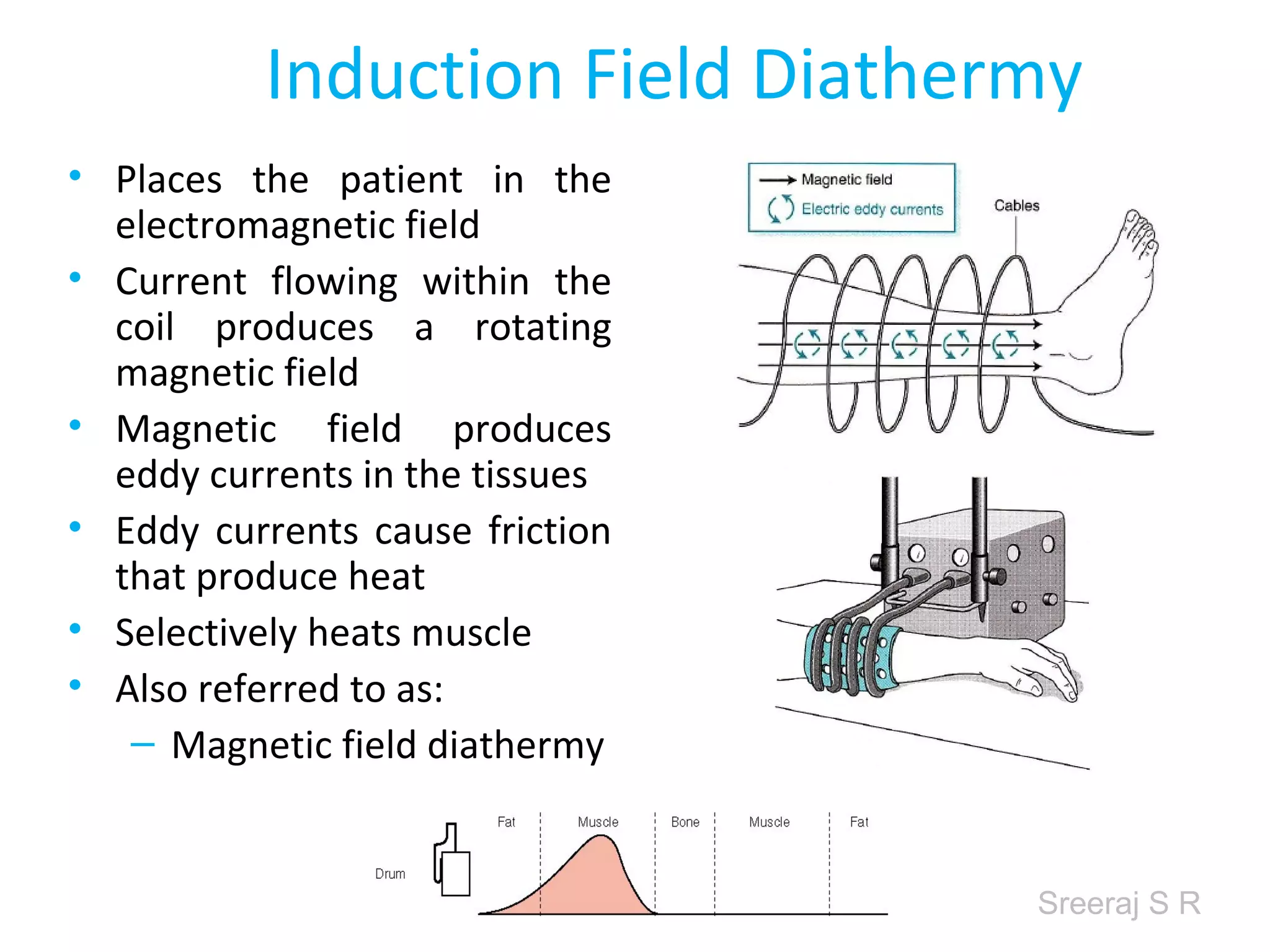
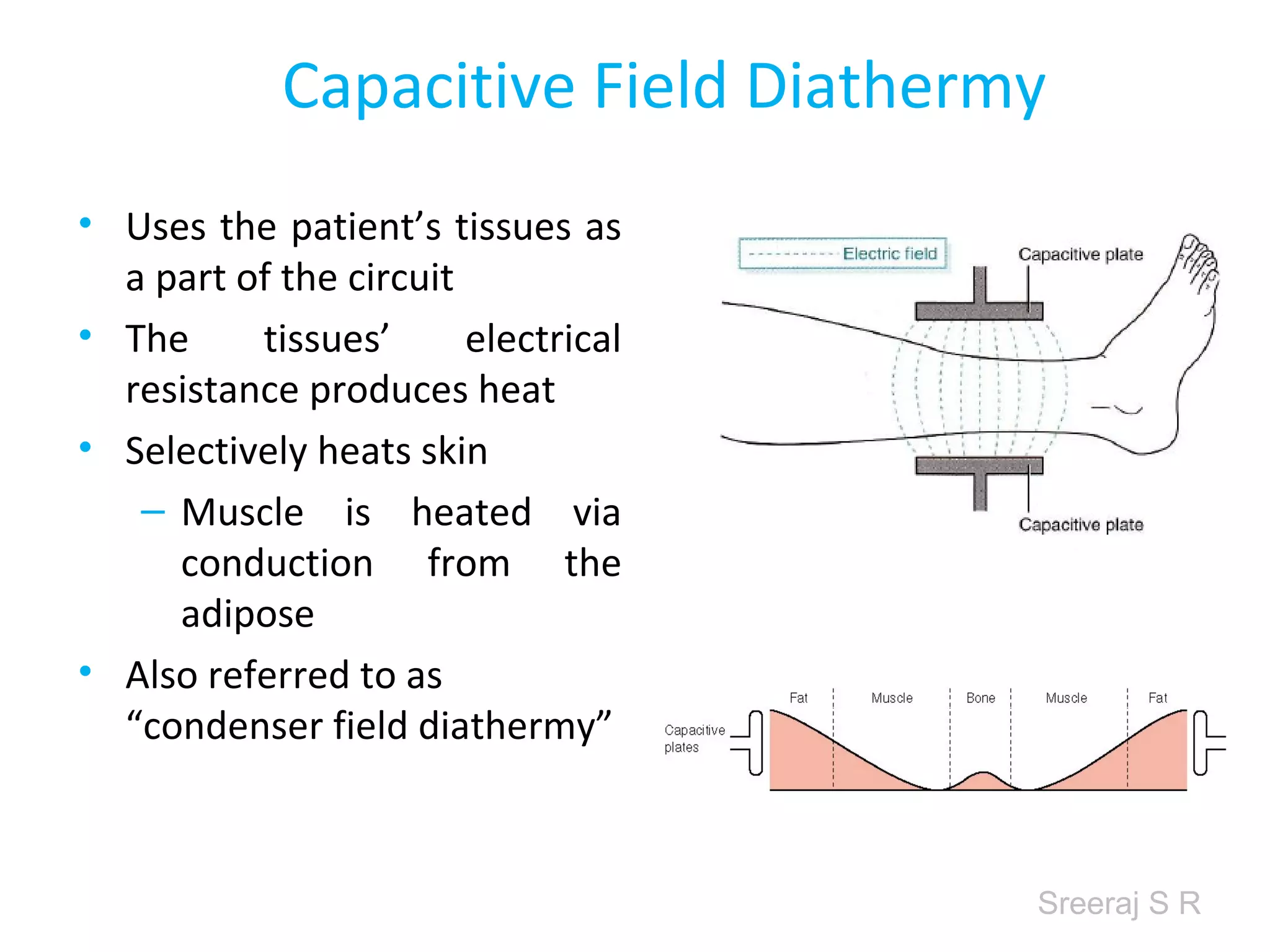
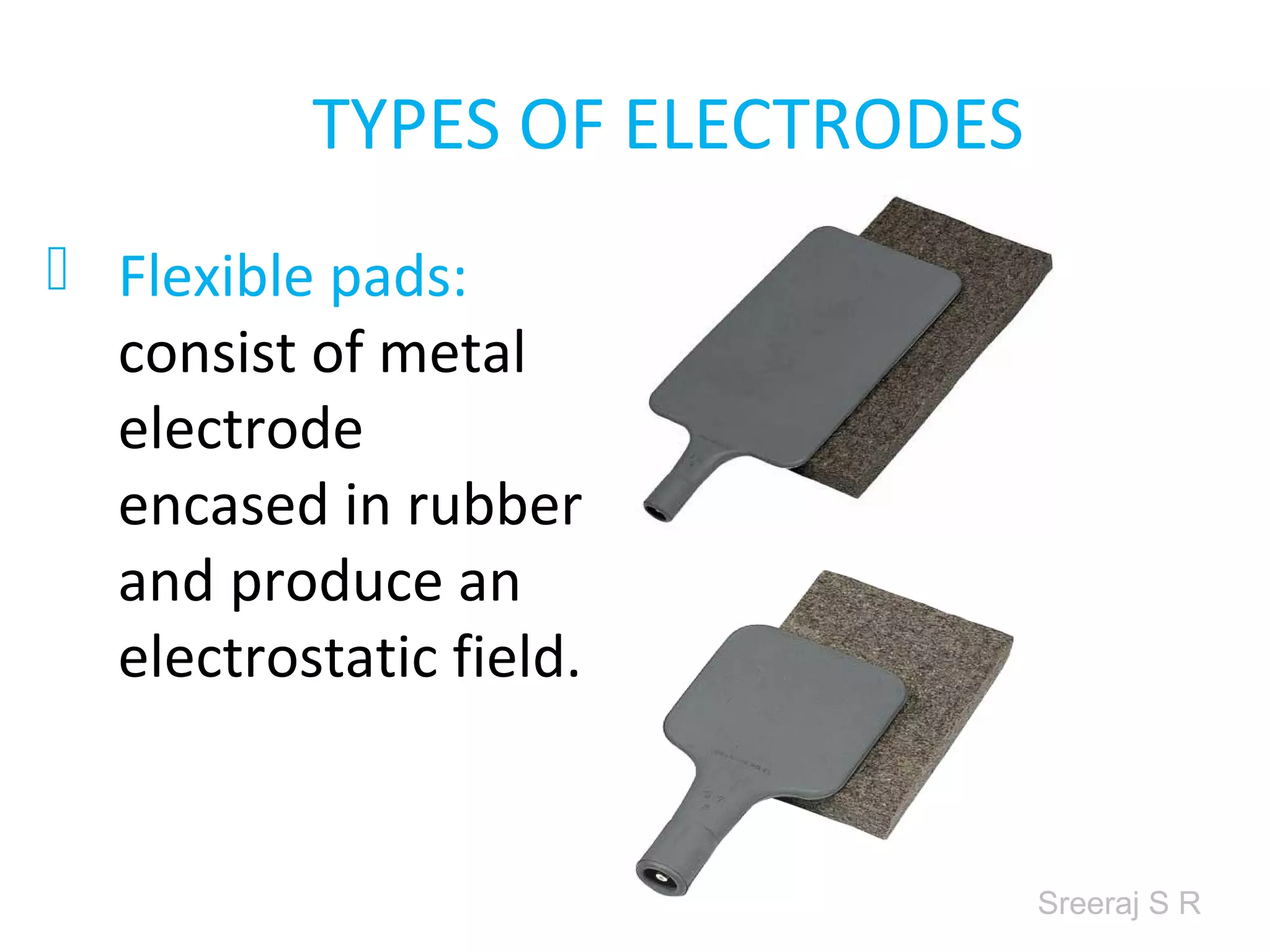
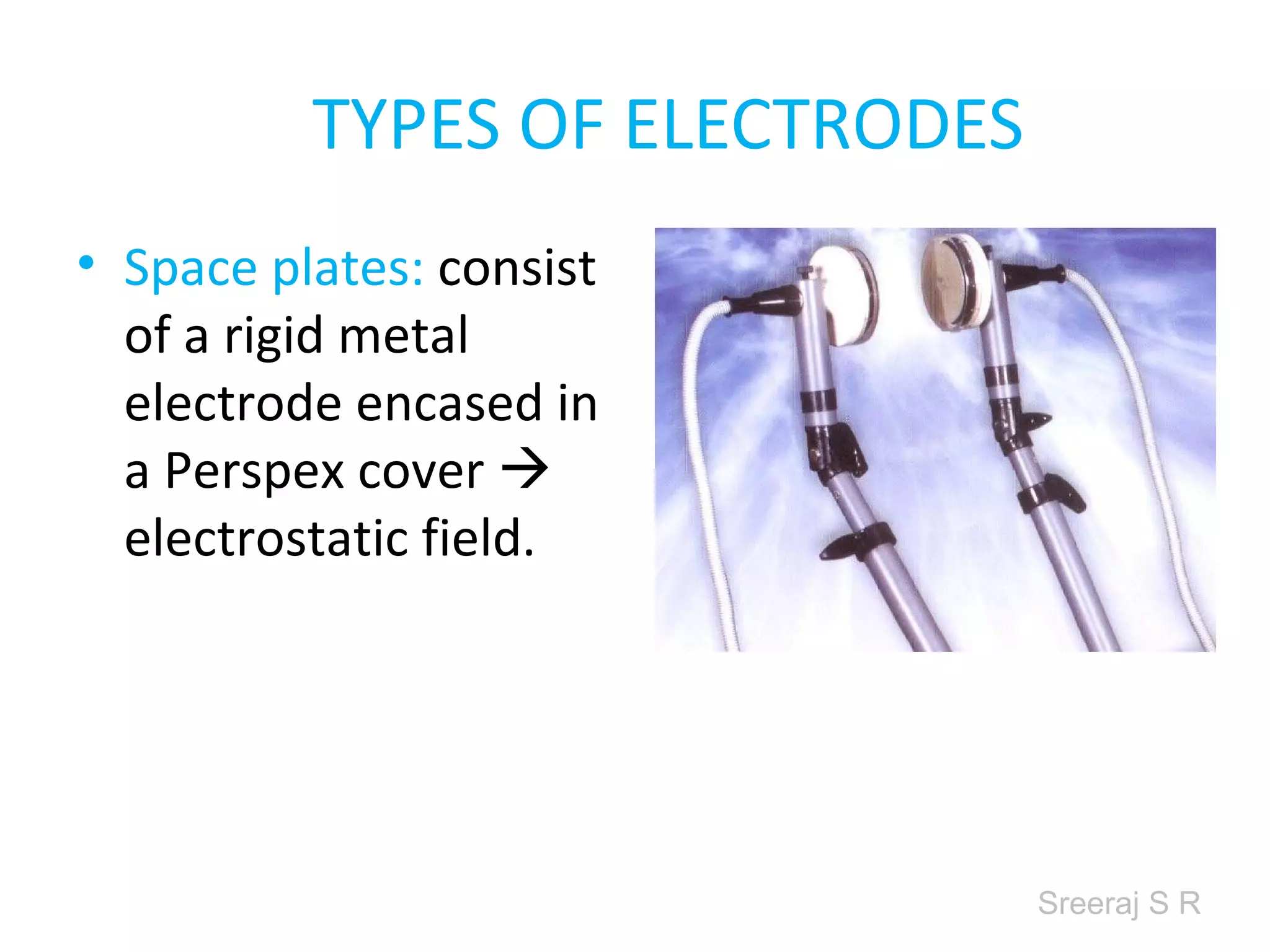
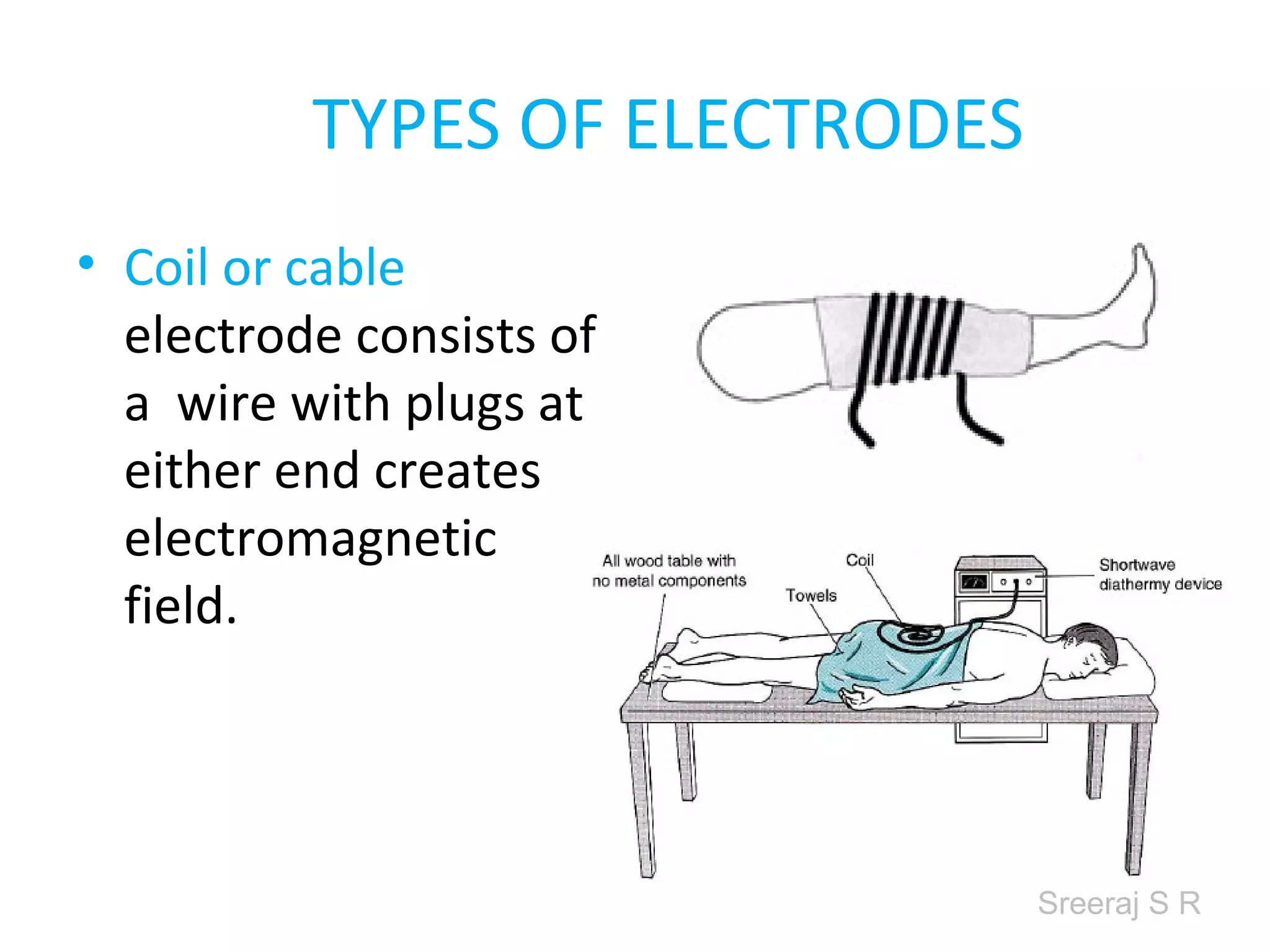
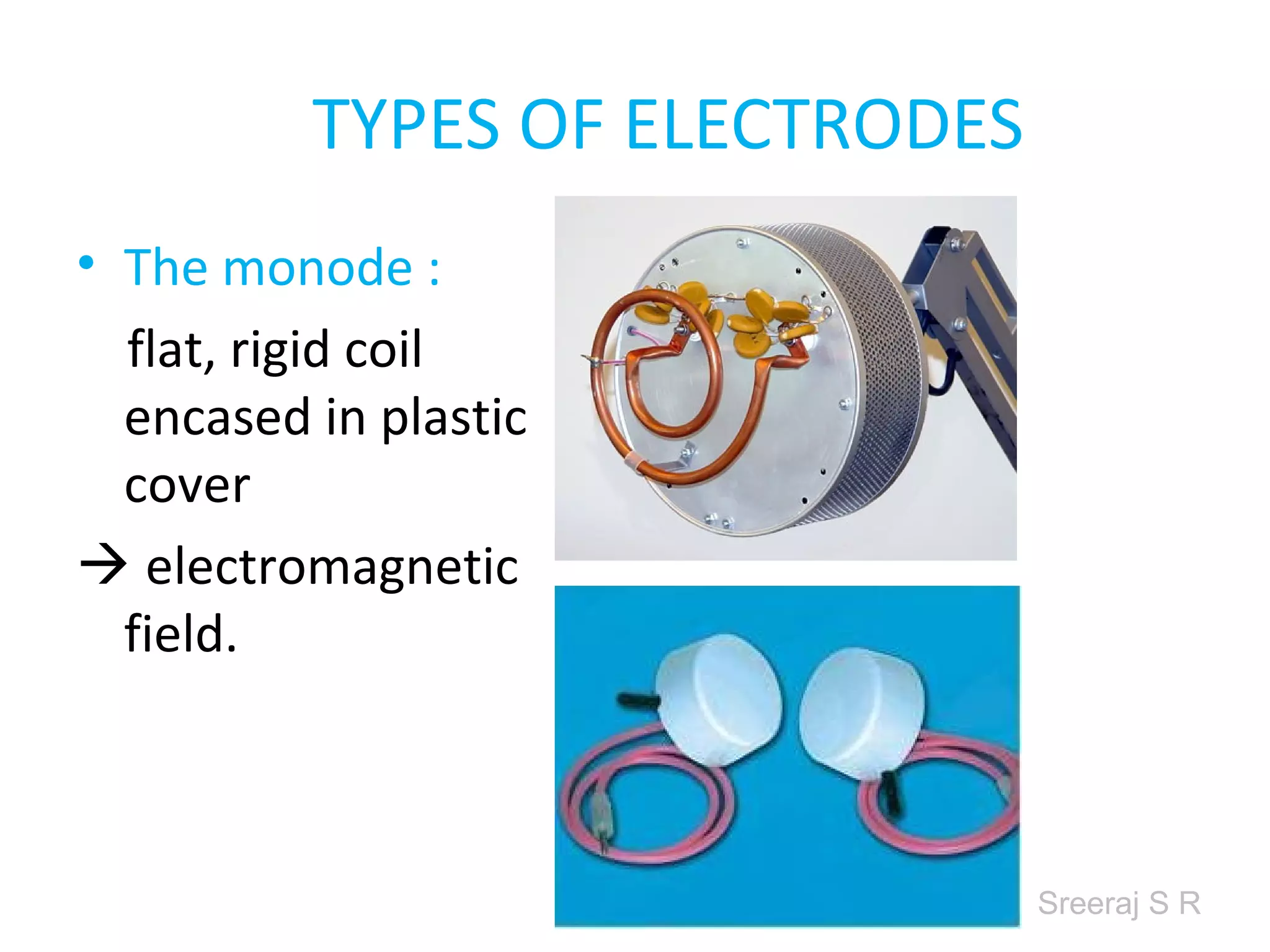
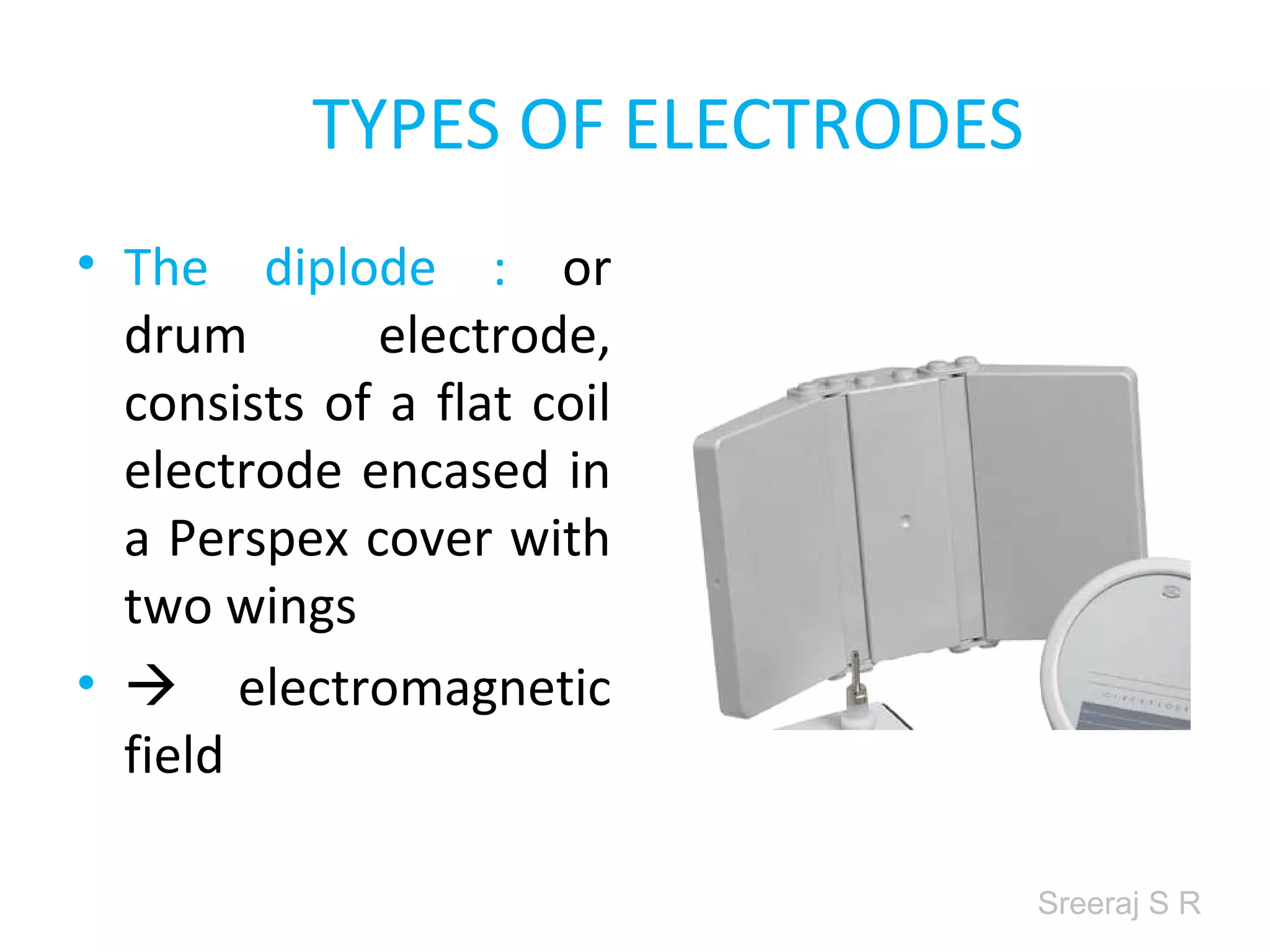
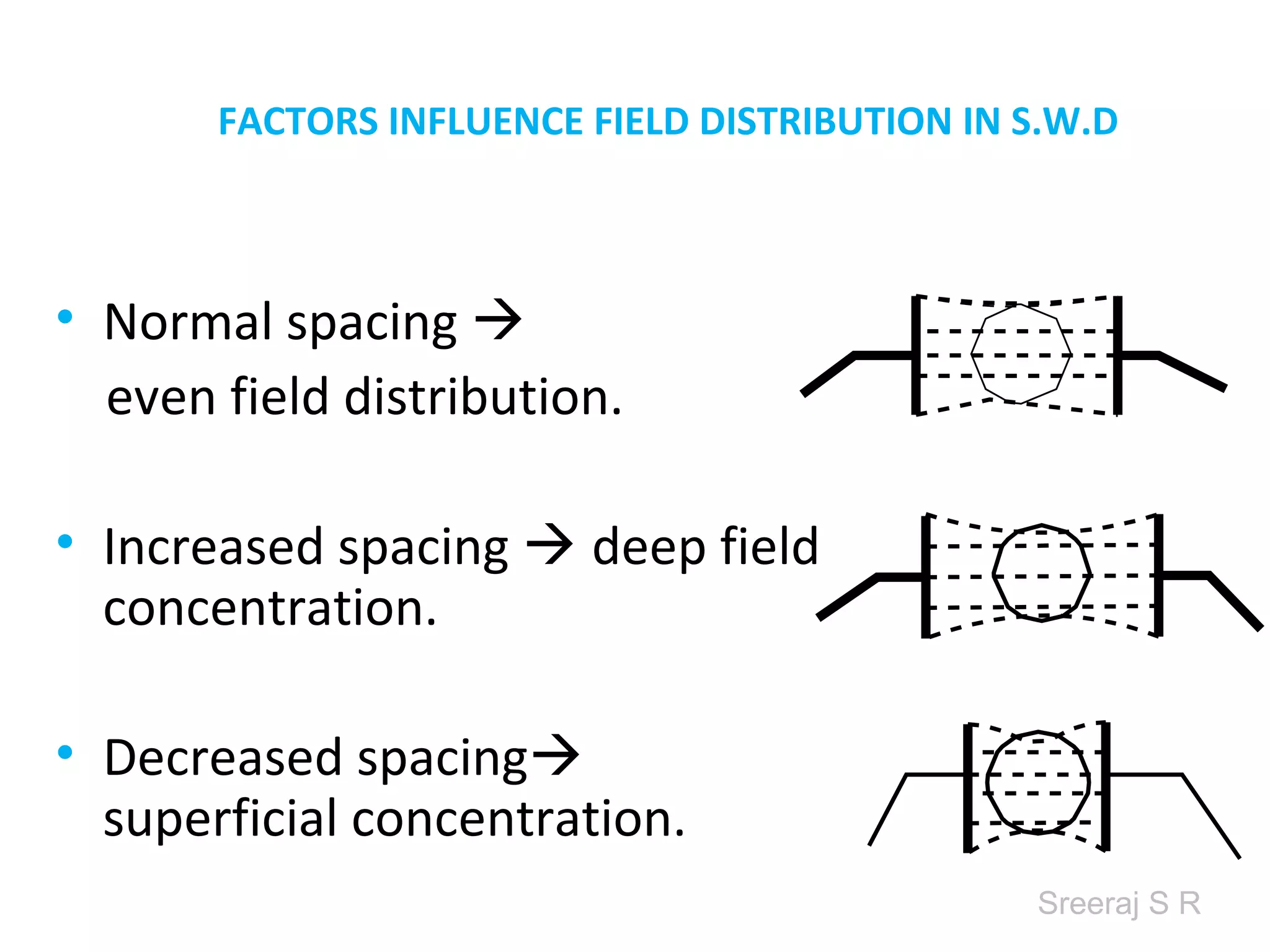
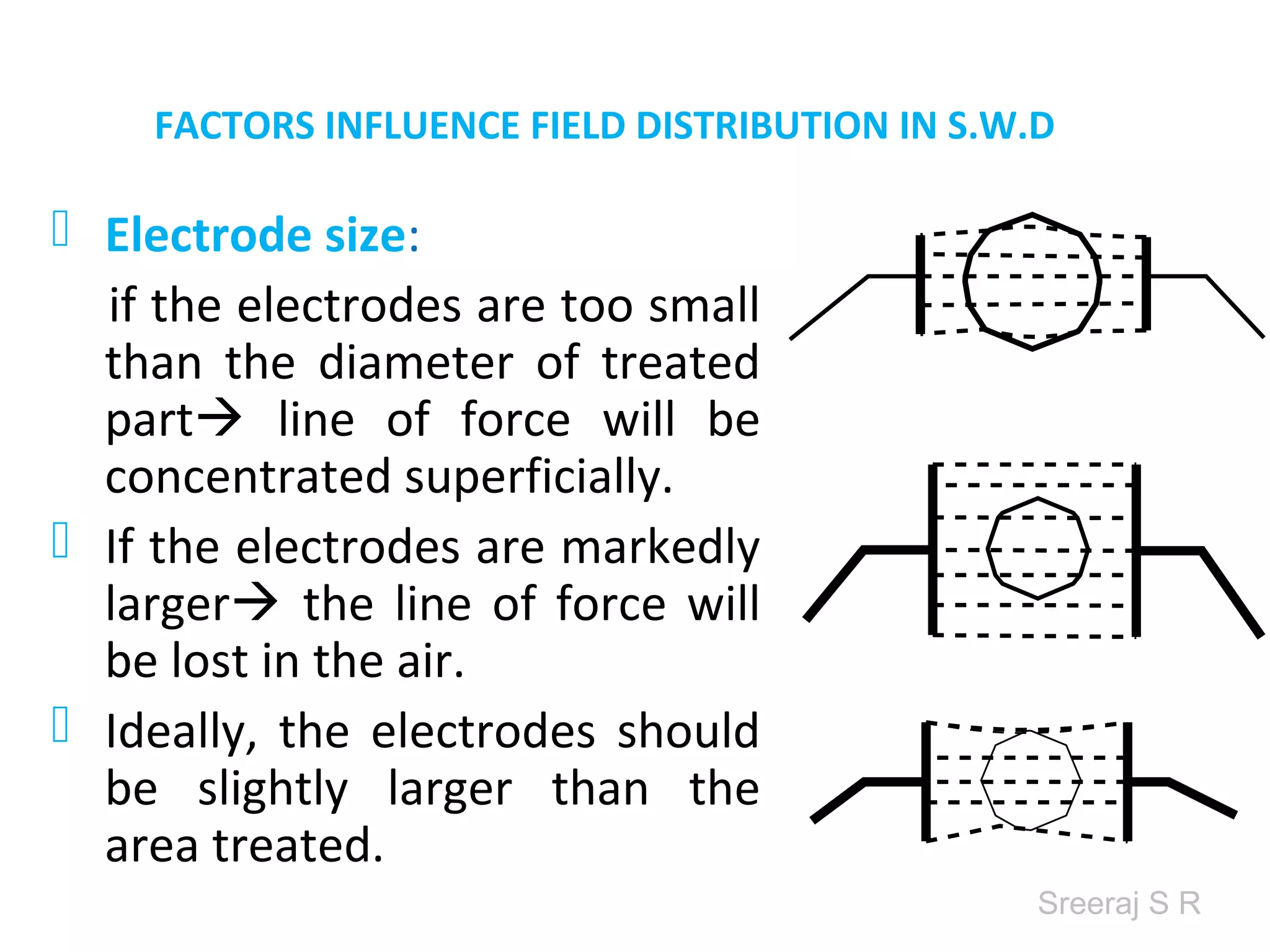
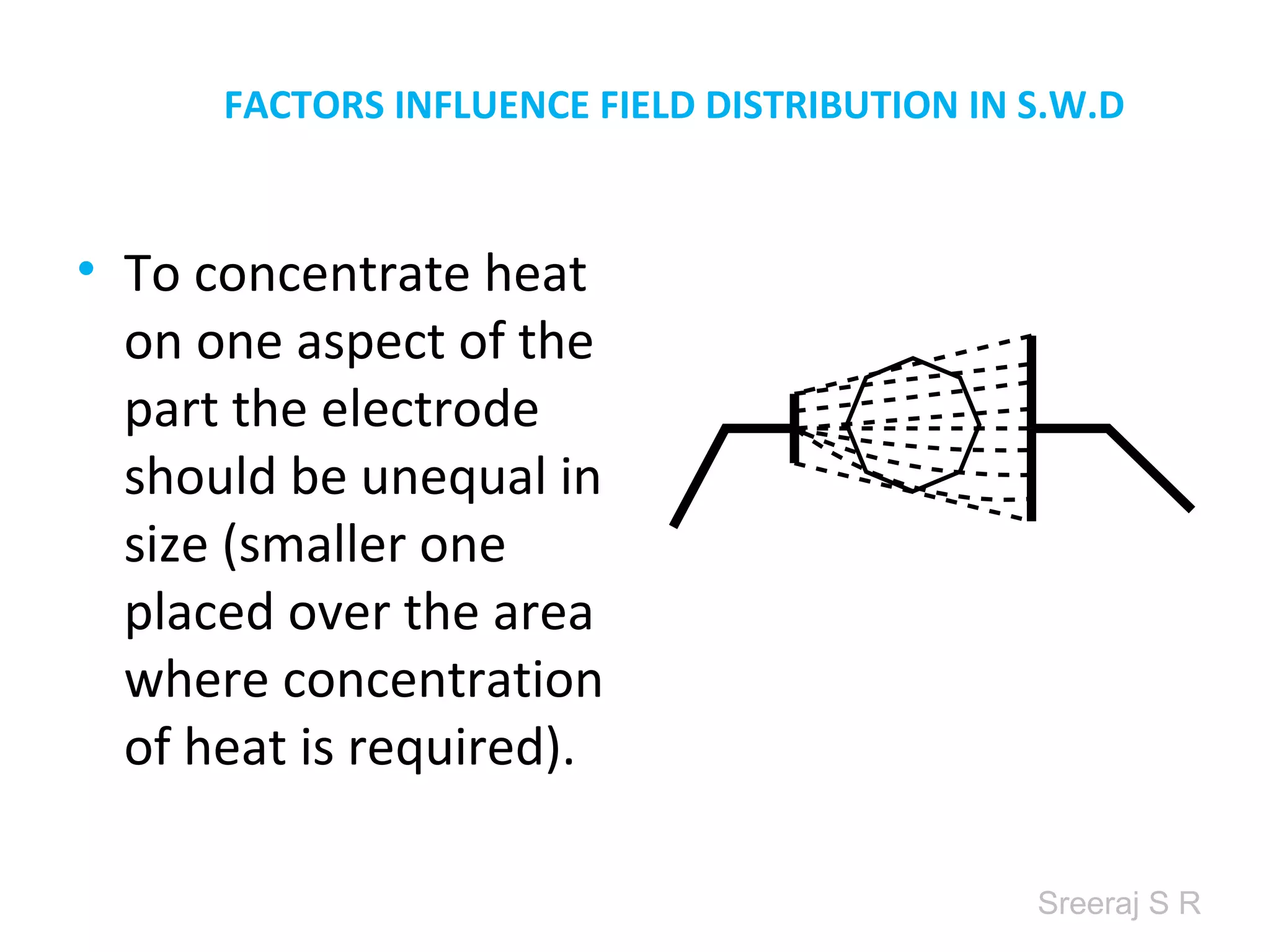
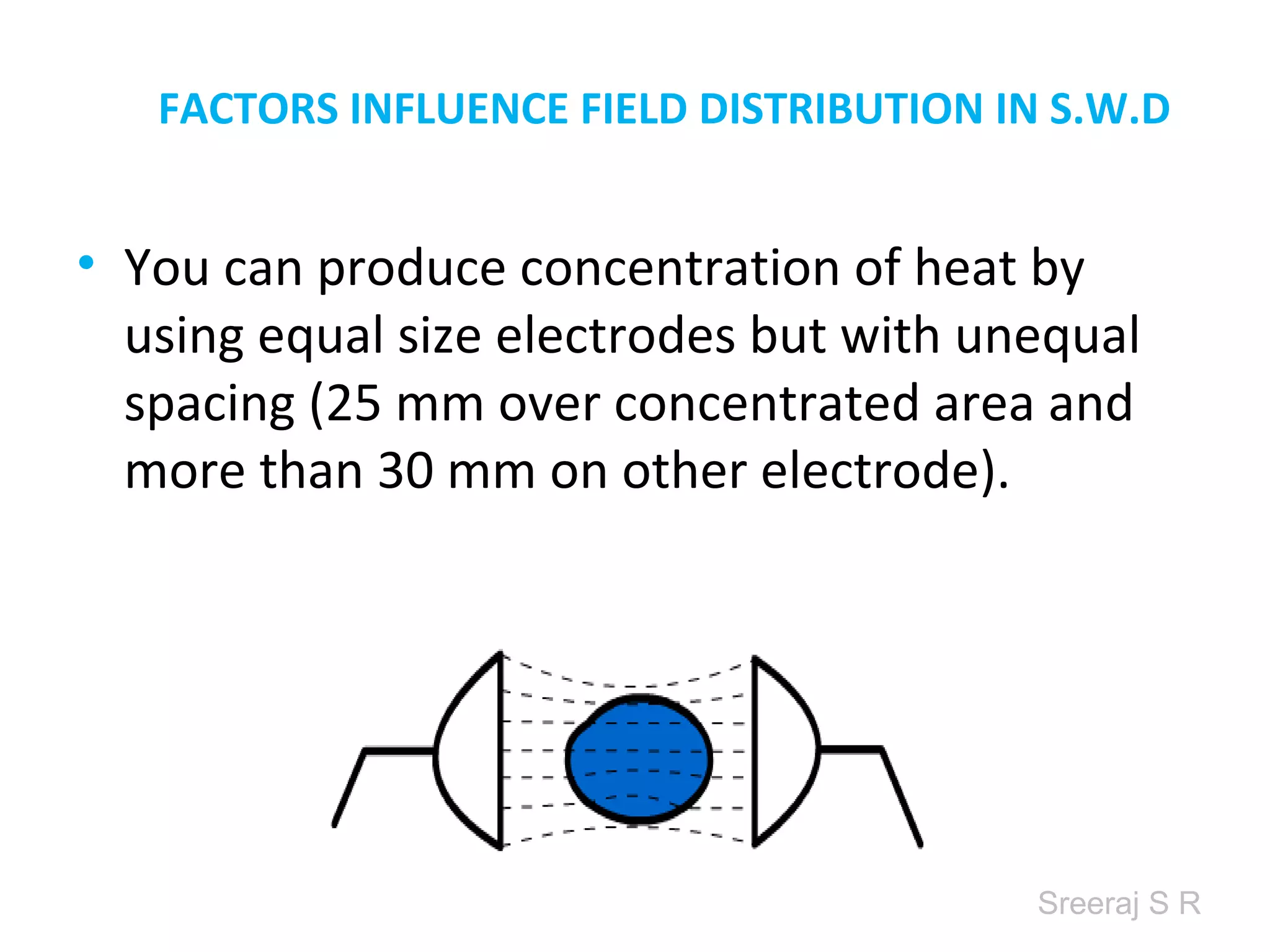
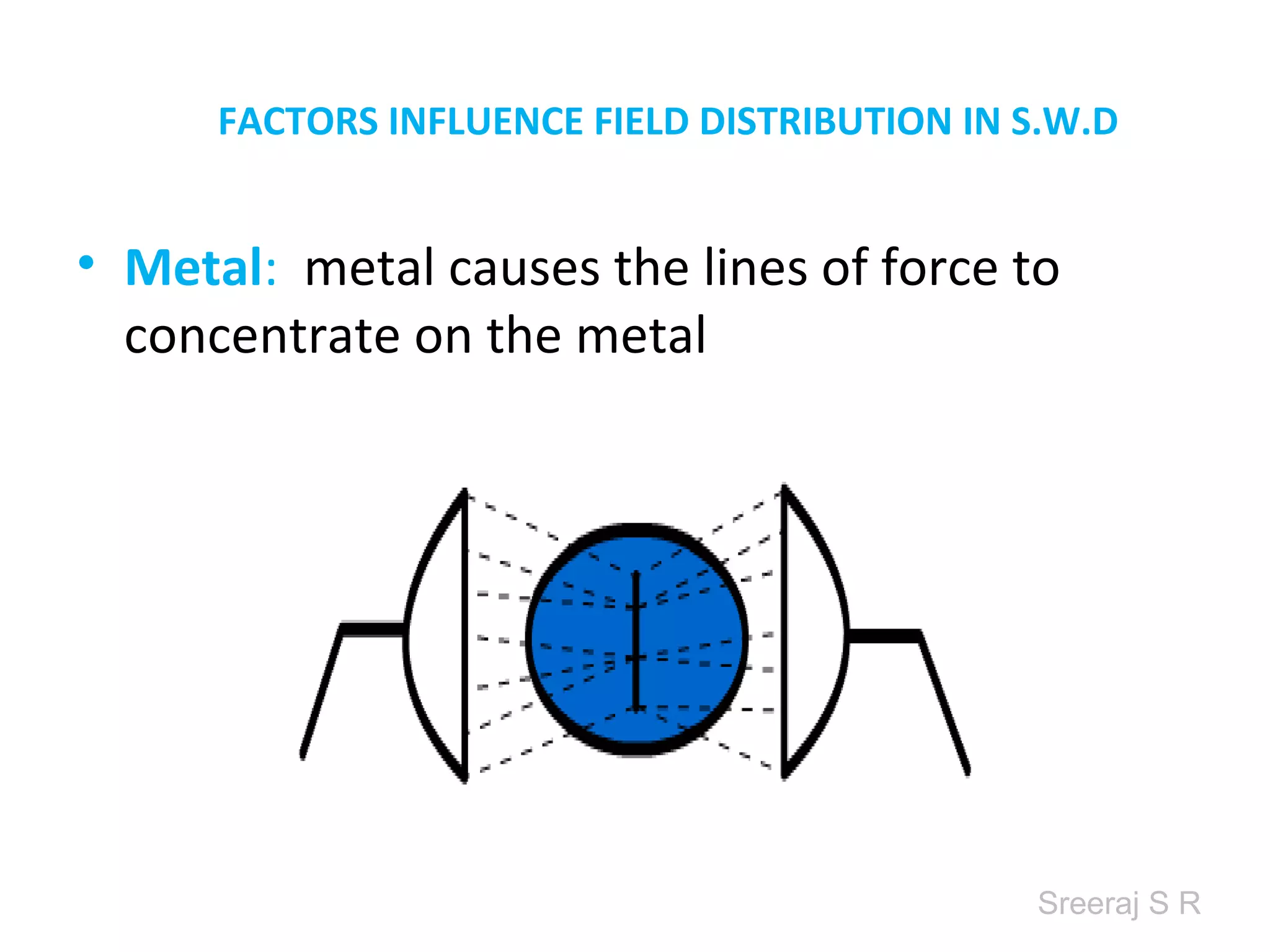
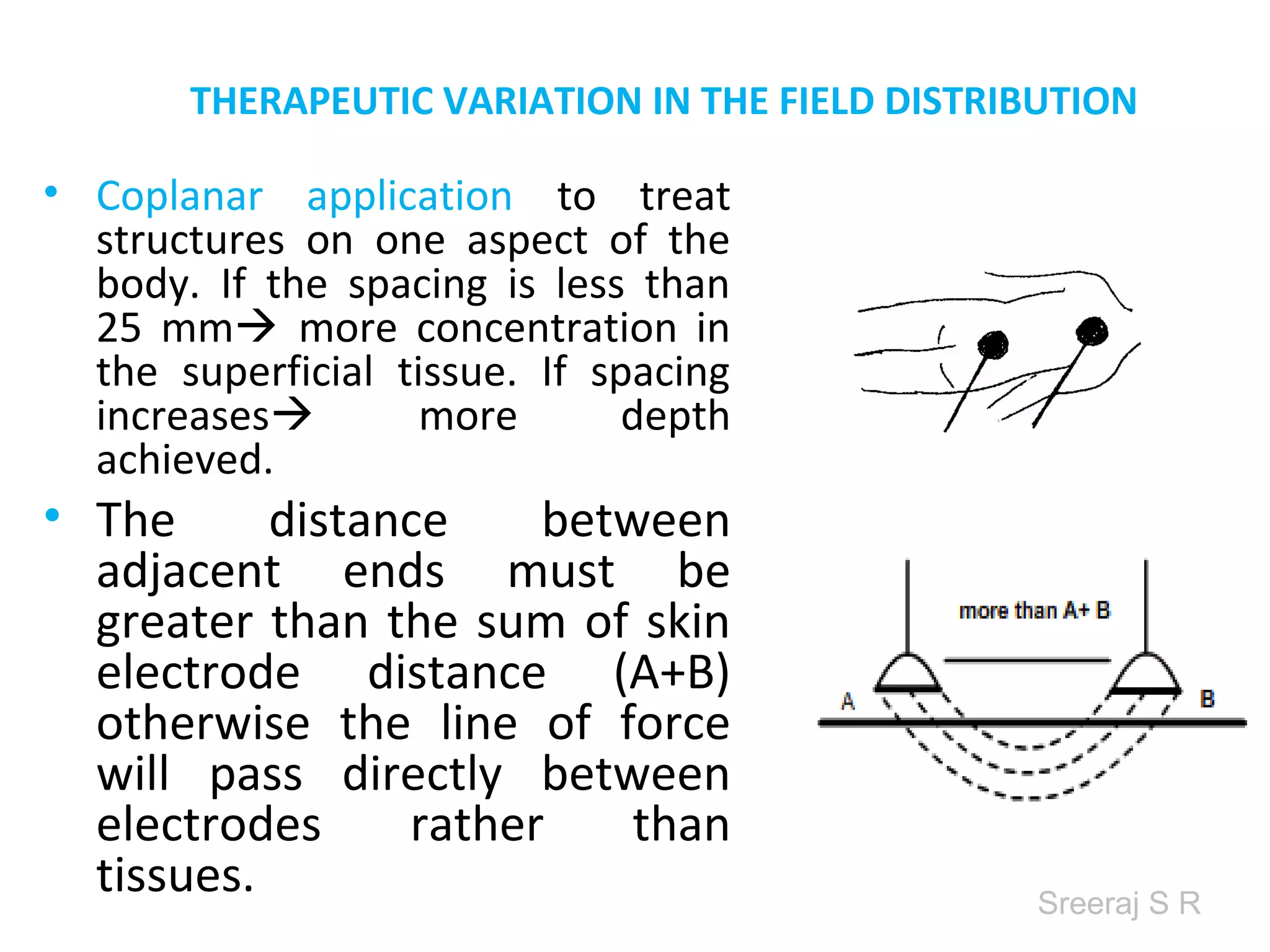
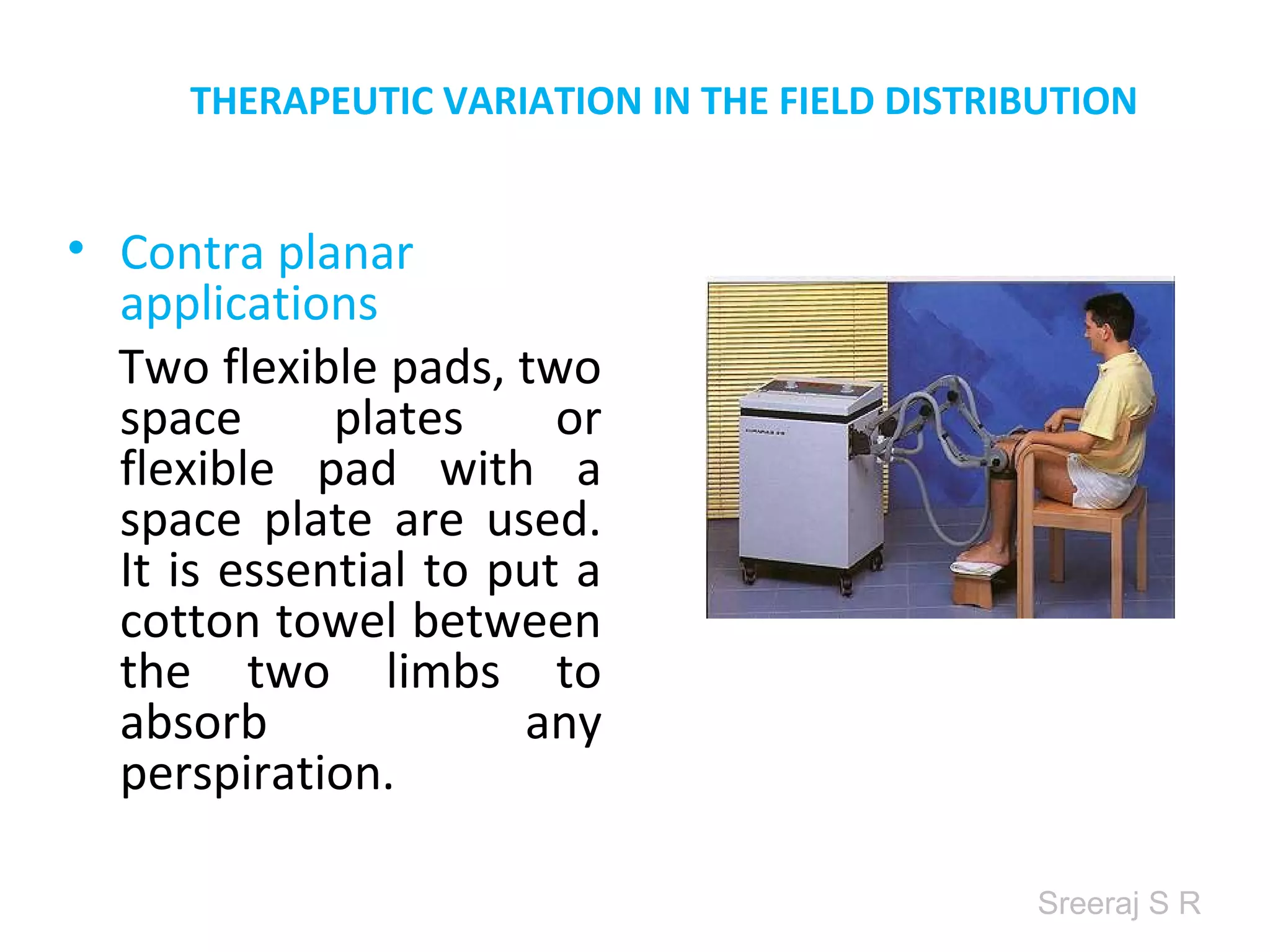
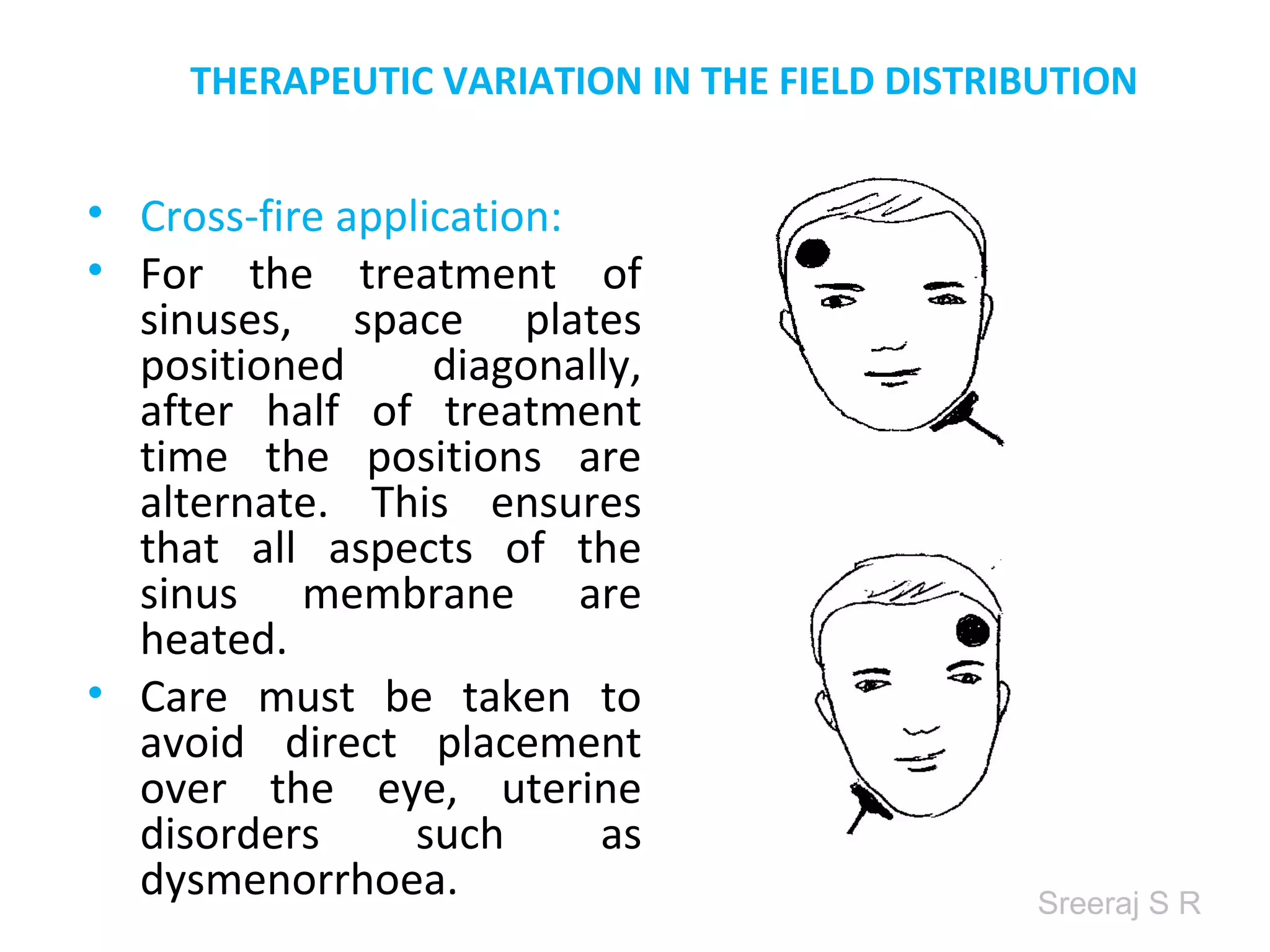
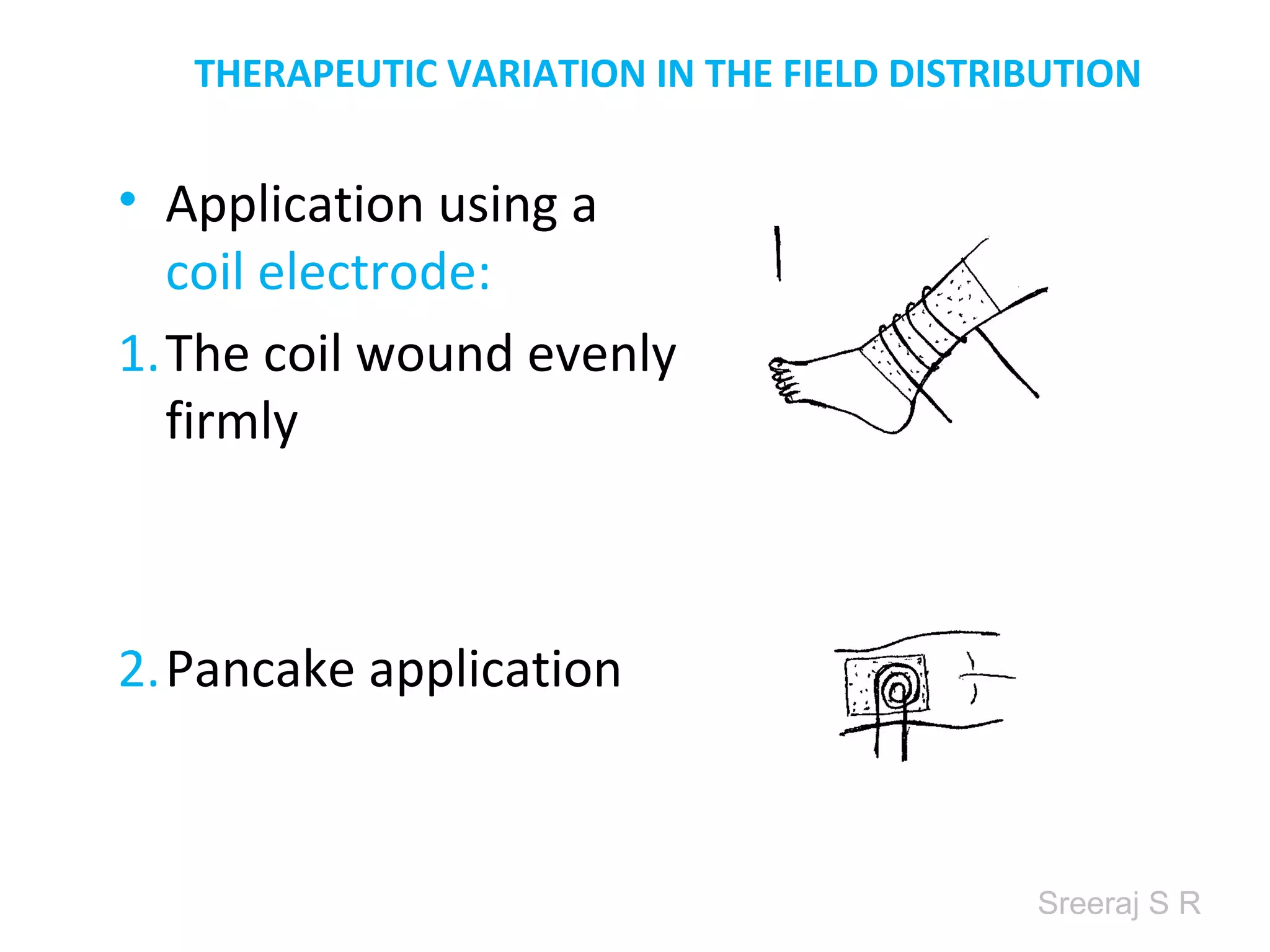
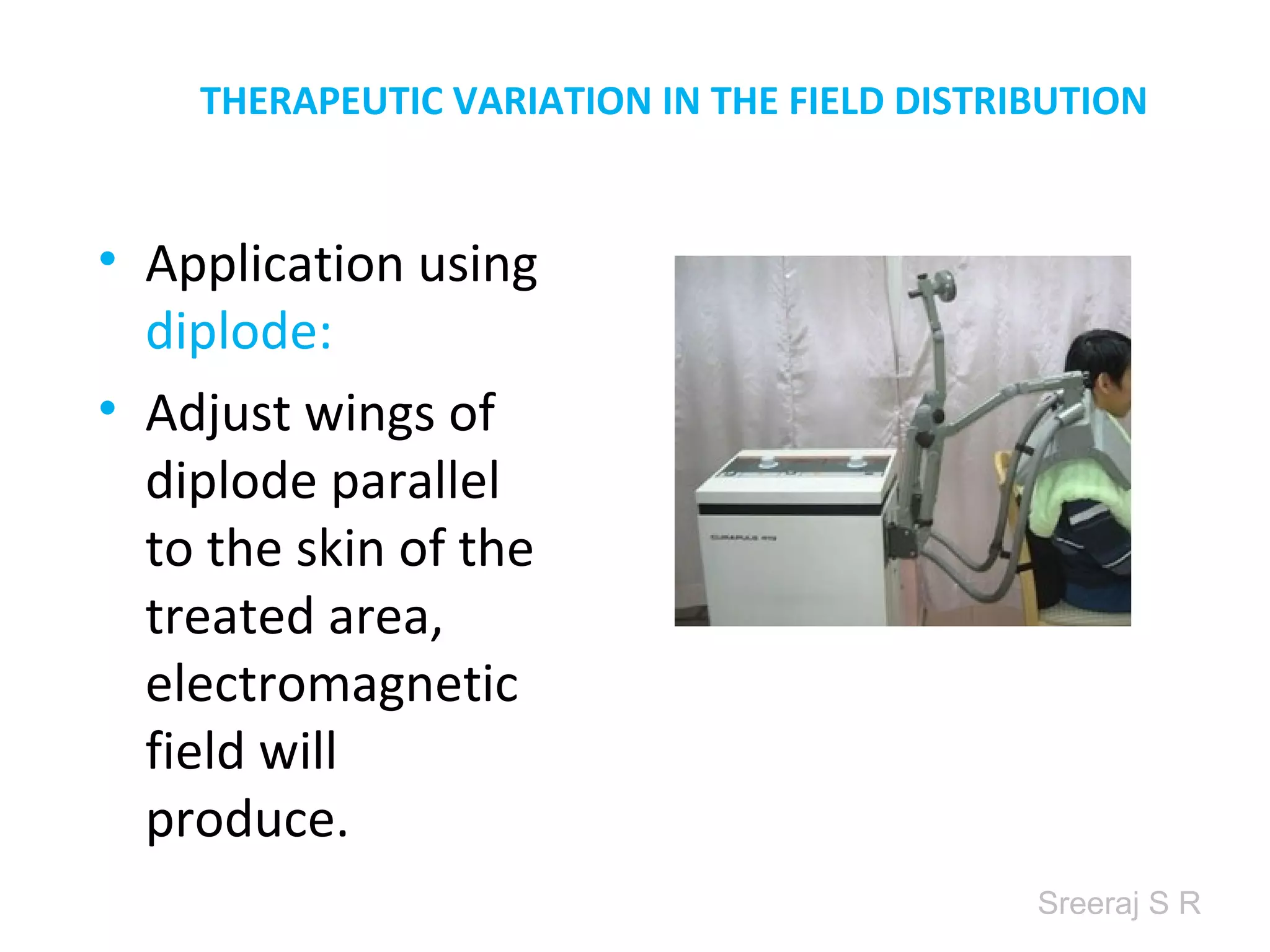
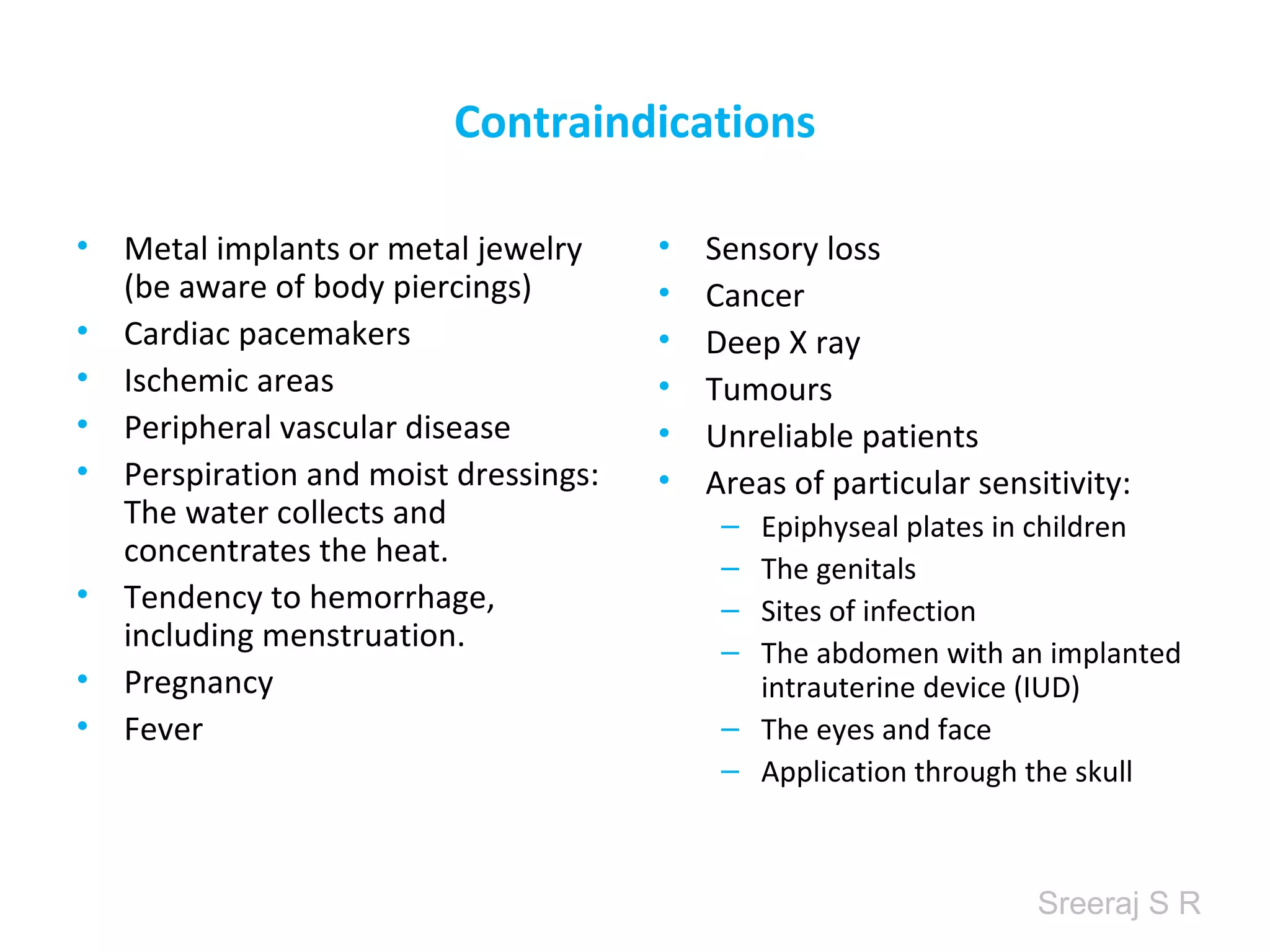
Short wave diathermy is a therapeutic modality that uses electromagnetic radiation in the frequency range of 27-100 MHz to generate deep heat in body tissues. It works by inducing molecular vibration through radio wave penetration of tissues, causing both thermal and non-thermal effects. Common applications include reducing pain, inflammation and healing time for injuries or post-surgical conditions. Different electrode types and placements can be used to concentrate the electromagnetic field in specific areas. Factors like electrode size, spacing, and positioning affect the depth and distribution of heating in the target tissues. Risks include burns and electric shock if not properly administered.