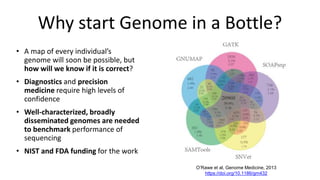
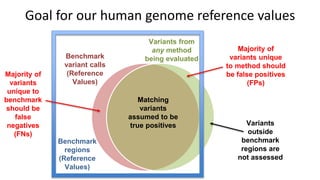
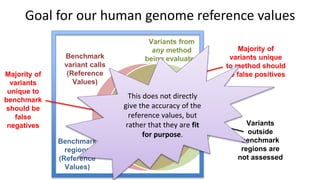
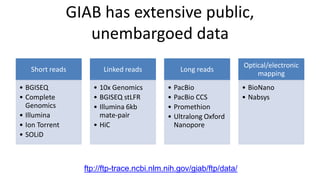
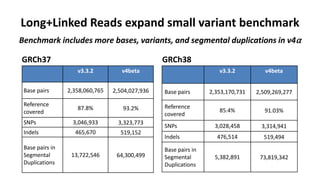
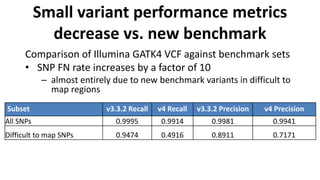
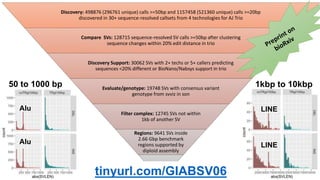
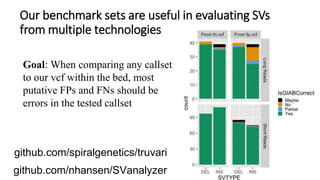
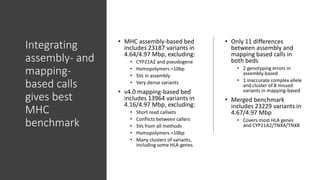
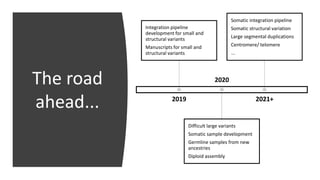
The document summarizes the Genome in a Bottle (GIAB) project, which aims to develop reference materials and benchmarks for evaluating human genome sequencing. GIAB has characterized 7 human genomes to high accuracy using multiple sequencing technologies and bioinformatics analyses. The characterized genomes and variant calls are made publicly available to benchmark sequencing performance. Recently, GIAB has incorporated linked and long read sequencing to expand reference benchmarks to more difficult genomic regions and develop benchmarks for structural variants.