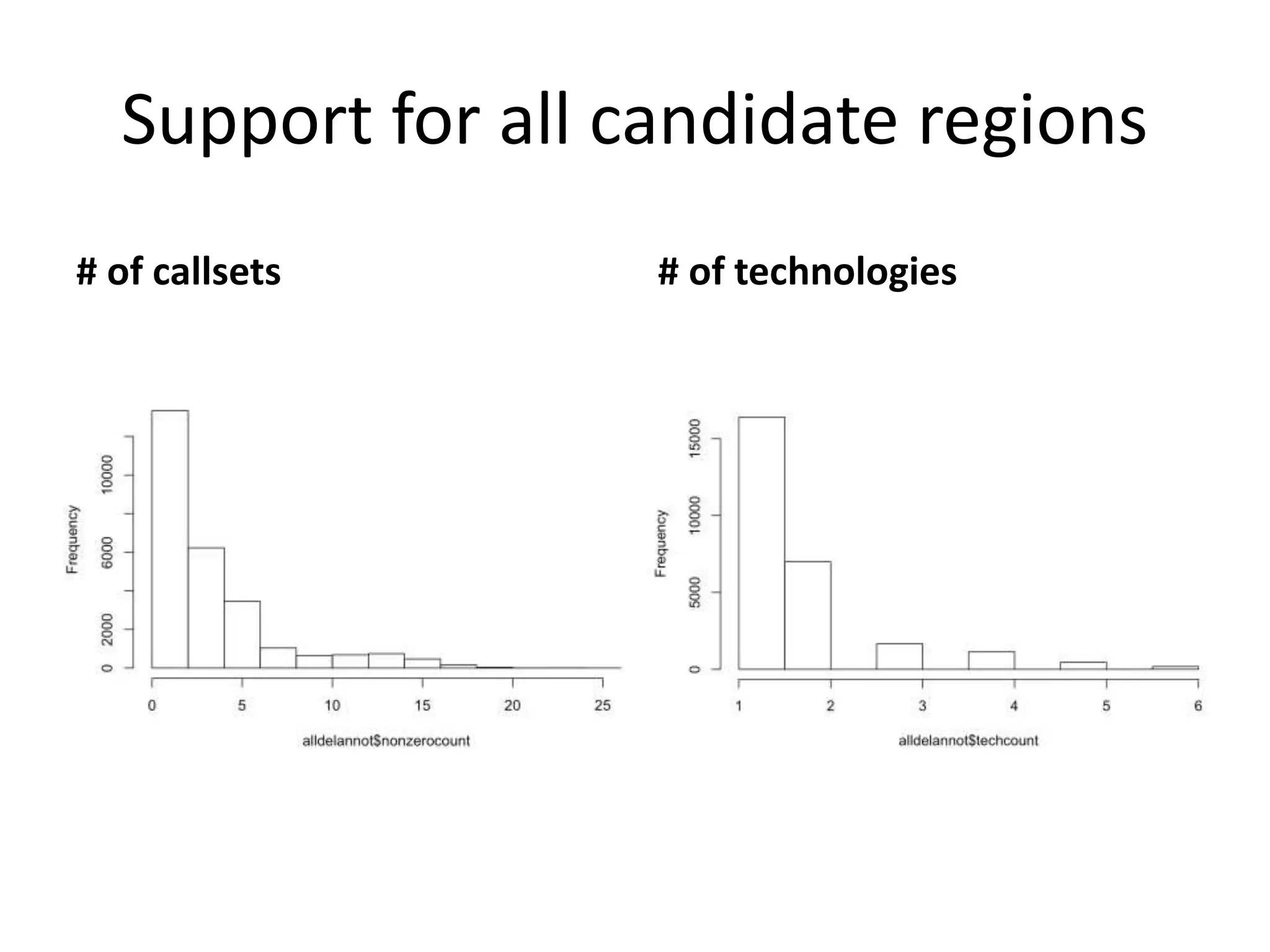
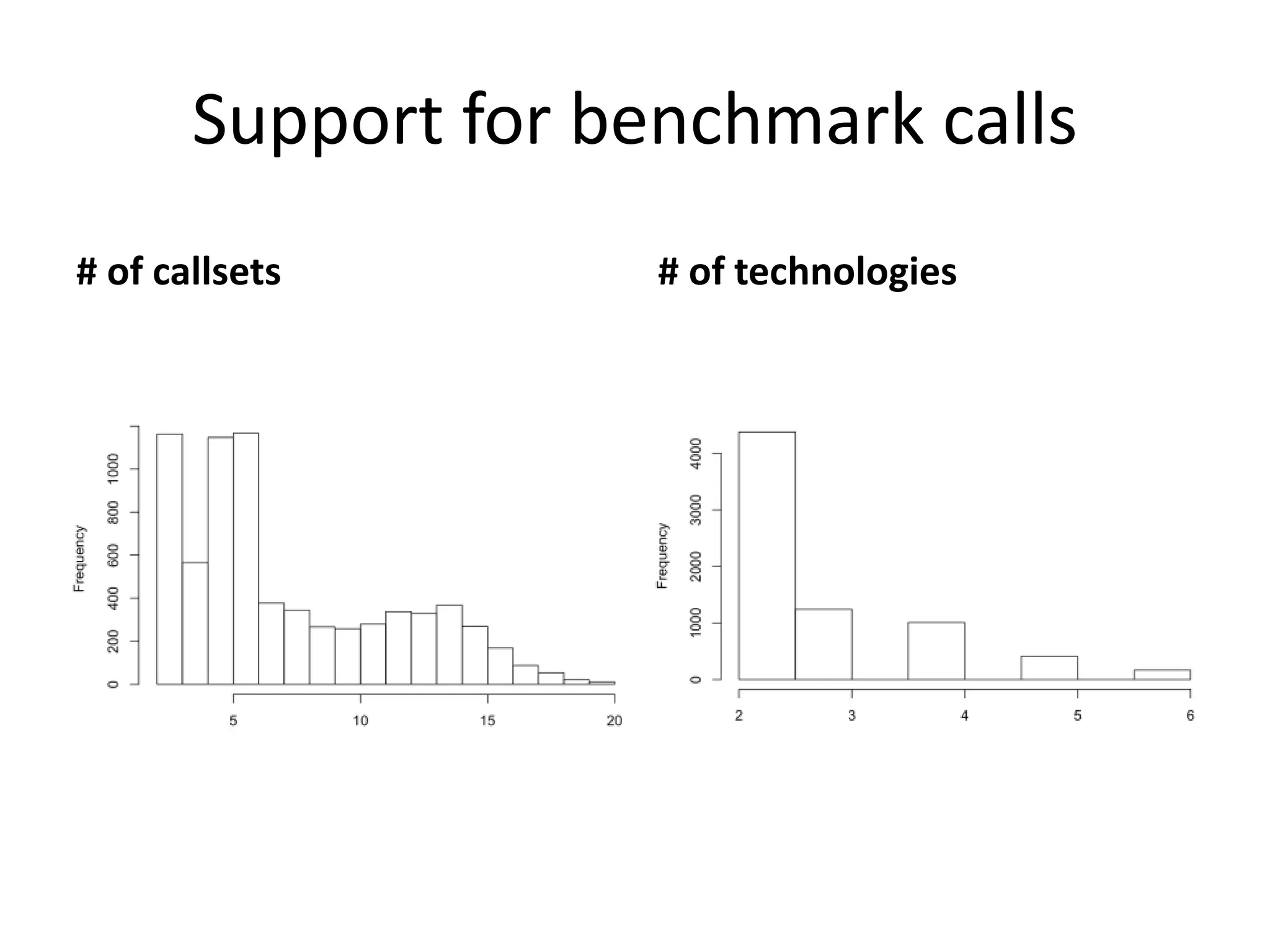
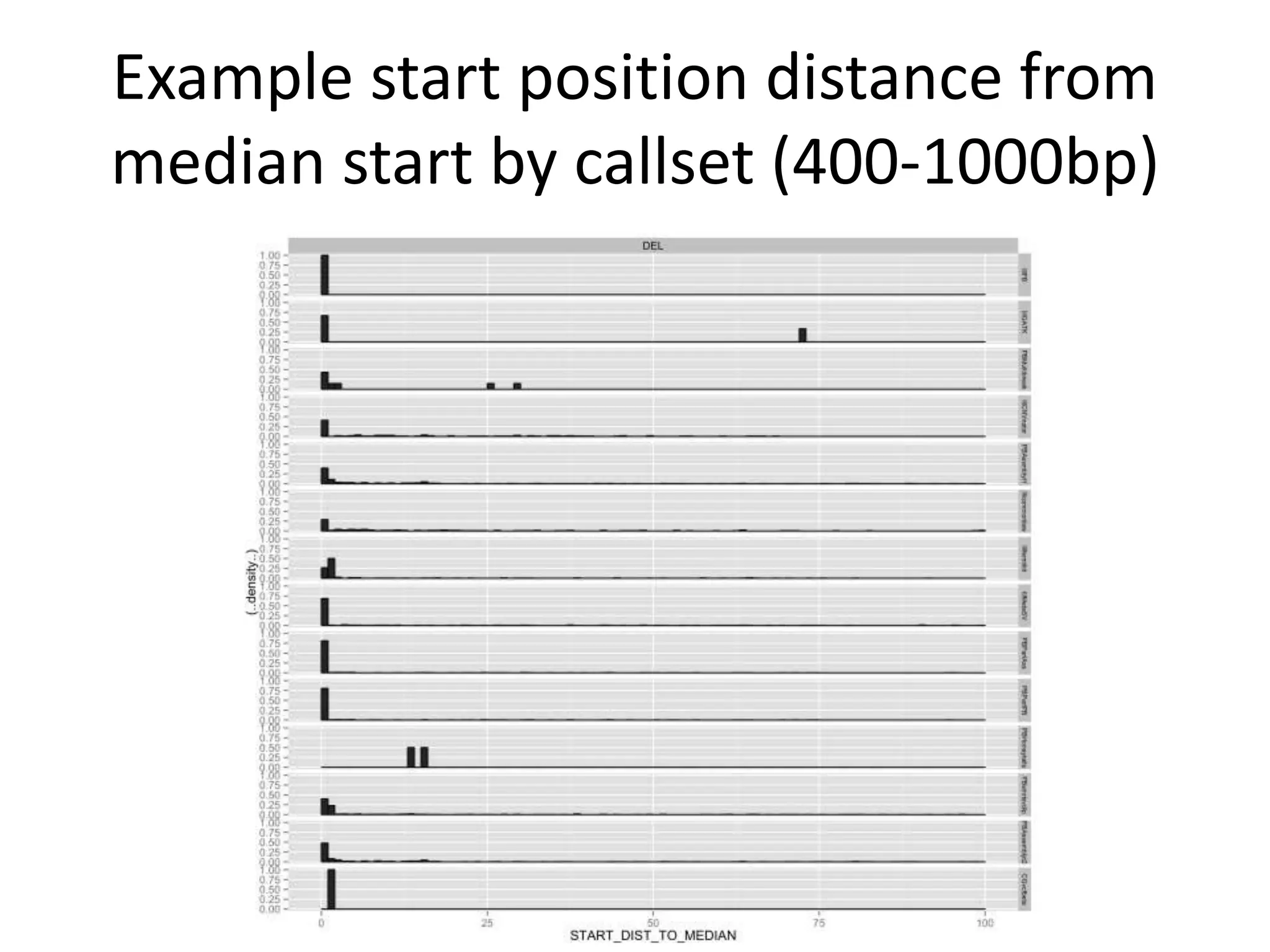
This document summarizes data from the Genome in a Bottle Consortium SV Data Jamboree. It discusses several approaches to integrating structural variant calls from multiple technologies to establish a benchmark set of high-confidence SVs:
1) Finding deletions supported by multiple technologies with concordant breakpoints and filtering questionable calls. This approach identified 524 deletions supported by 2+ technologies ranging in size from 20bp to over 3kb.
2) A method called svcompare that compares SV calls across technologies and outputs a multi-sample VCF with variant details from each caller. This identified over 2,000 regions with structural variants called by multiple technologies.
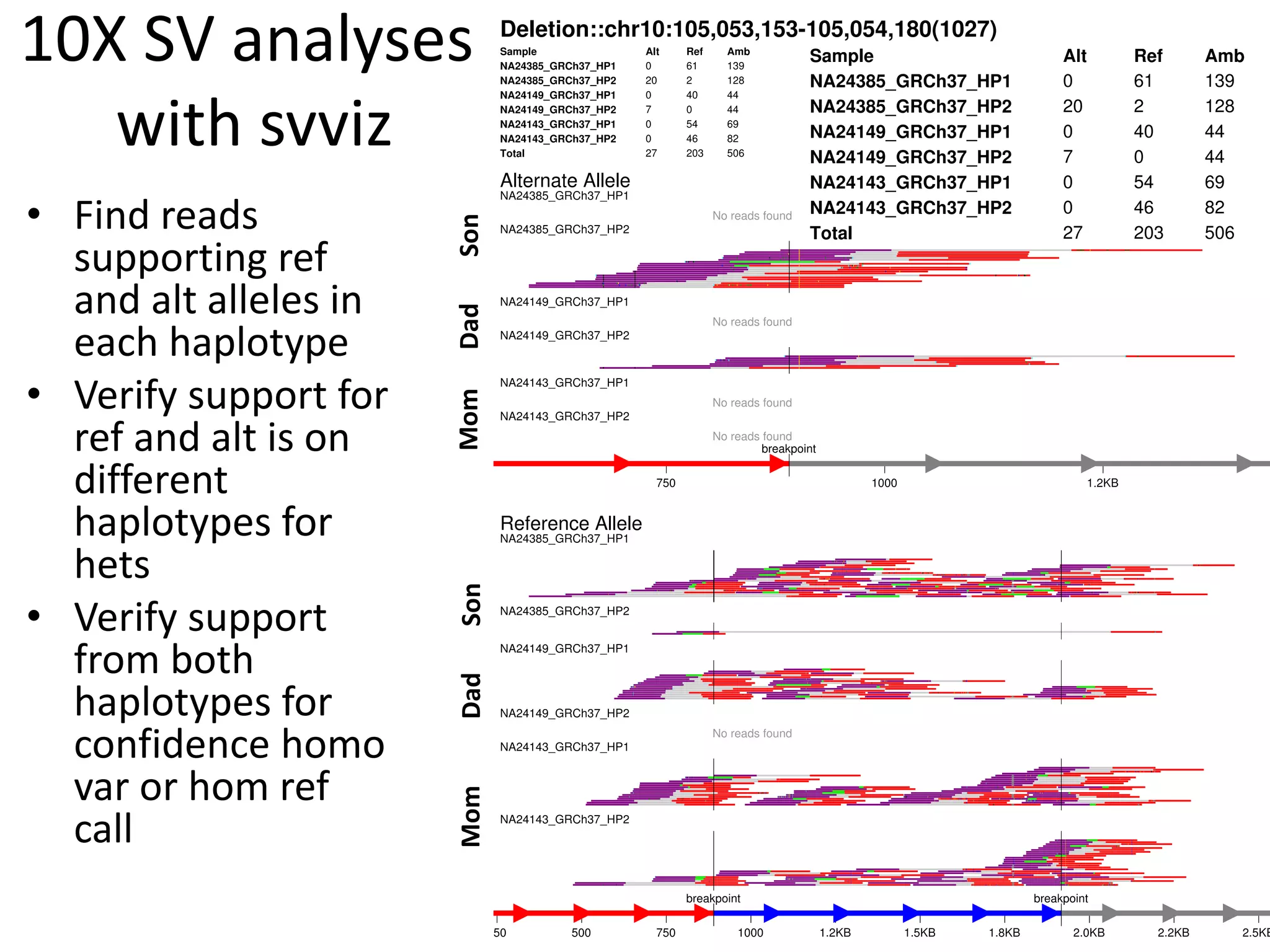
3) A method called svviz that analyzes read support for