1) This document discusses 10X Genomics' linked read technology and its ability to improve genome assembly and variant calling compared to standard short read sequencing.
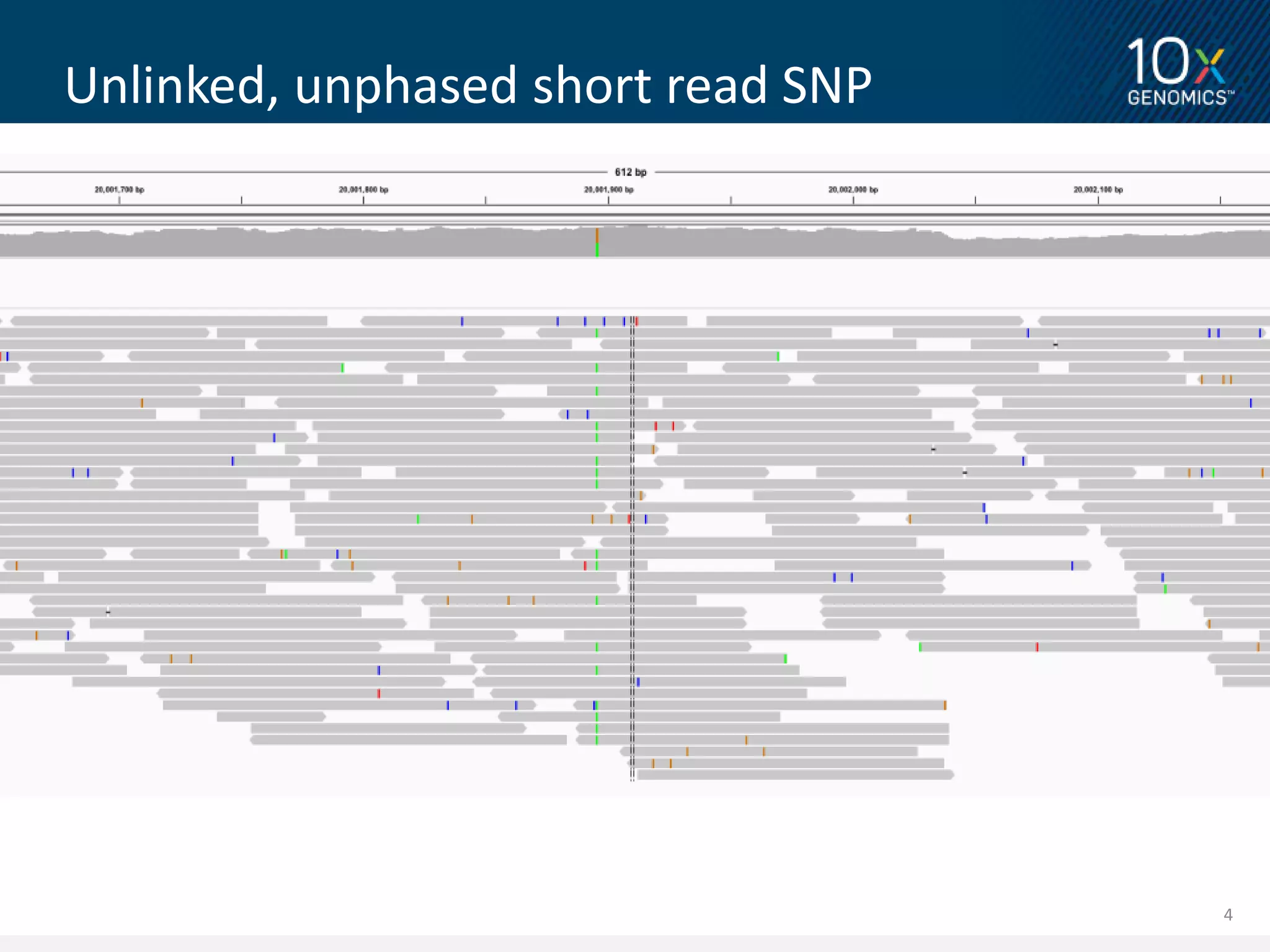
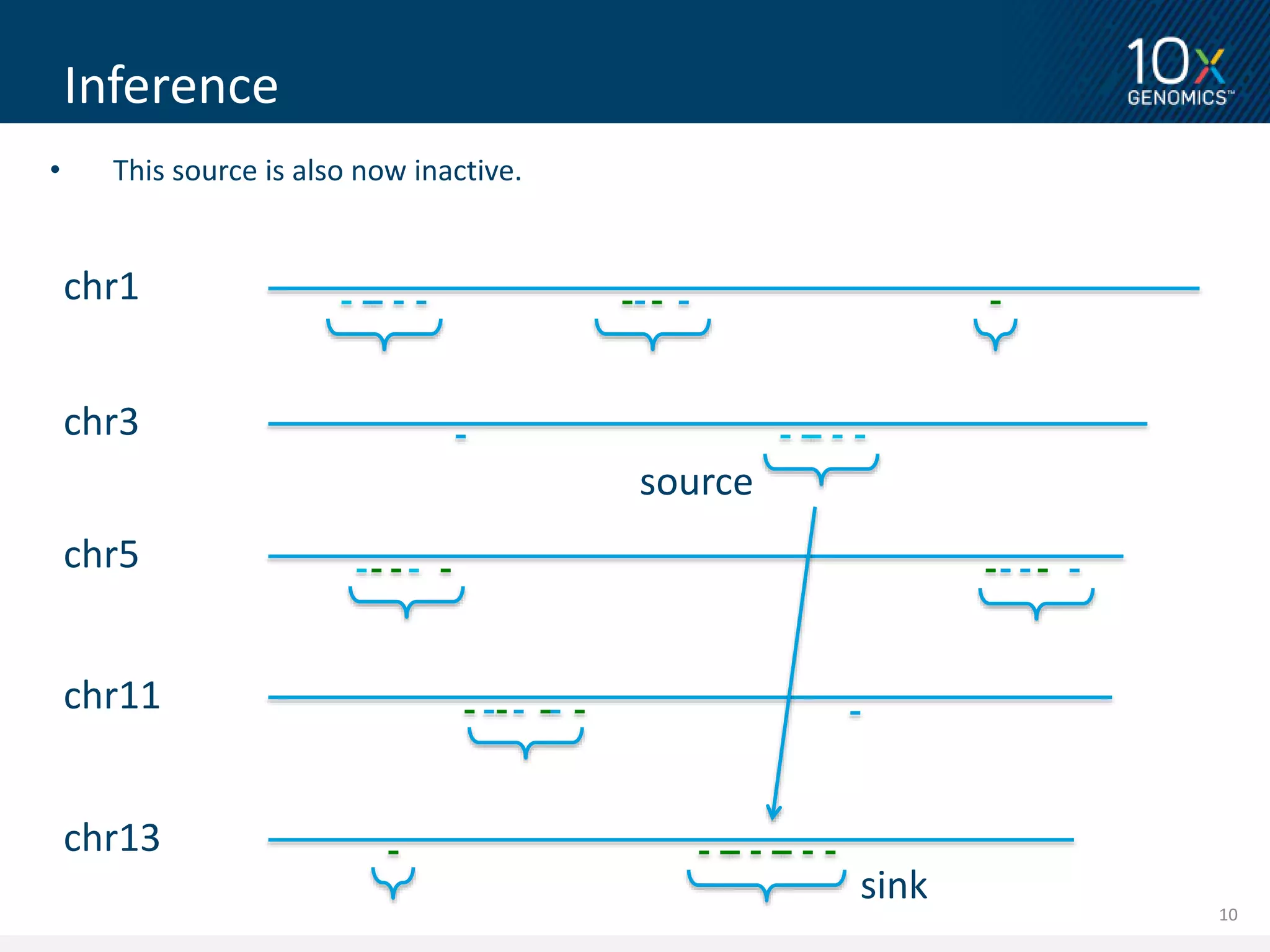
2) The linked read data from 10X Genomics can correctly place short reads into paralogous loci, improving genome alignment. This leads to improved variant calling compared to standard short read data.
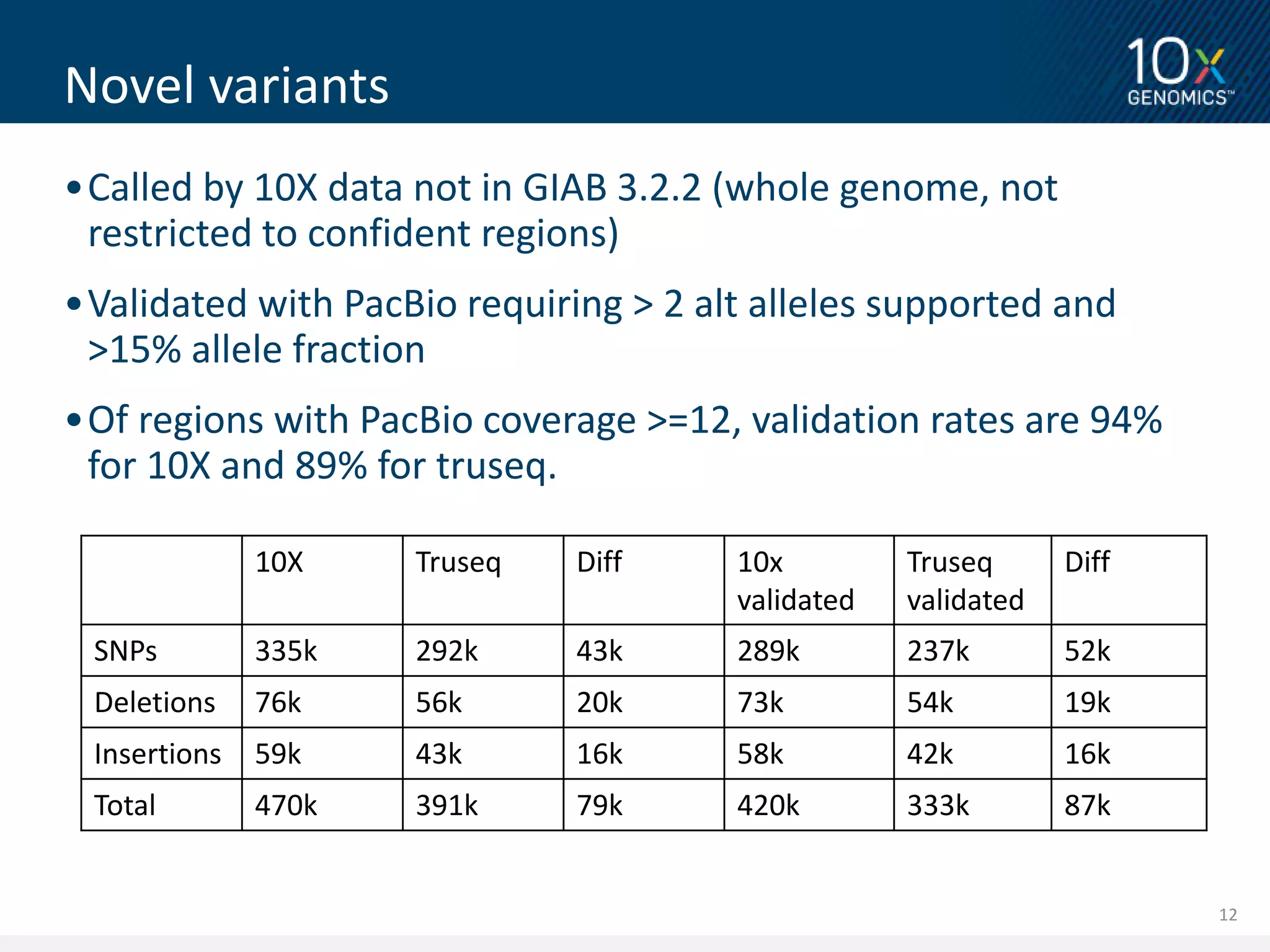
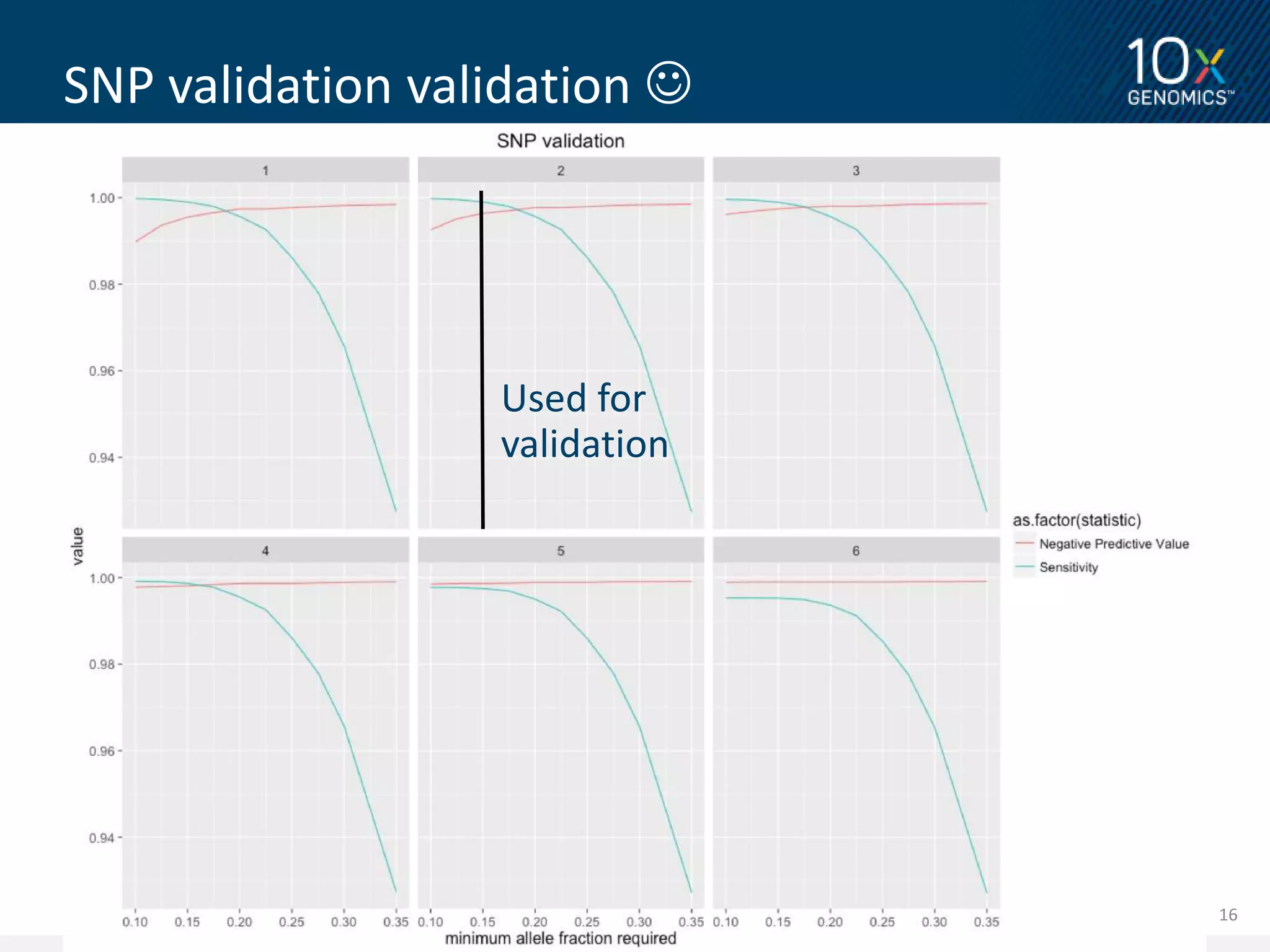
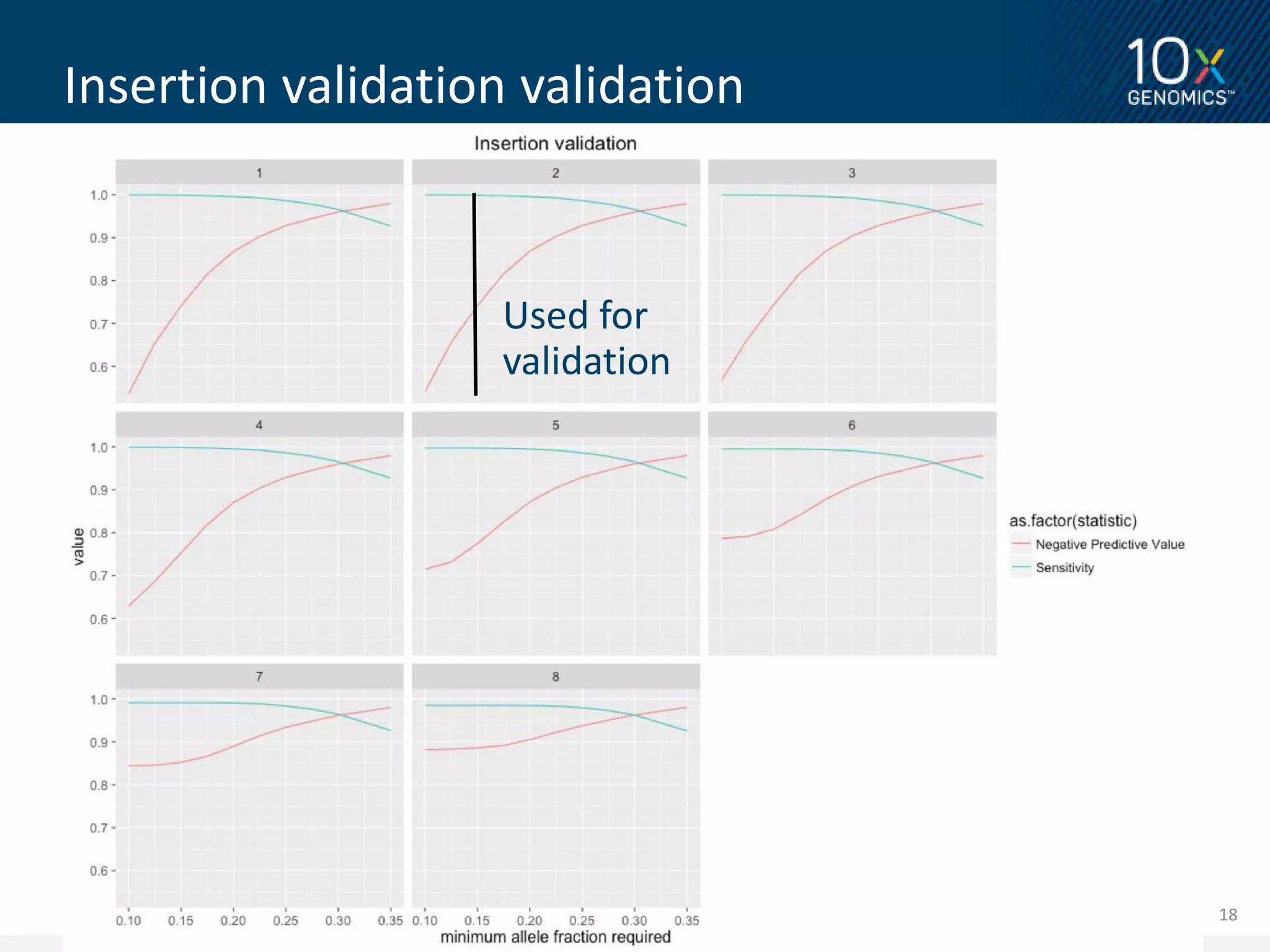
3) Novel variants called from 10X Genomics data and validated using PacBio long reads showed higher validation rates compared to variants called from standard short read data. The document proposes further validation of the variant validation method.