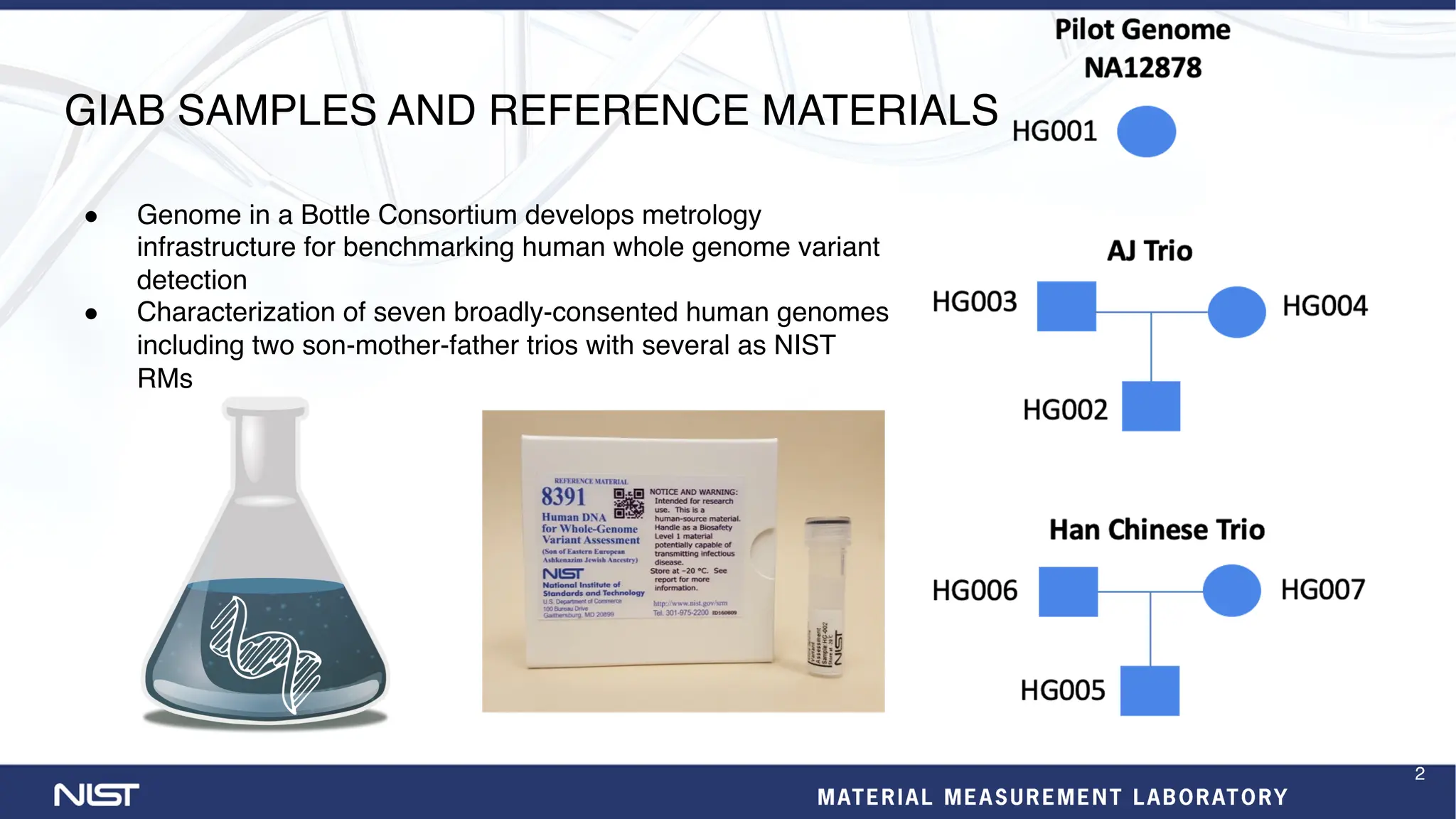
The document provides an update on the Genome in a Bottle (GIAB) Consortium. Key points include:
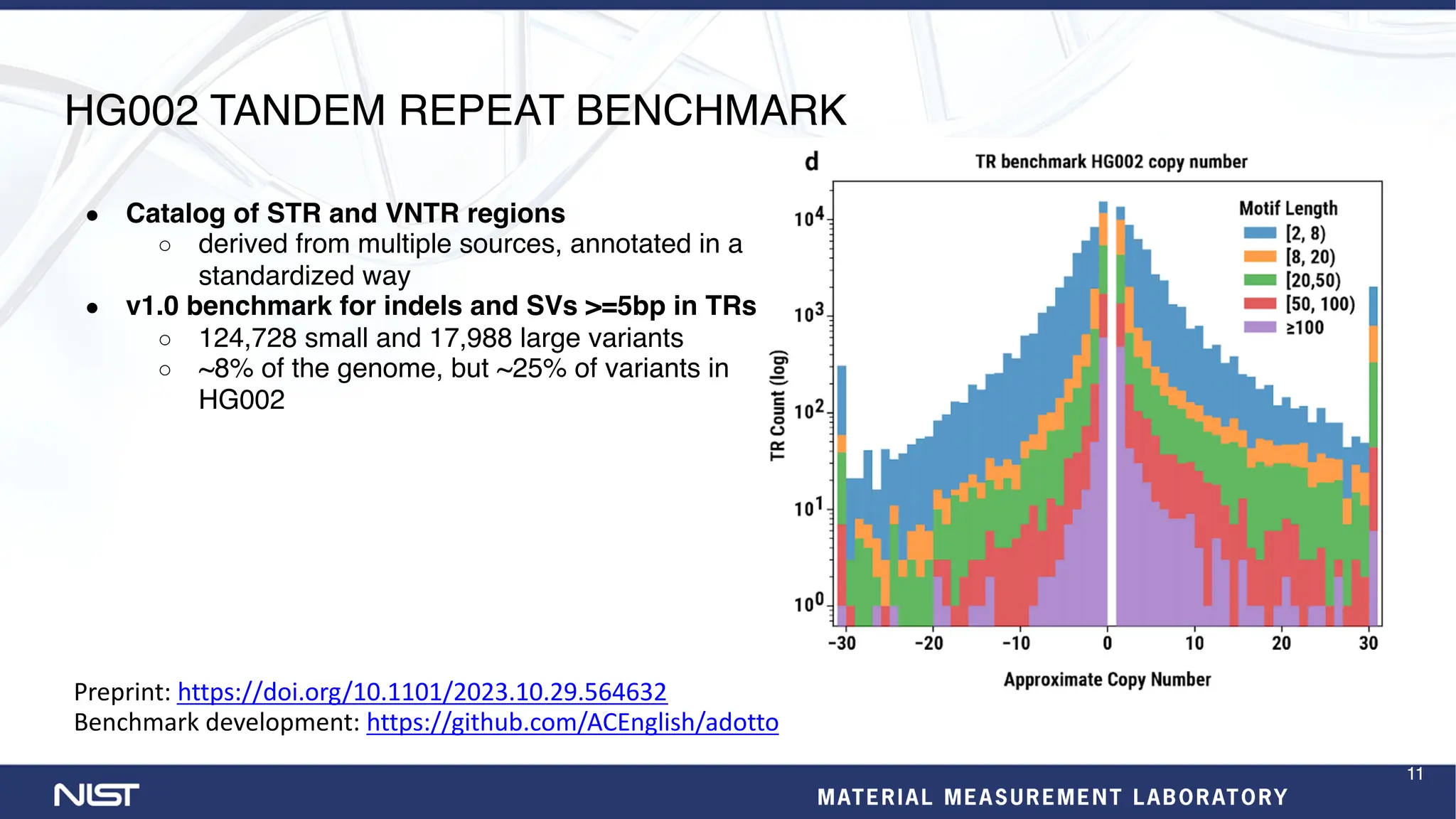
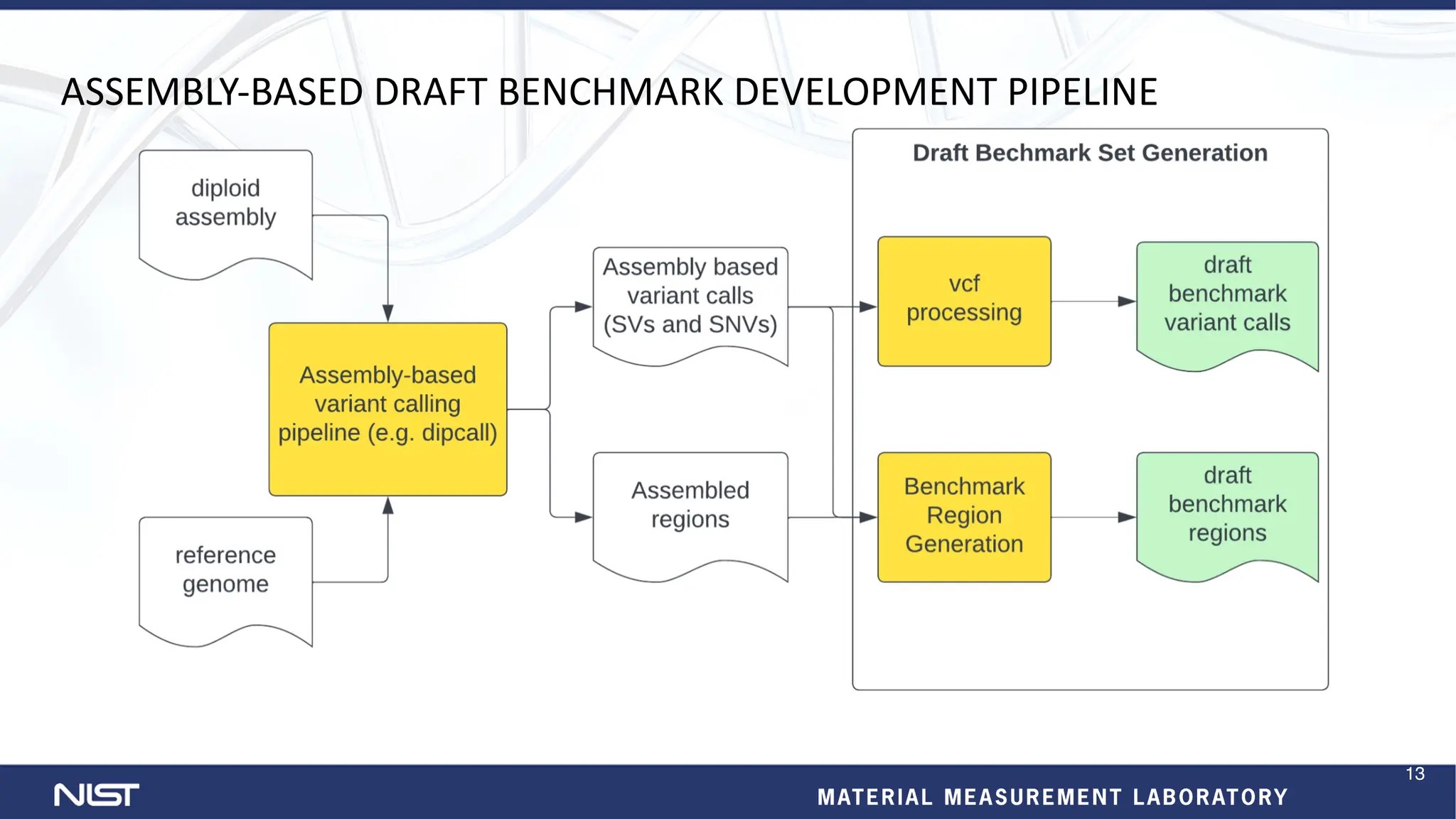
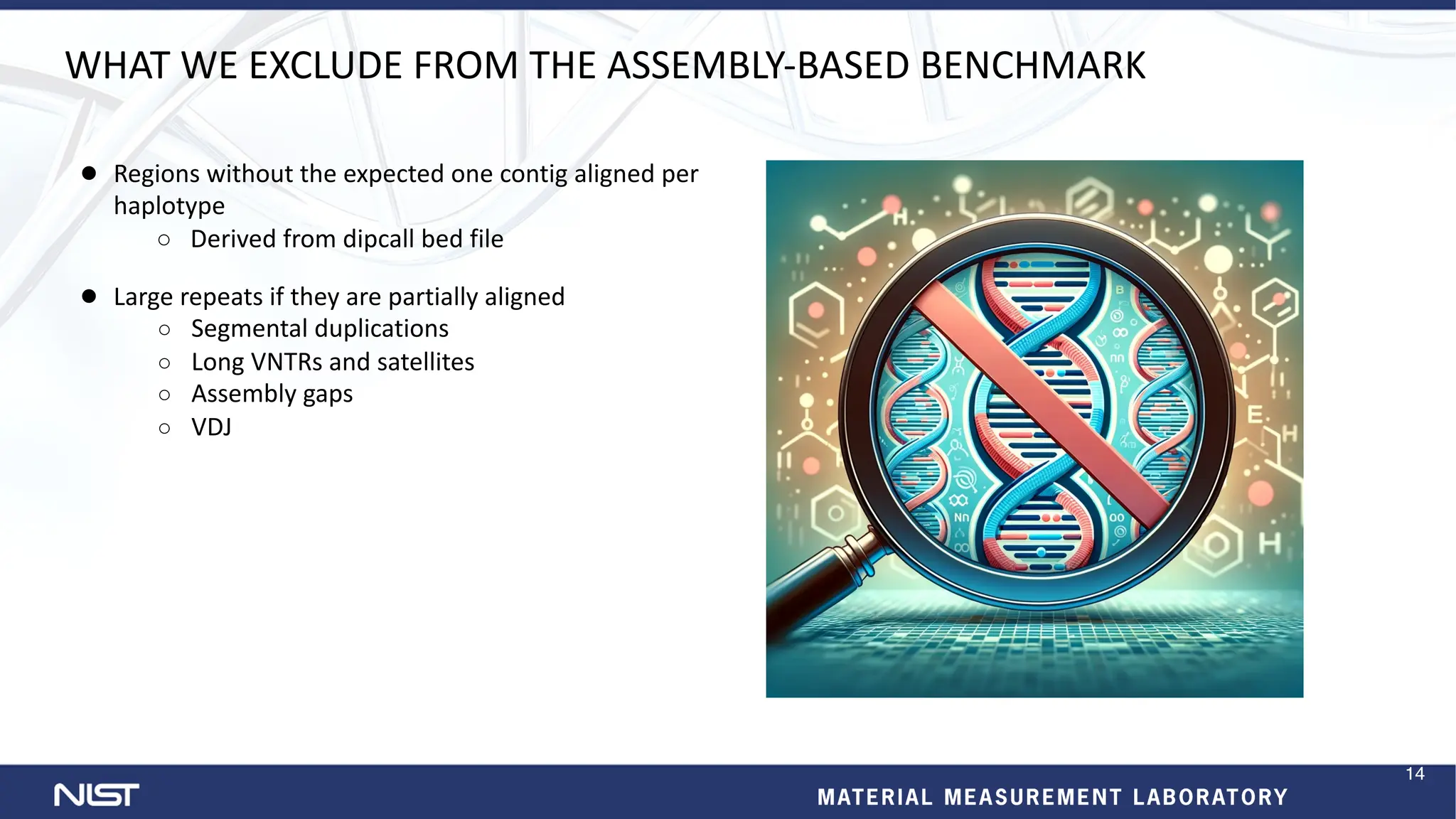
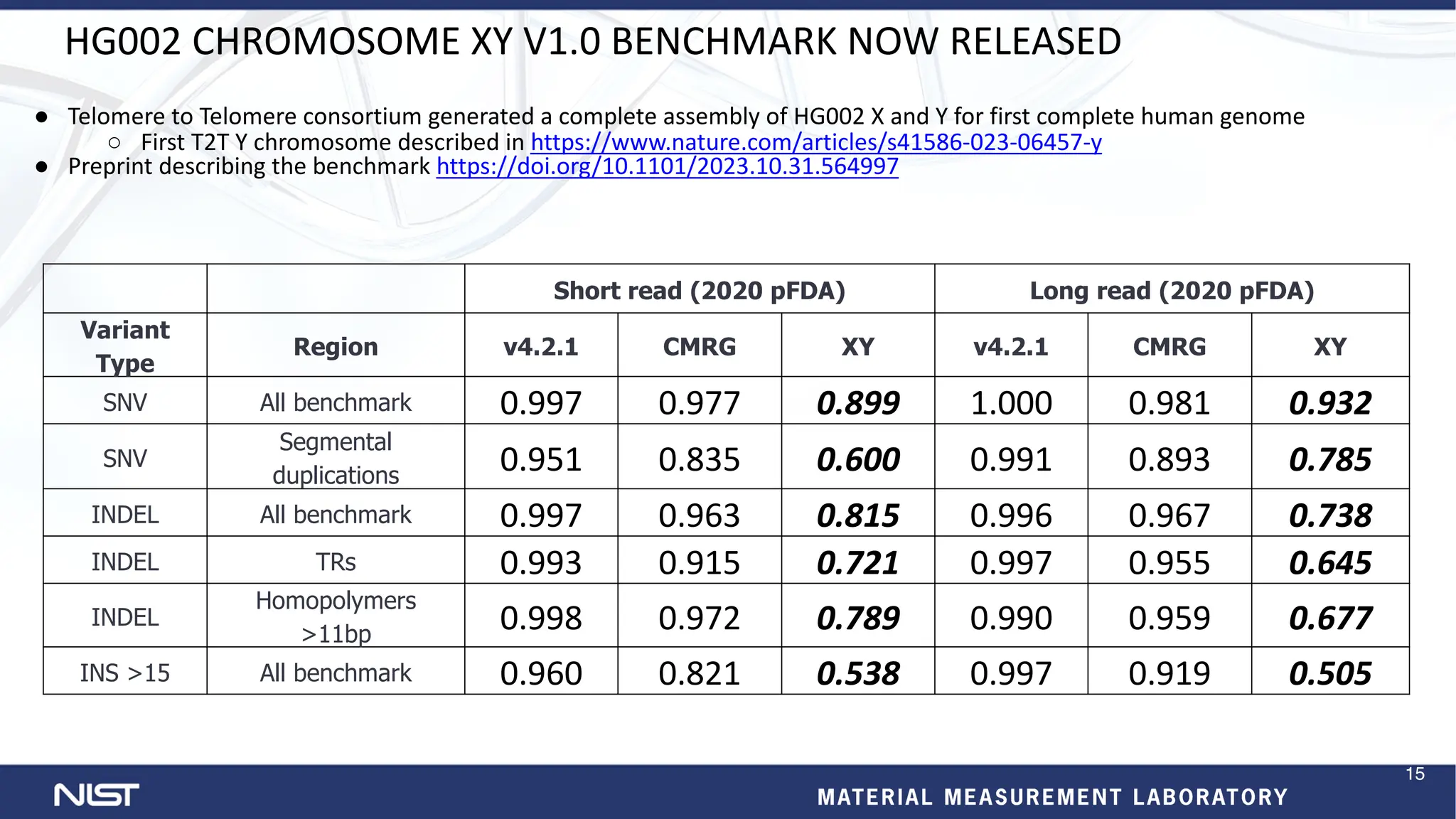
- New benchmark sets have been developed for mosaic variants, tandem repeats, and chromosomes X and Y using whole genome assemblies.
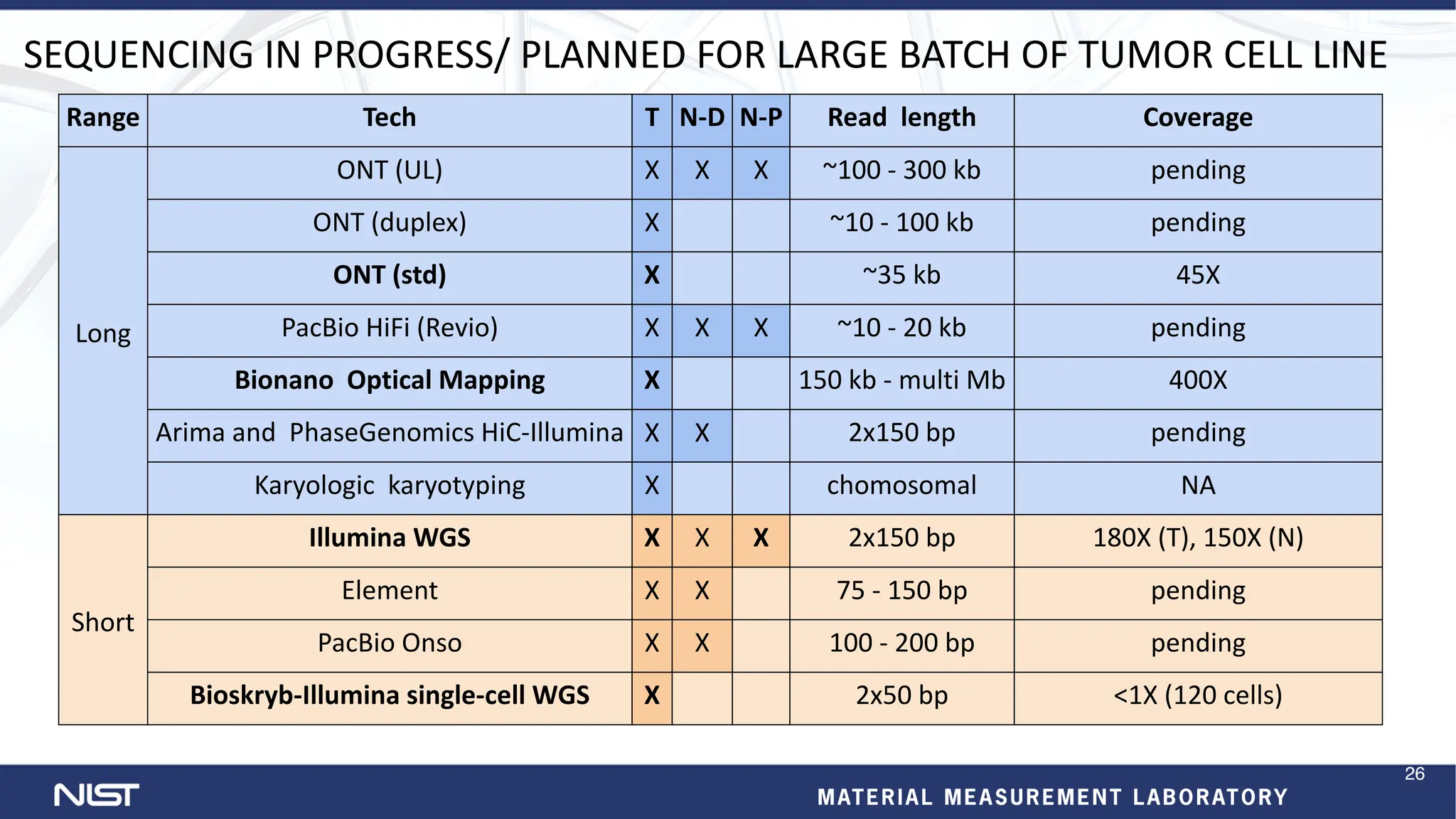
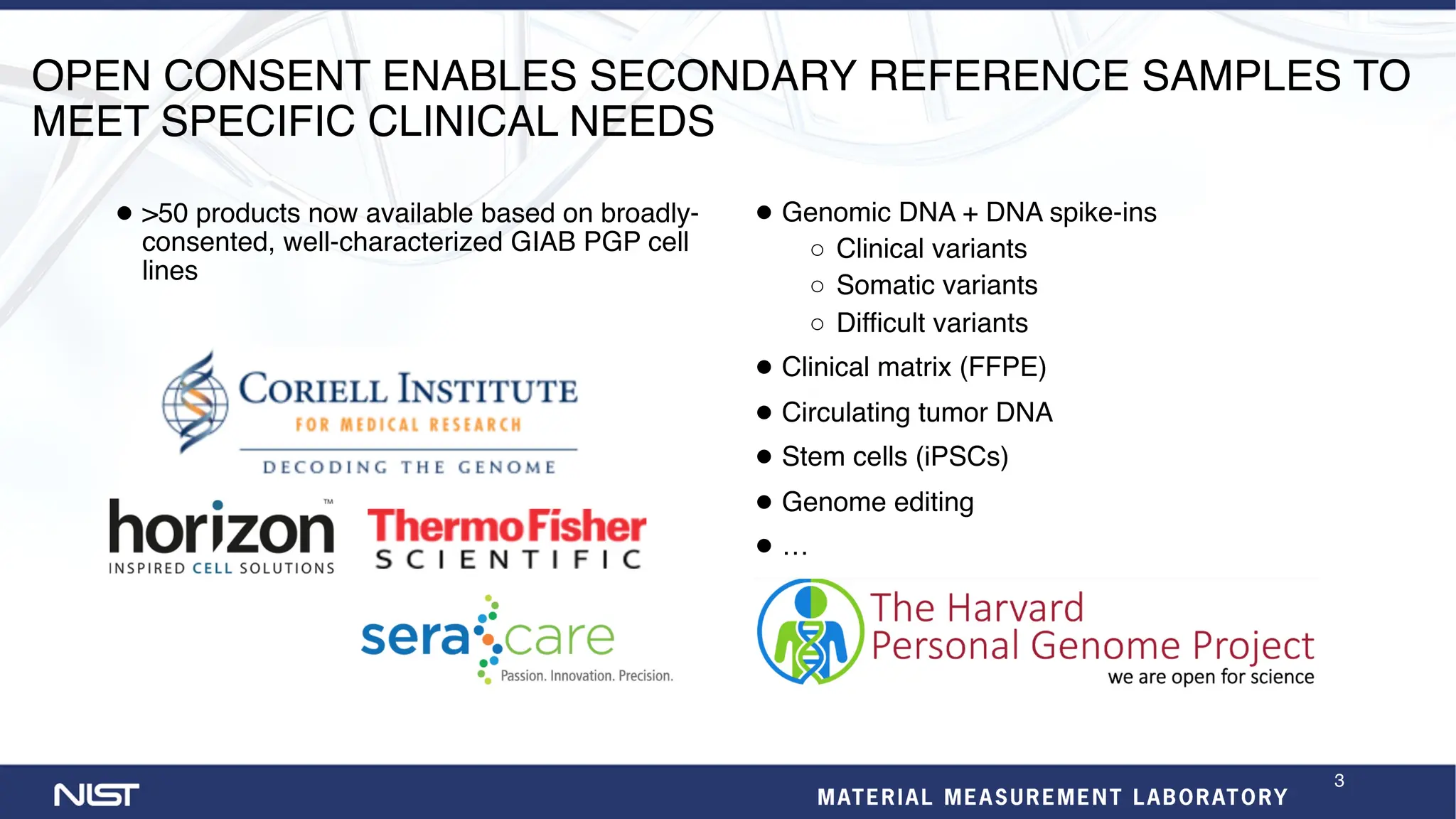
- Additional reference materials and samples are available, including a new tumor/normal cell line and over 50 products based on broadly consented genomes.
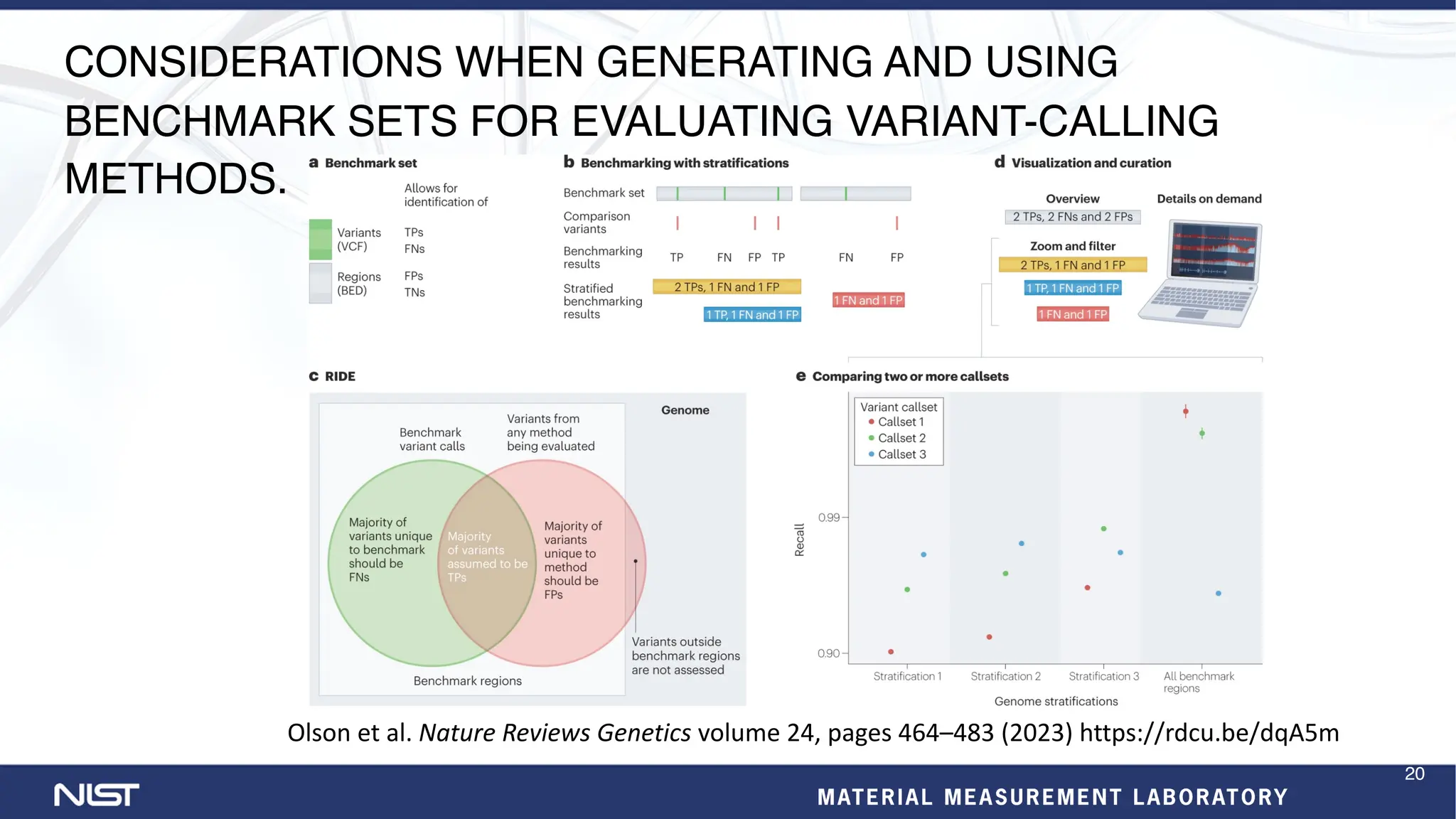
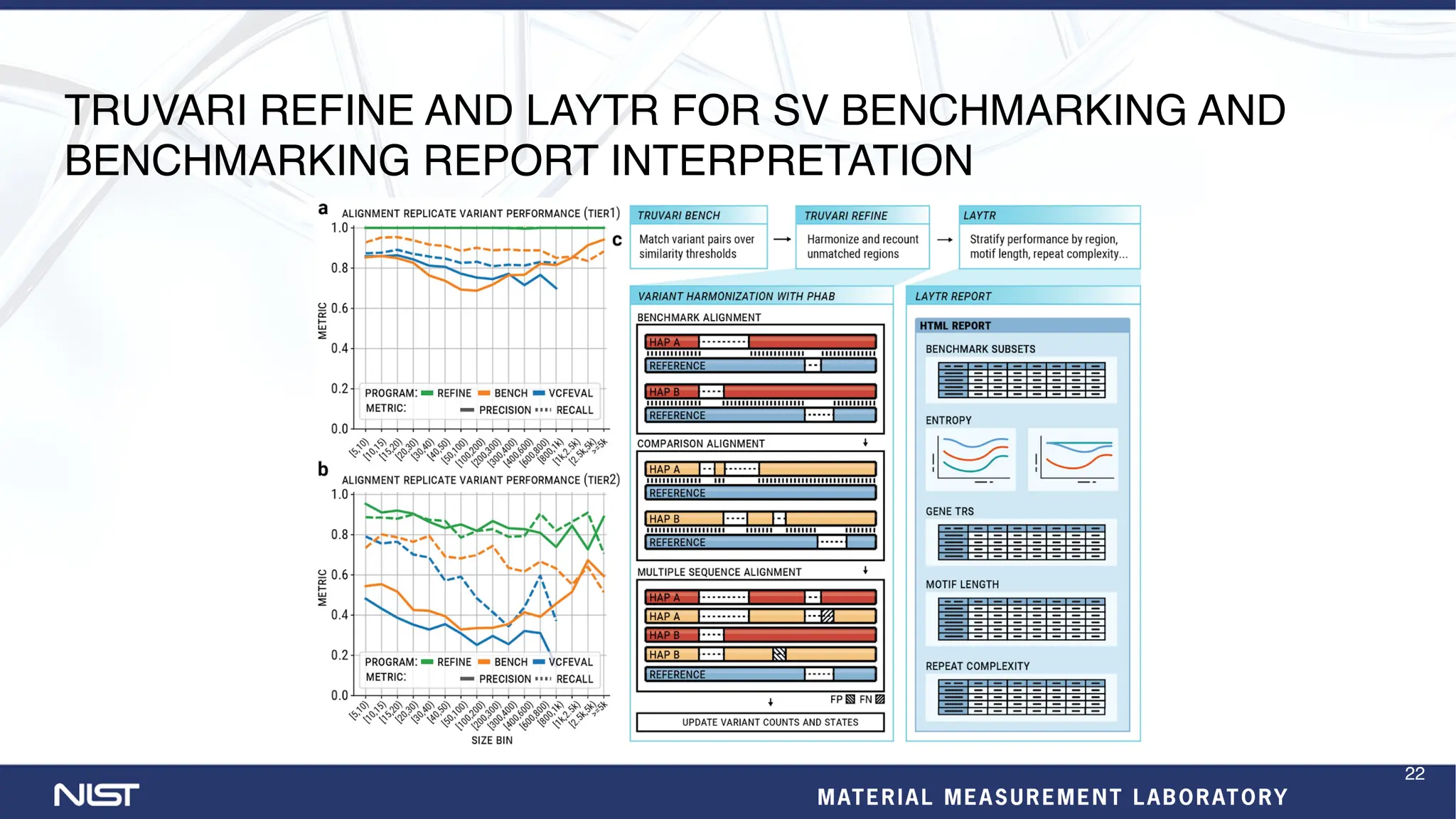
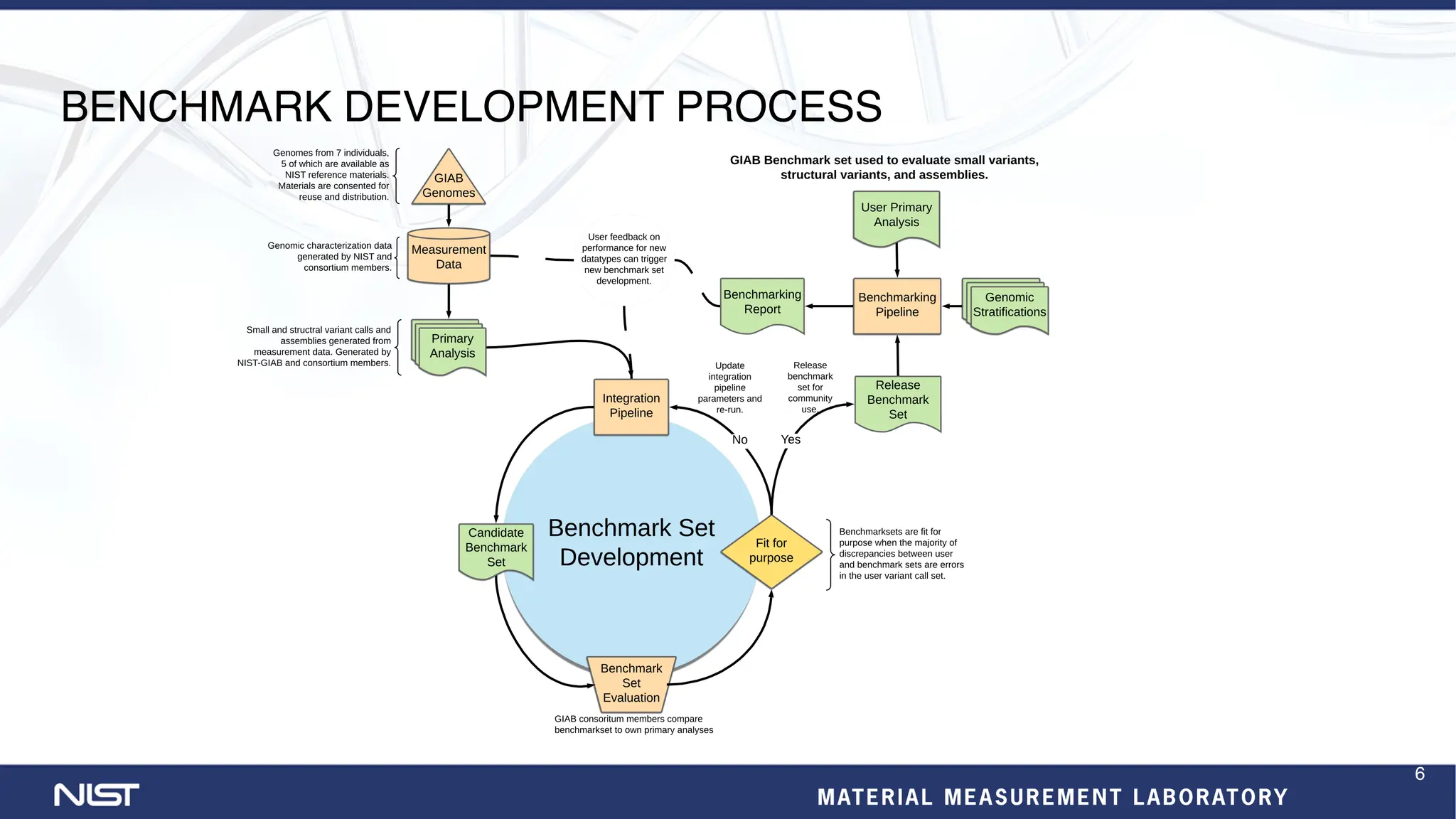
- Benchmarking methods are improving to better evaluate variant calling, including for structural variants and different data types like RNA sequencing.
- Future plans include developing more somatic benchmarks, assembling the HG002 genome to near perfection, and a searchable public data registry.



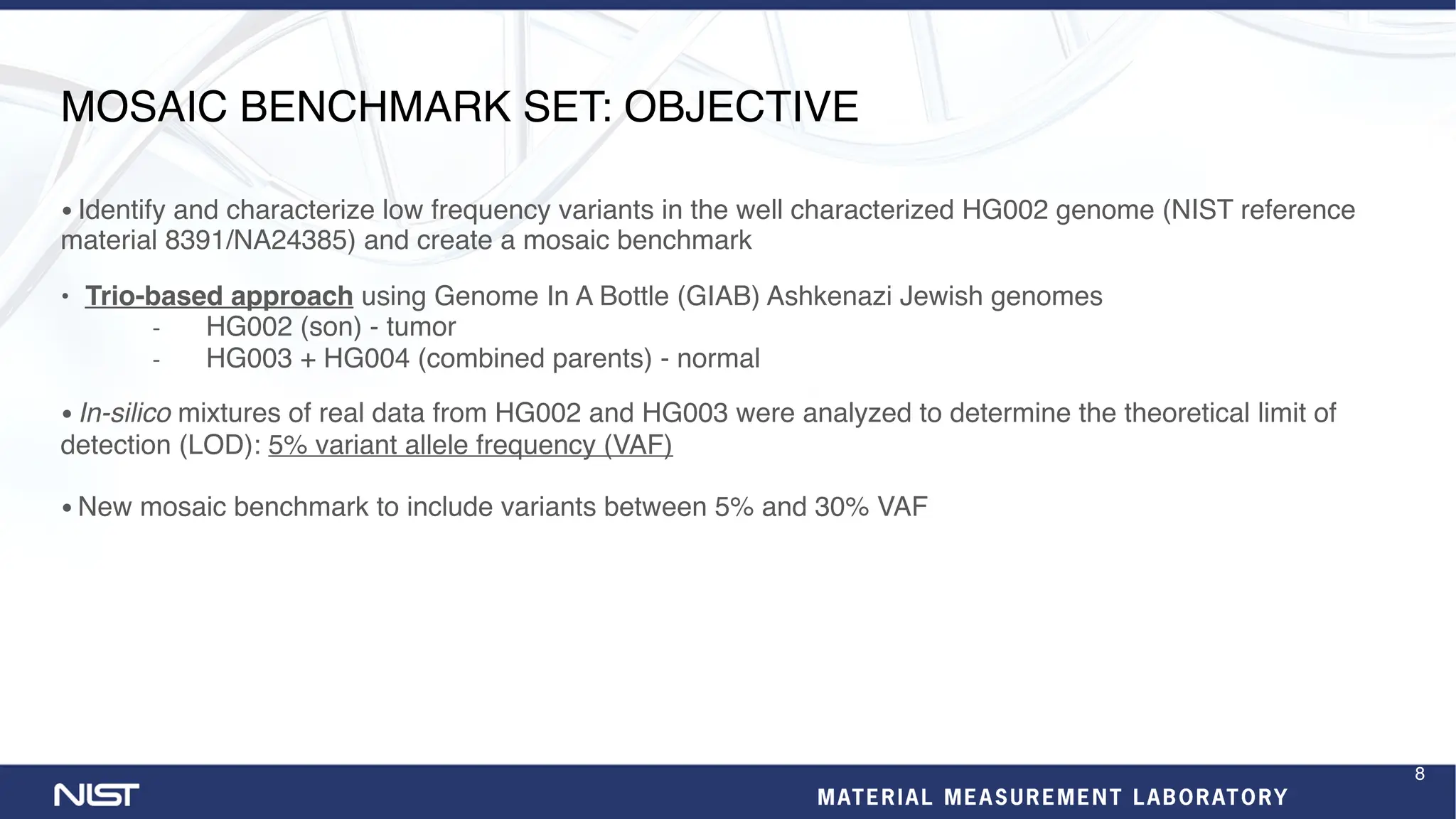
![HG002 MOSAIC BENCHMARK GENERATION
HG003 + HG004
.bam
(normal)
HG002
.bam
(tumor)
custom scripts
AJ trio benchmark
and mosaic intersections to
exclude complex variants
Strelka2
(somatic)
.vcf
vcfeval
Callset against GIAB v.4.2.1
benchmark (squash-ploidy)
normals excluded
vcf reformat
false positive
.vcf
list of potential
mosaic variants
.vcf
.fastqs
Novoalign
(GRCh38)
300X
each
GIAB AJ trio
Illumina PCR free,
HiSeq 2500
son combined parents
Potential mosaics
366,728
True positives
389,494
False positives
425,679
Strelka2
1,273,474
Potential mosaic variants
overview
● 1,930 candidate variants
(passing)
- 1,915 SNVs
- 15 indels
- 178 [5%-30%] VAF
● 364,798 putative variants
(non-passing)
- 364,792 SNVs
- 6 indels
- 15,743 [5%-30%] VAF
• 125 potential mosaic variants passed
decision tree heuristics for manual curation
- 105 easy-to-map with combined
orthogonal lower confidence
interval >=5%
- 20 not easy-to-map, non-
homopolymer, Pacbio lower
confidence interval >=5%
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2023-amp-rm-forumgiab-update-ndolson-231116151021-b5207874/75/2023-GIAB-AMP-Update-9-2048.jpg)