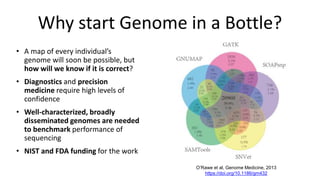
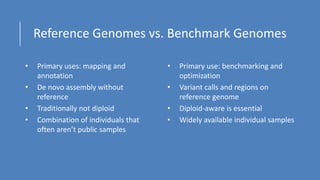
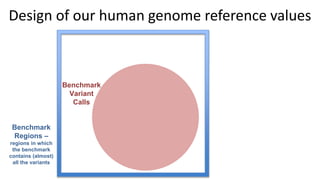
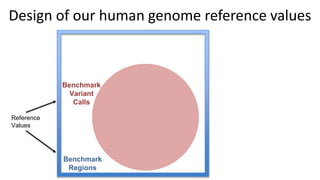
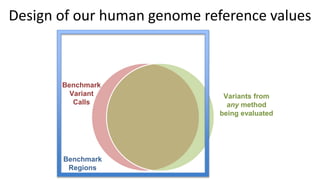
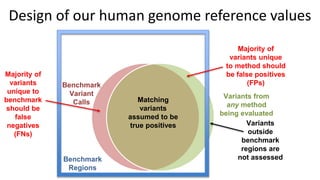
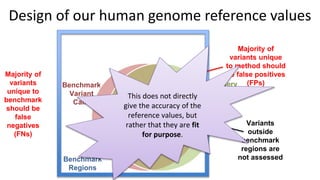
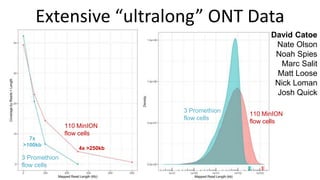
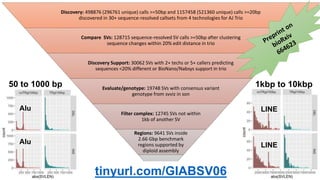
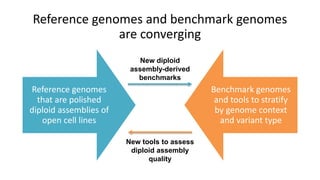
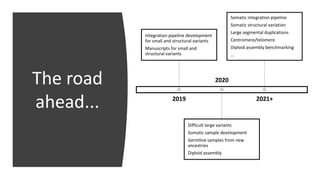
This document summarizes the Genome in a Bottle (GIAB) project, which develops reference materials and benchmarks for evaluating human genome sequencing and variant detection. GIAB has characterized 7 human genomes to high accuracy using diverse sequencing technologies. It provides extensive public sequencing data for benchmarking along with well-characterized variants. GIAB aims to improve benchmarks for difficult variants using linked reads, long reads, and diploid genome assemblies. The project collaborates widely and its reference materials and data are openly available to support innovation in genome sequencing and analysis.