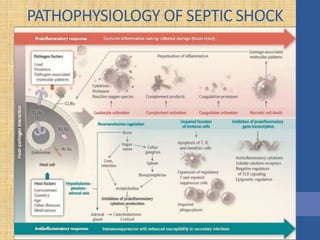
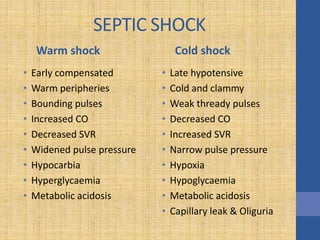
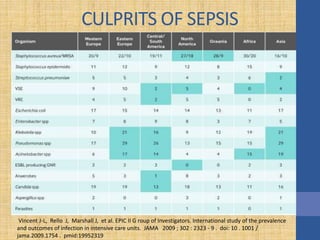
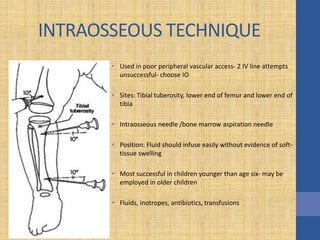
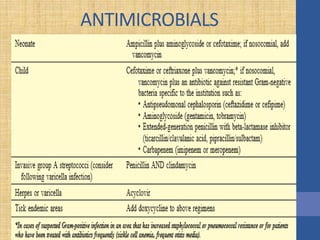
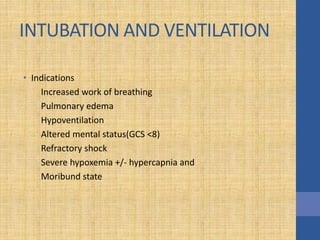
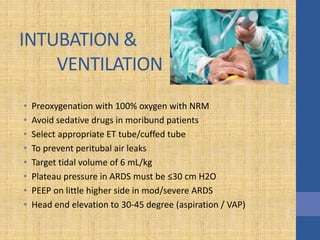
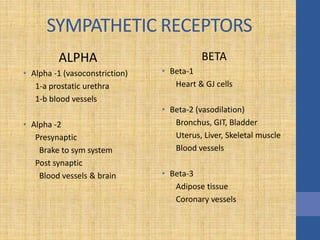
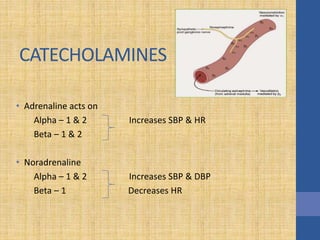
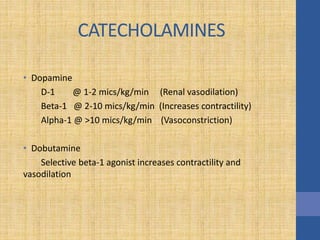
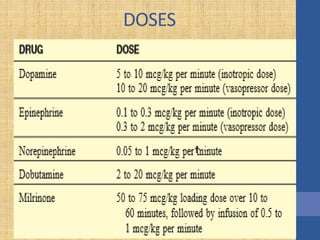
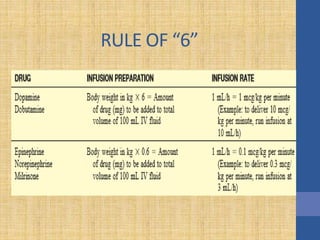
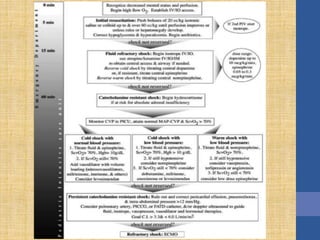
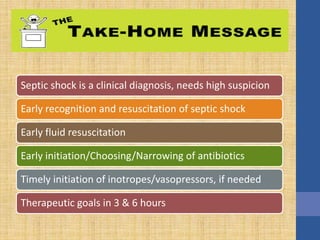
This document discusses the management of septic shock in children. It defines septic shock and describes the pathophysiology involving the immune response and cytokine release. It outlines the criteria for systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. The stages of warm and cold shock are described. Early recognition of septic shock through clinical signs is emphasized. Primary resuscitation involves oxygen, antibiotics, IV access, fluids and inotropes to achieve therapeutic goals within 3-6 hours. Intubation, ventilation, transfusions and steroids may be needed in refractory cases. Catecholamines act on different receptor types to increase blood pressure and cardiac output.