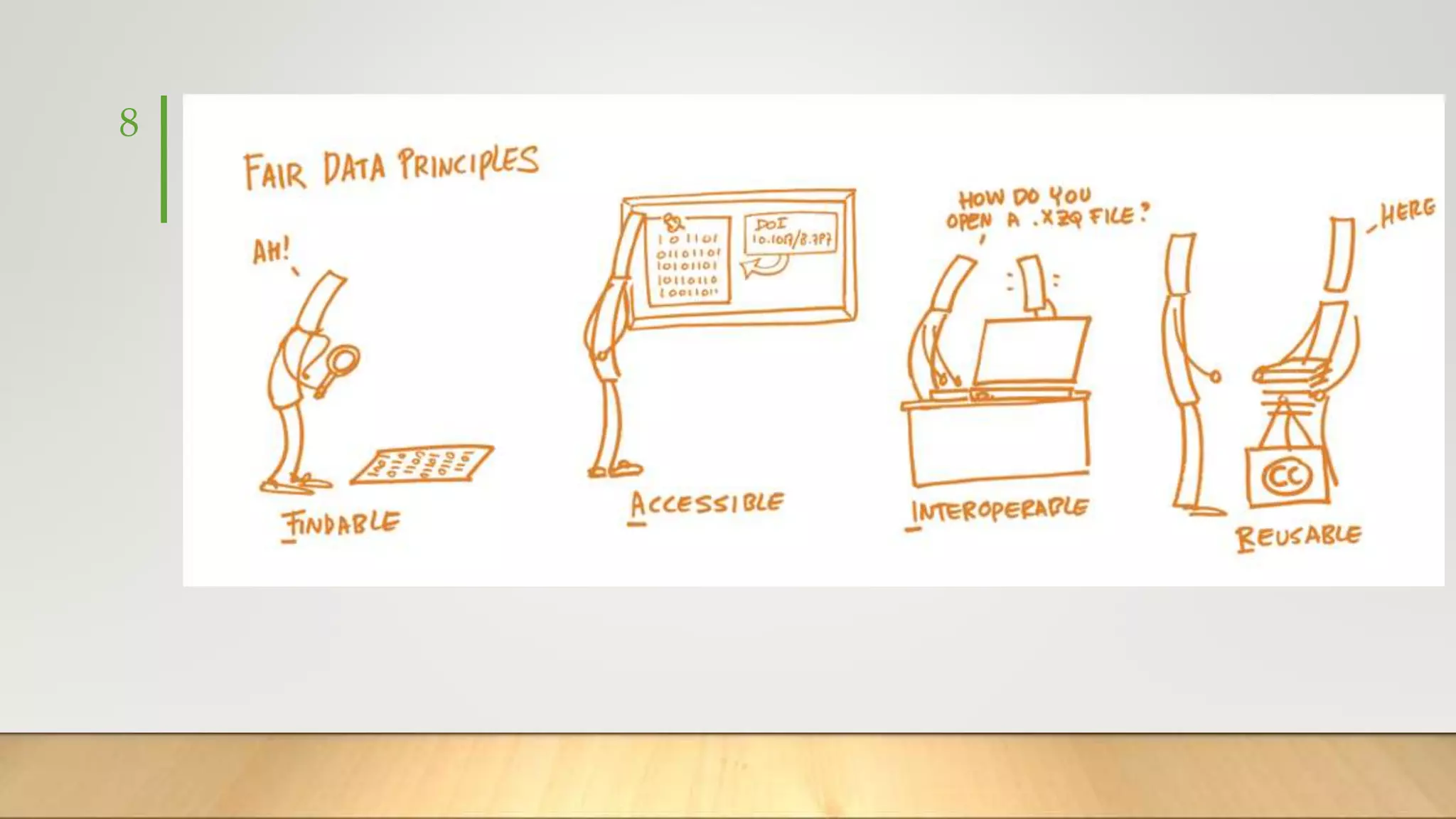
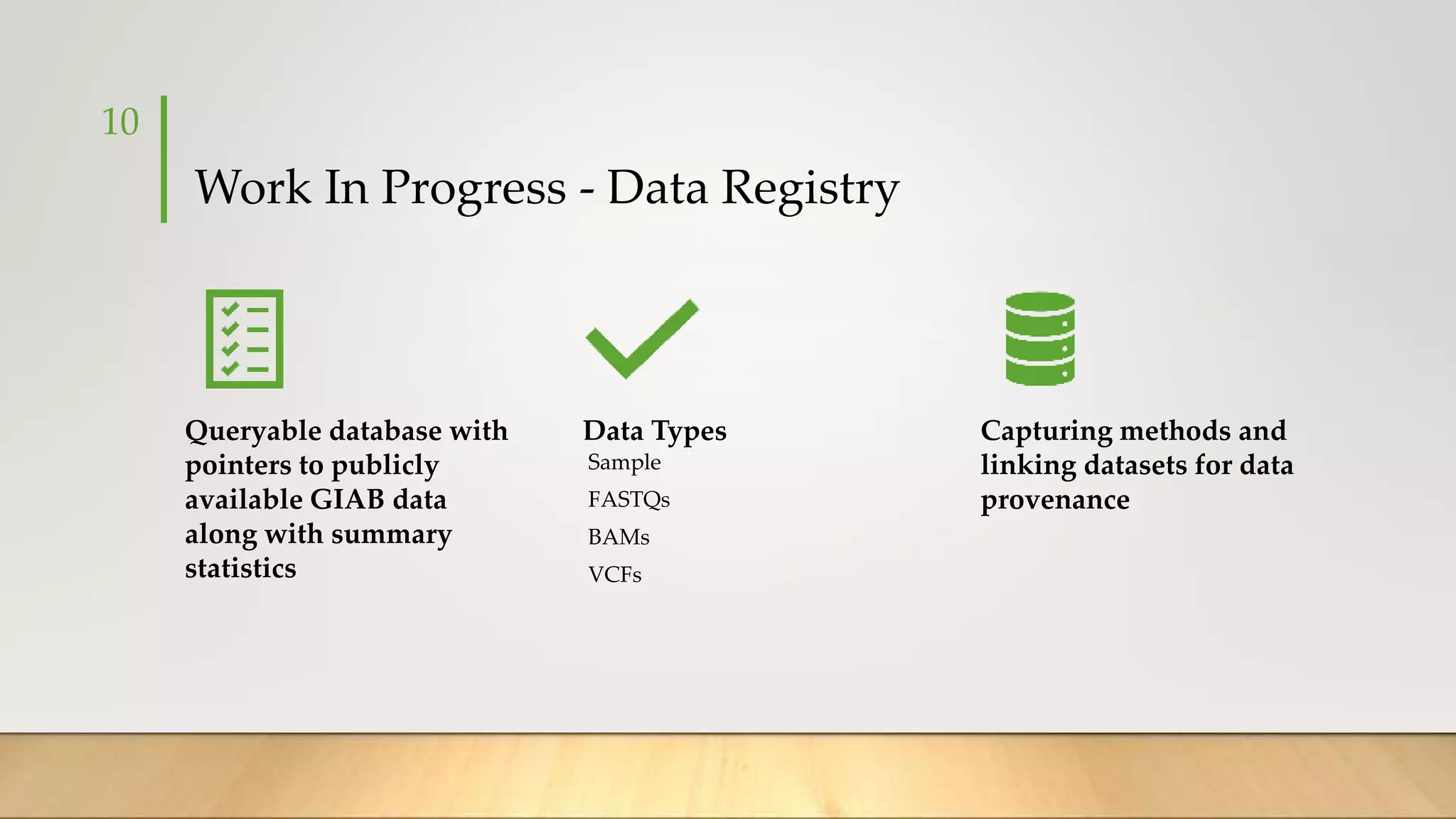
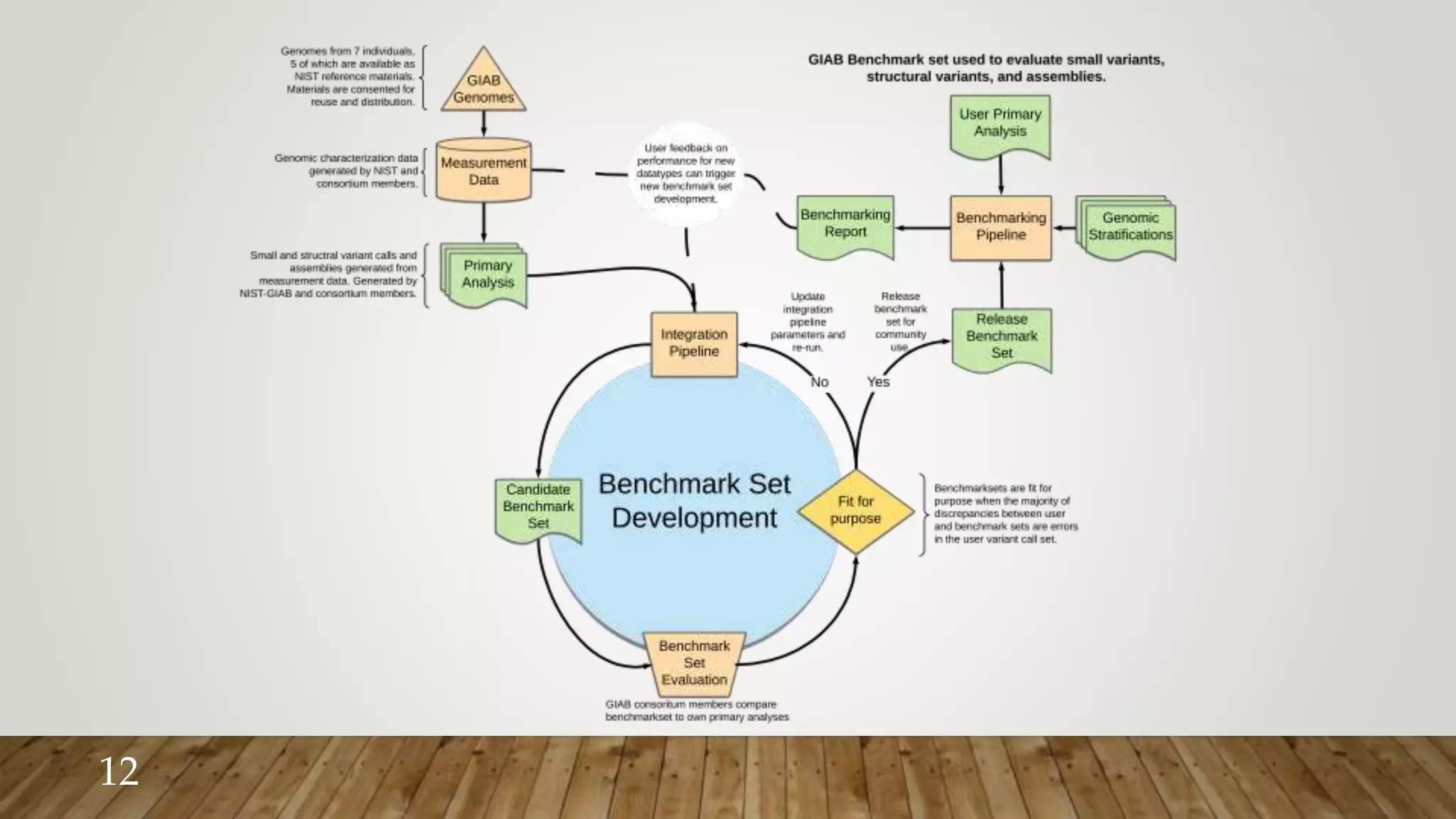
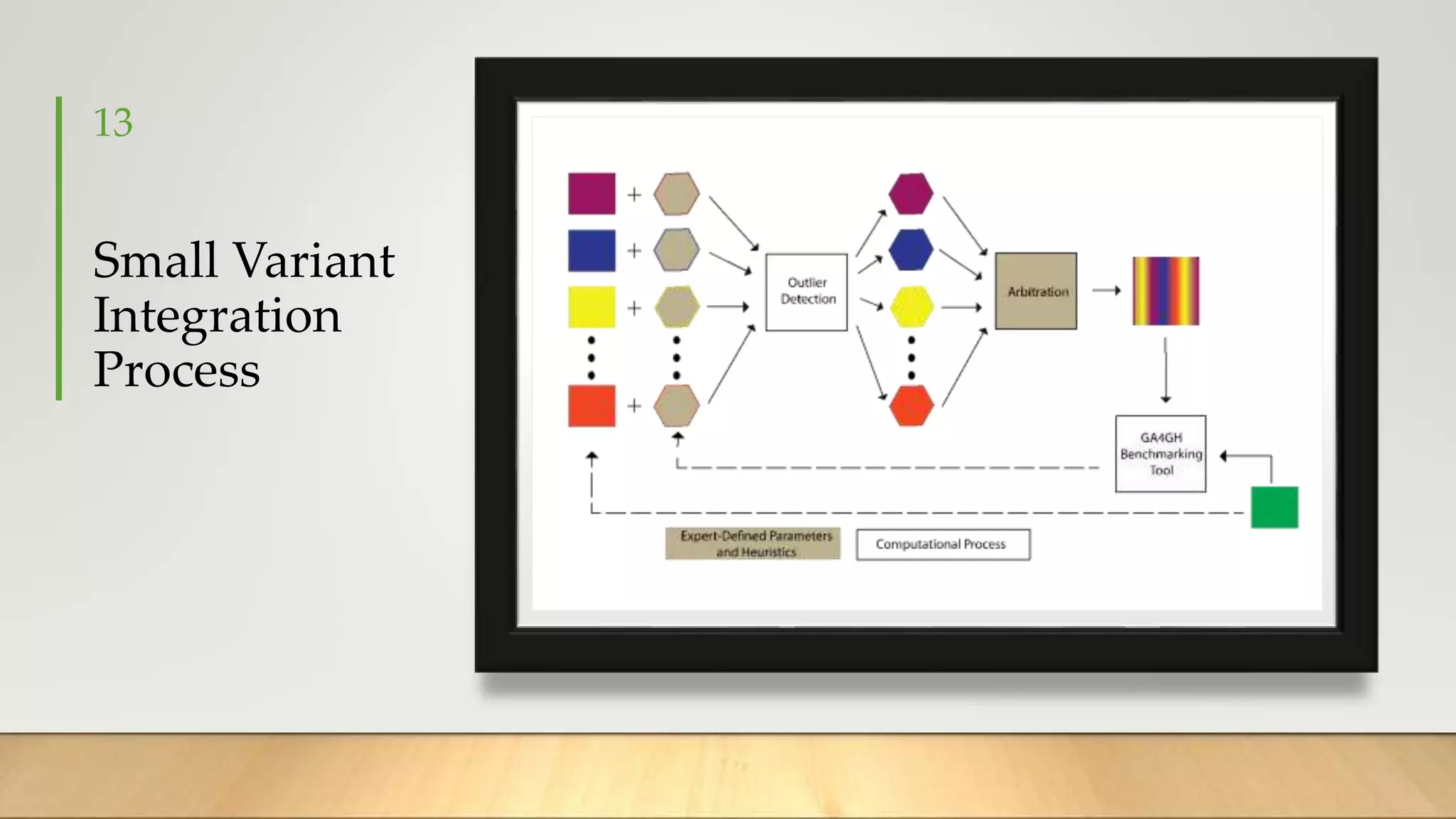
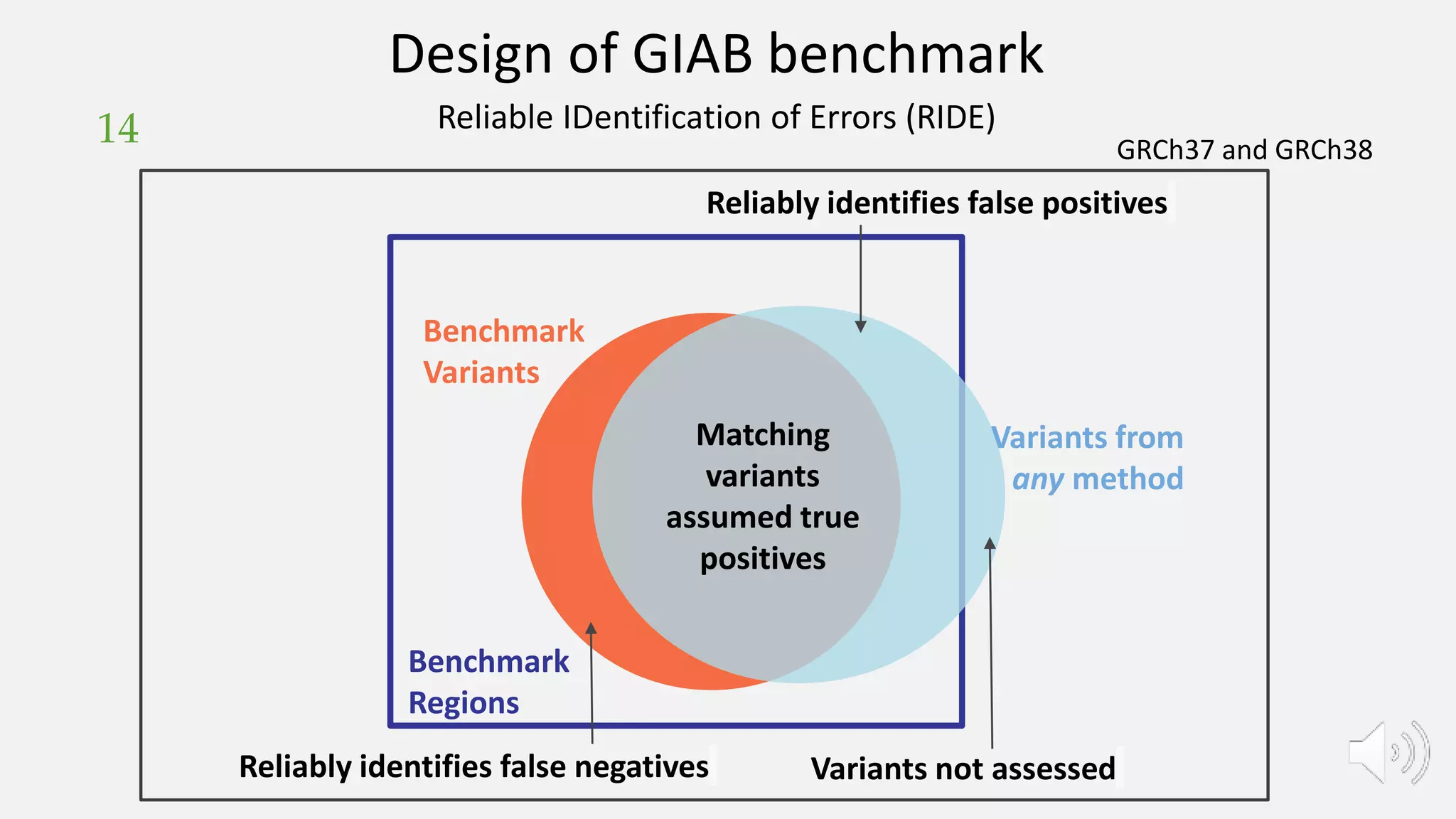
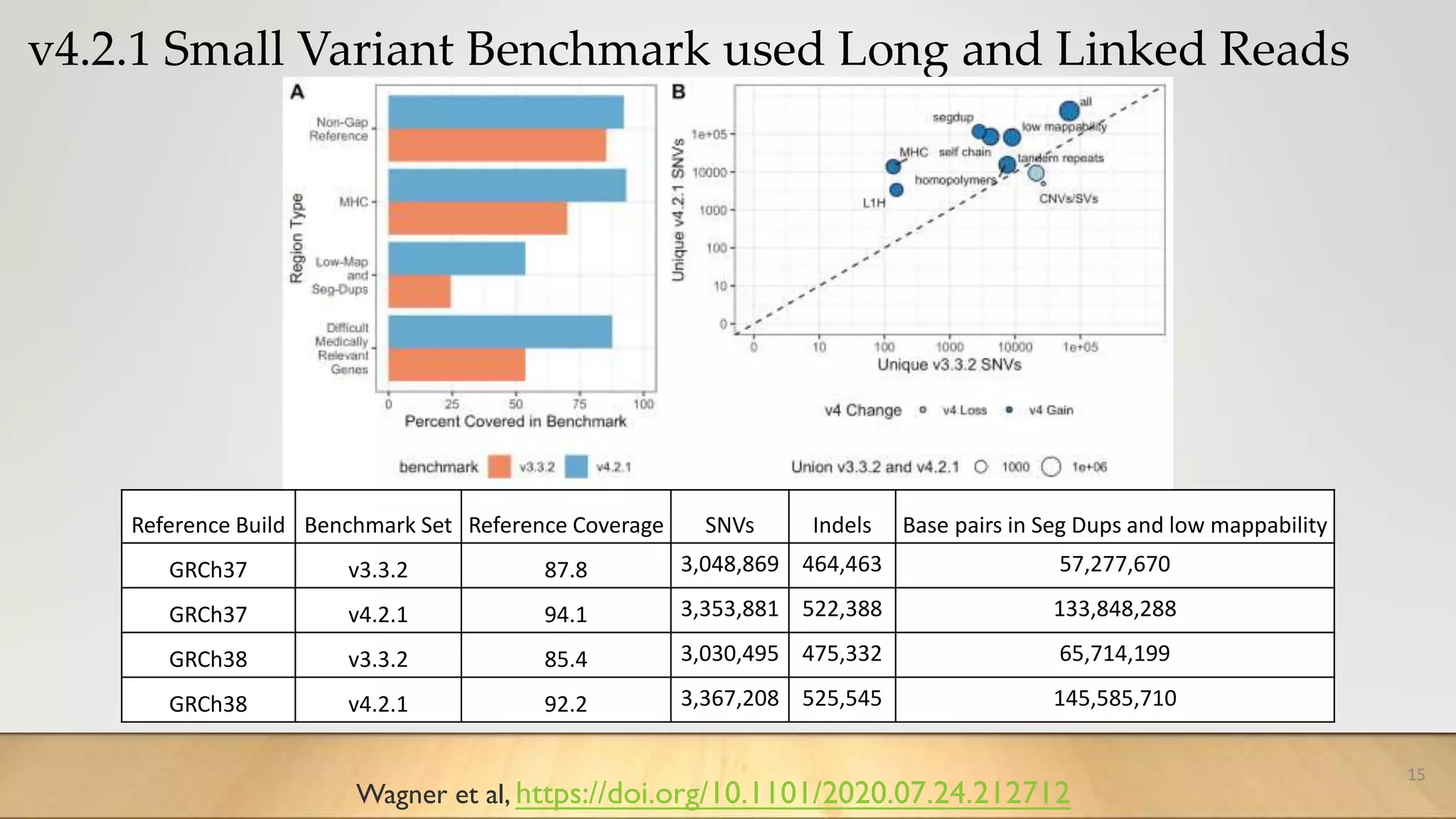
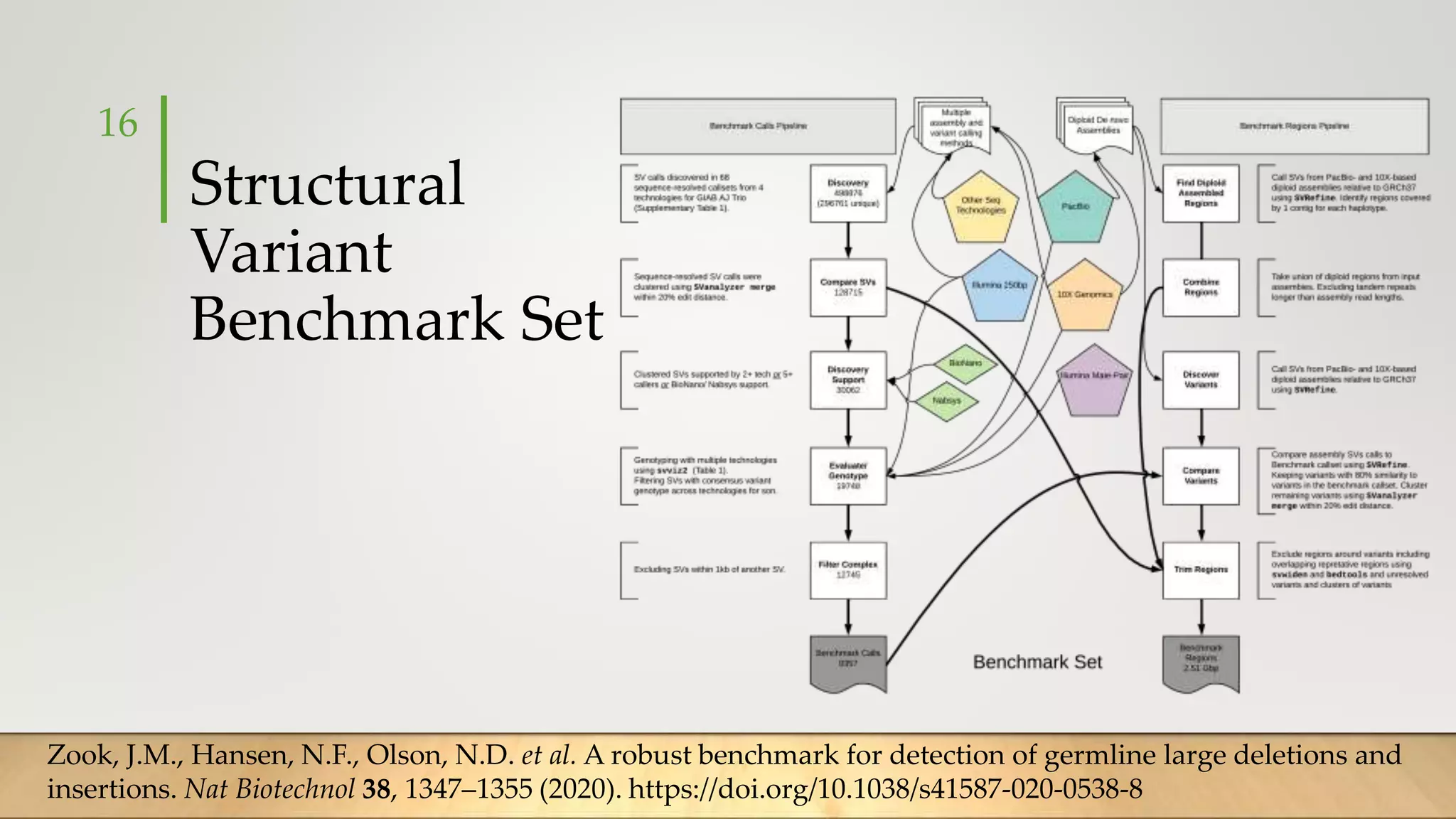
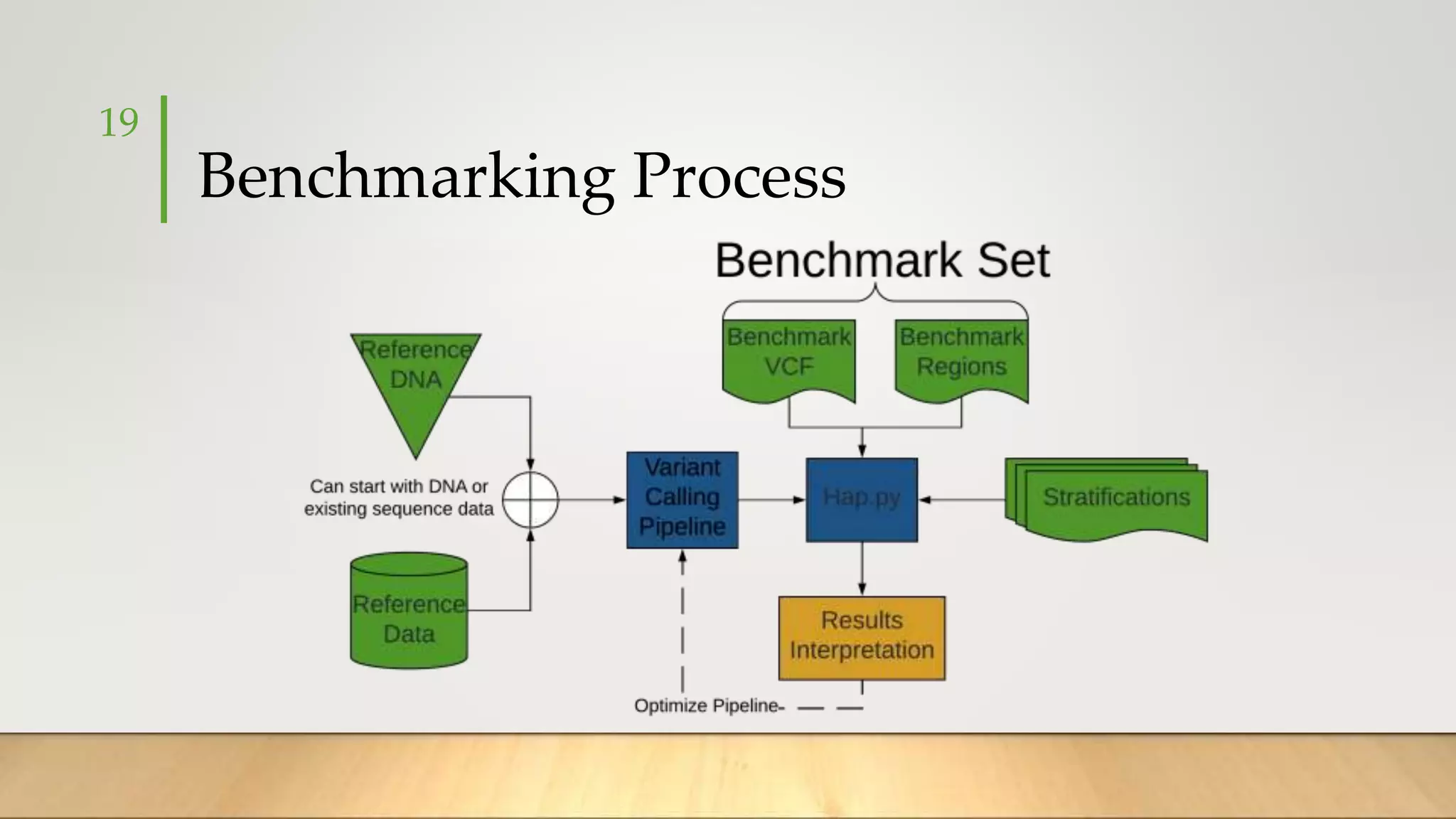
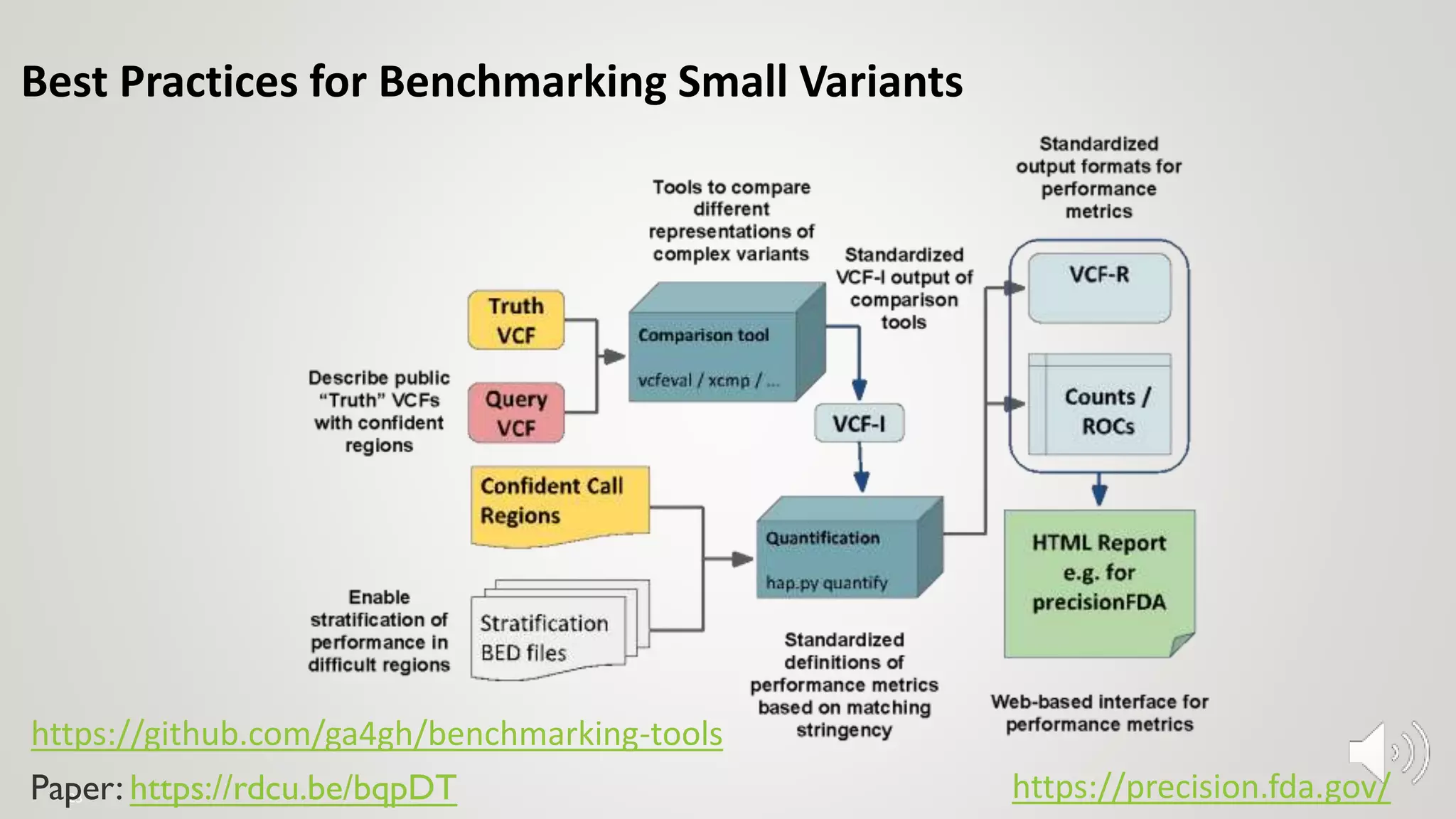
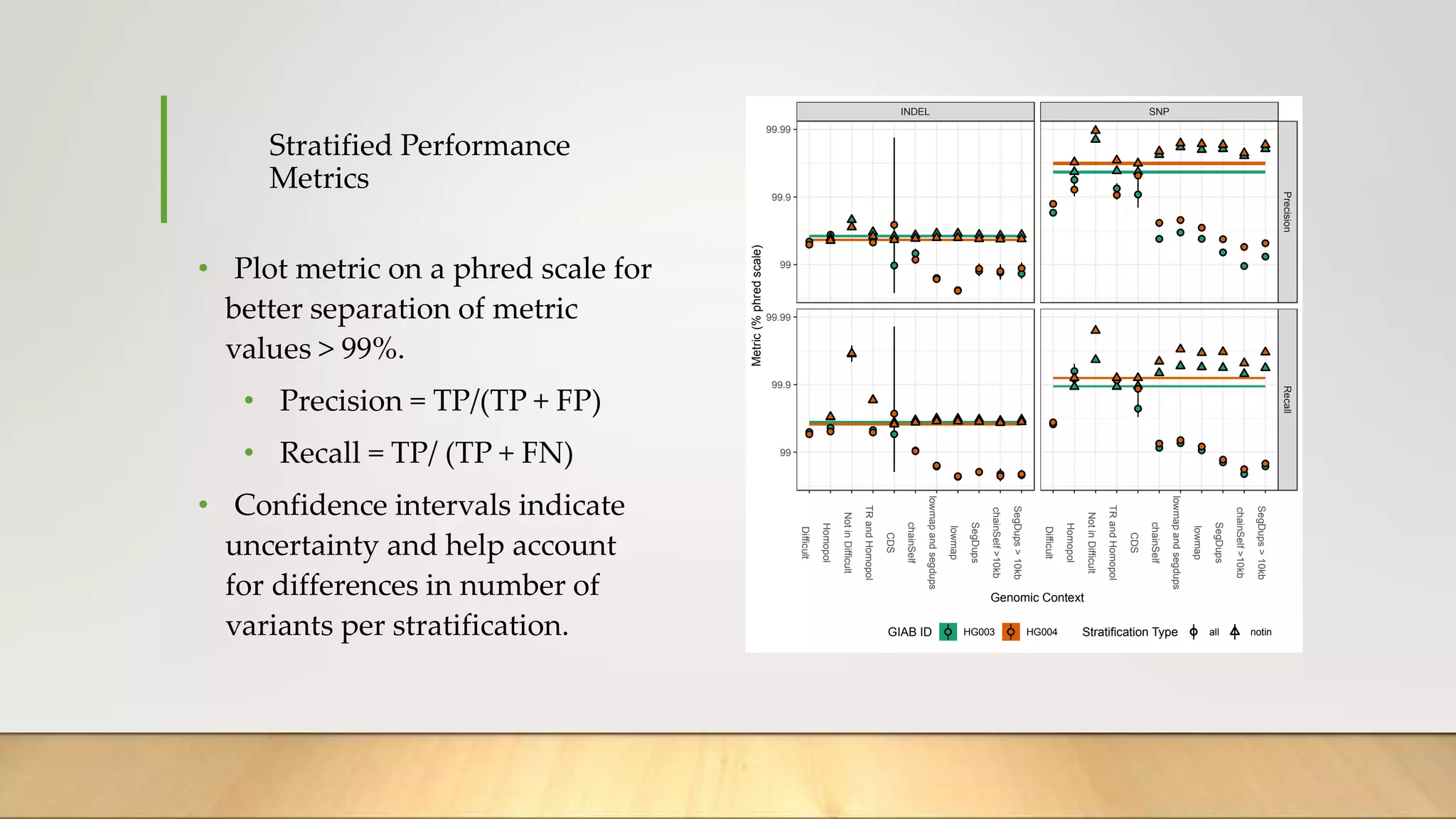
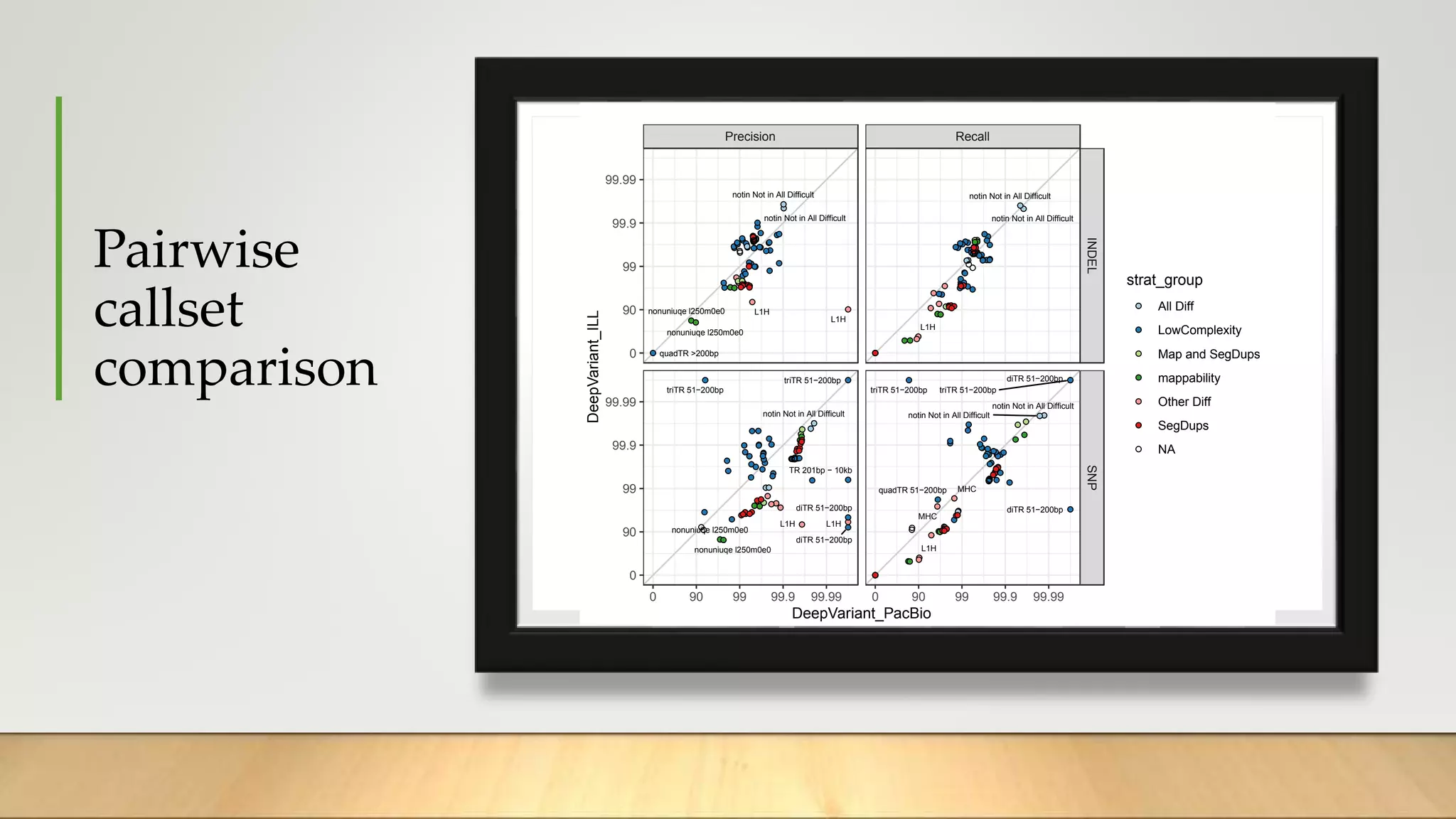
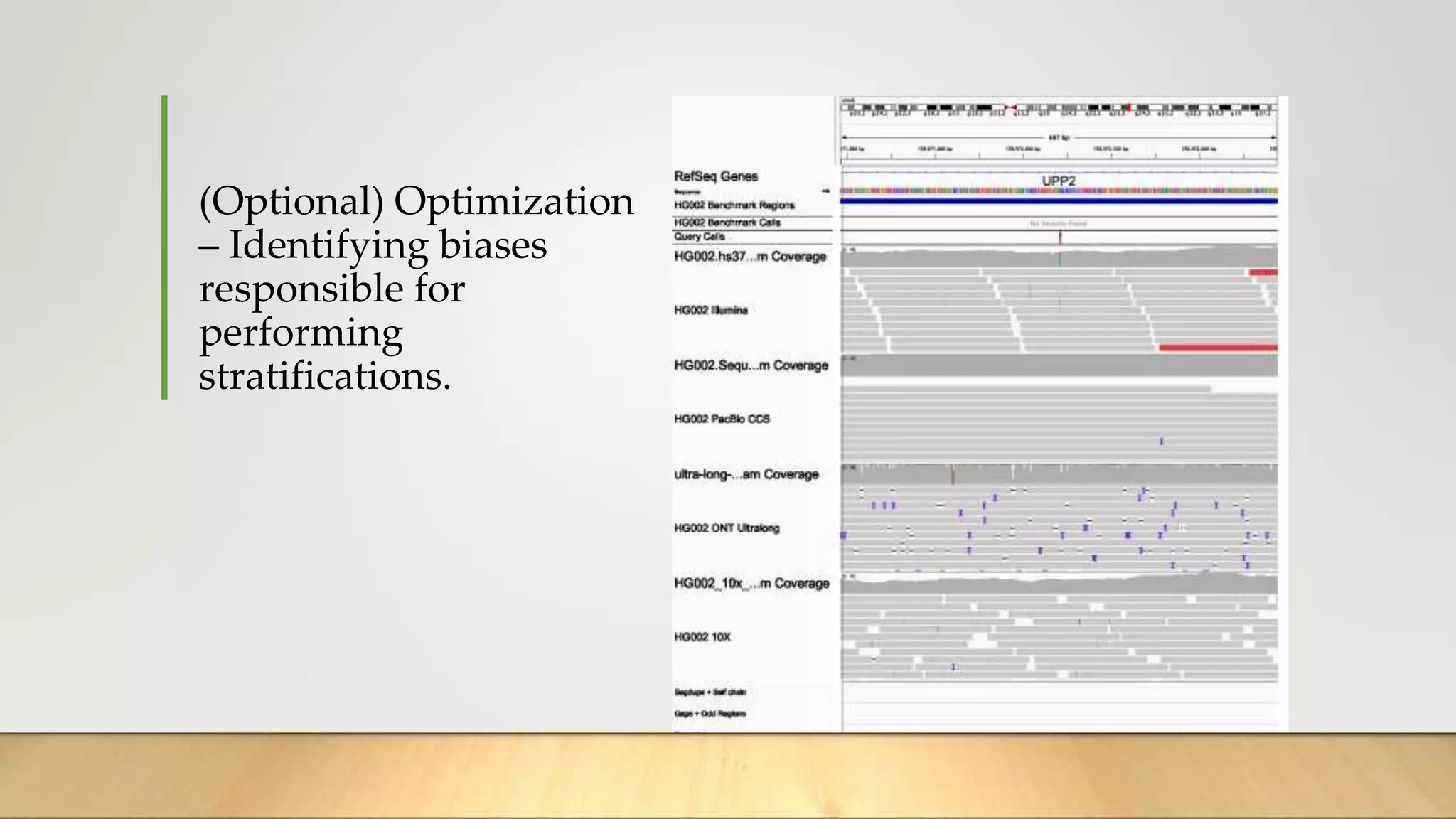
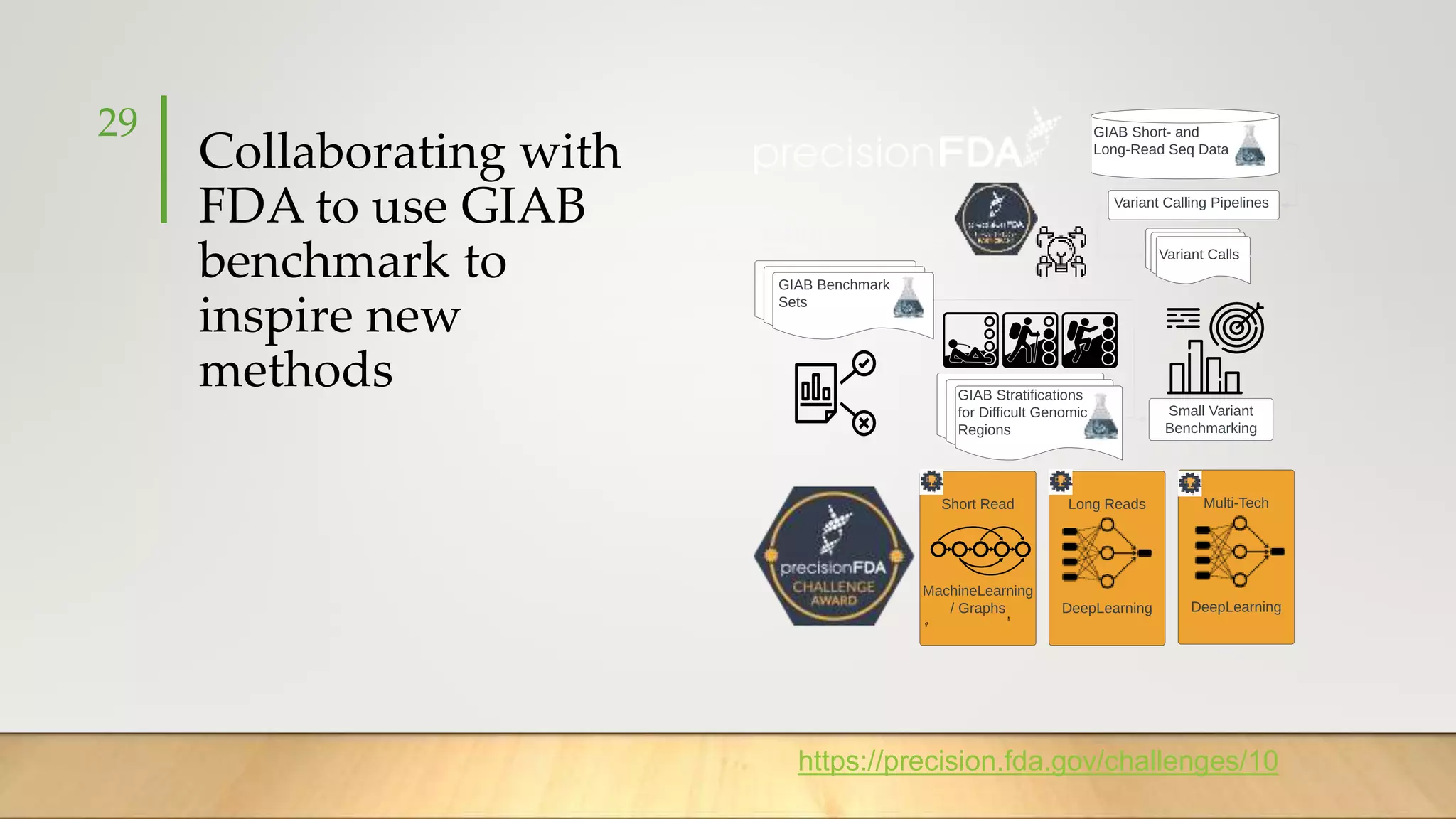
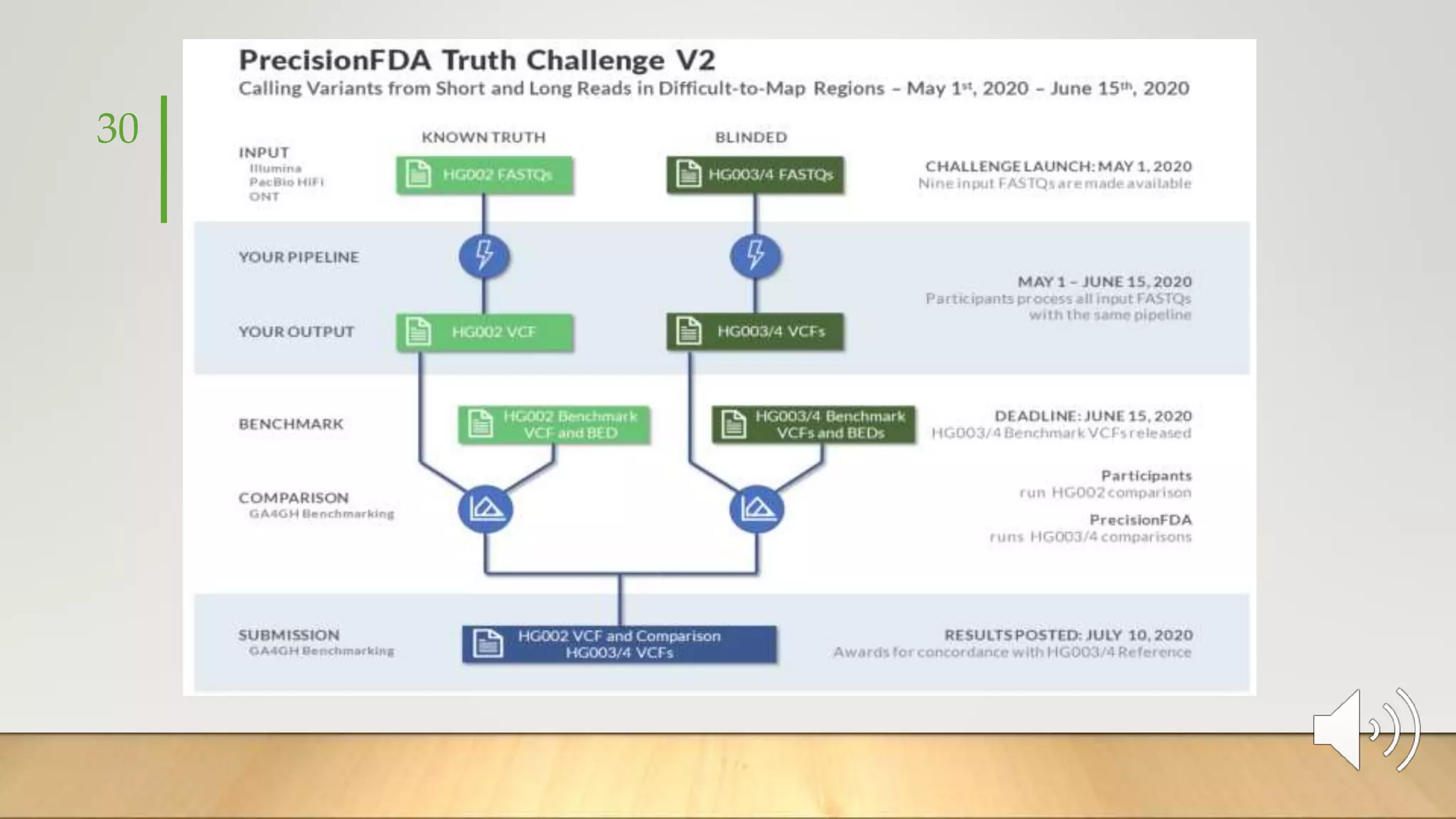
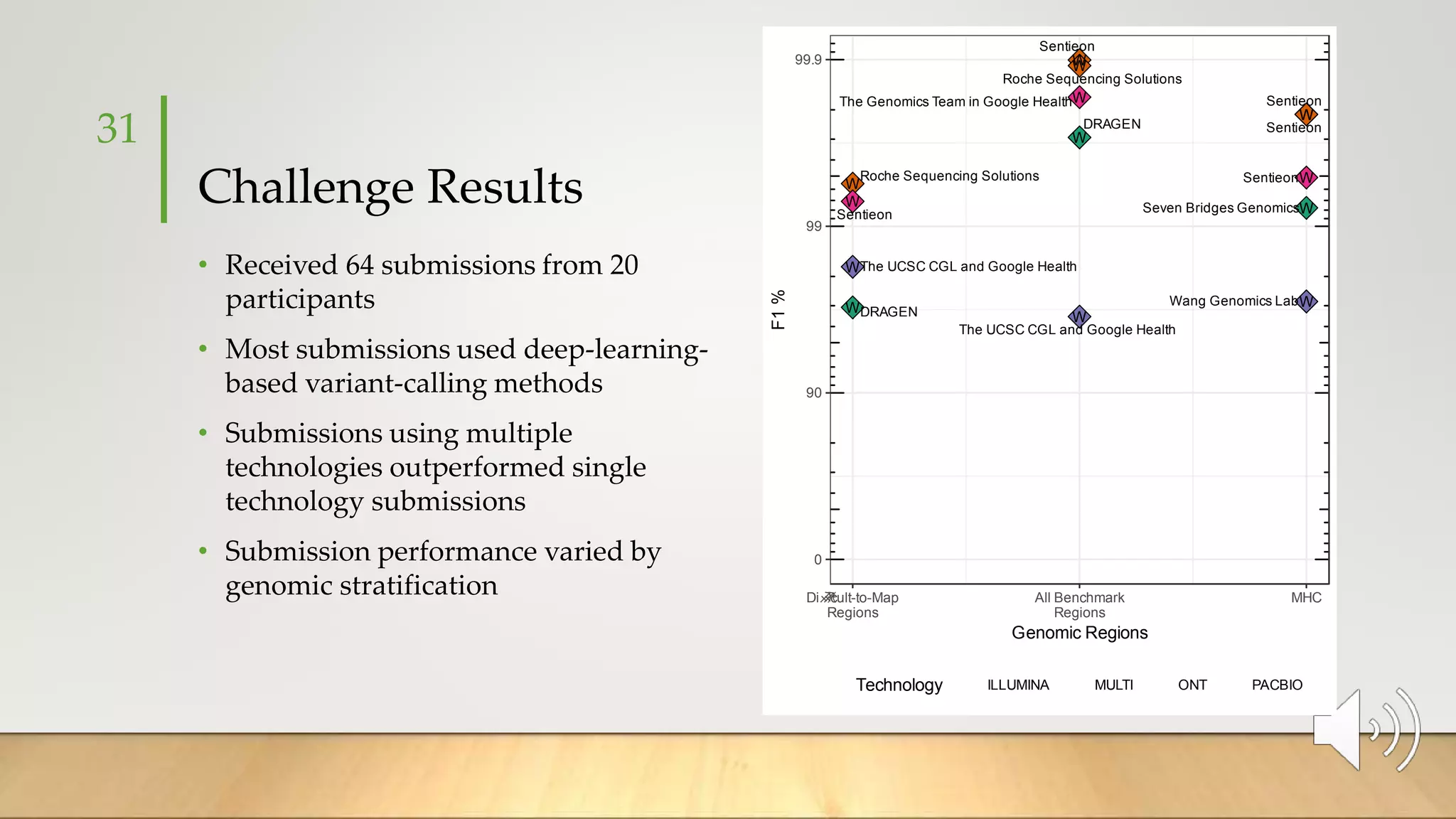
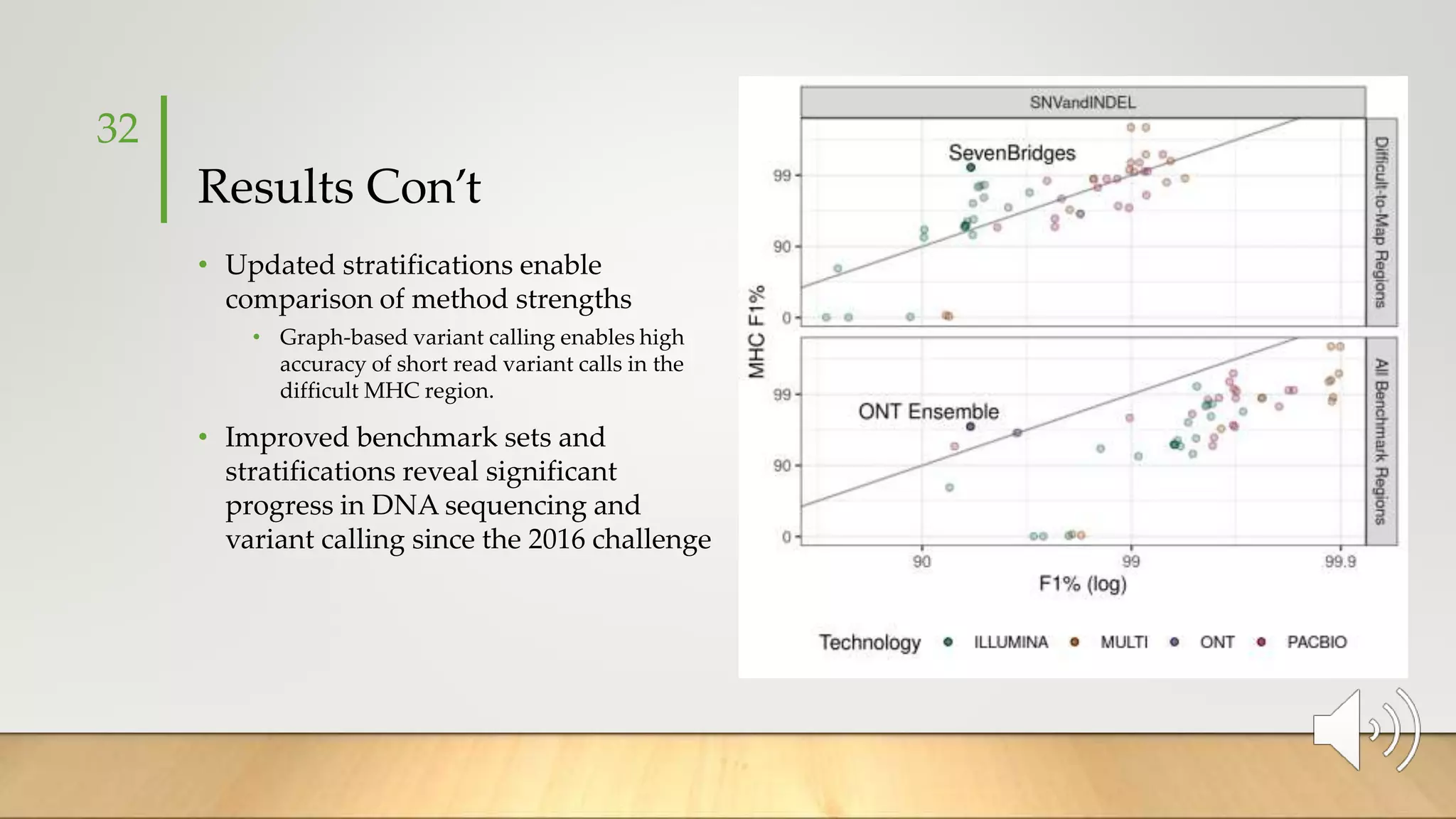
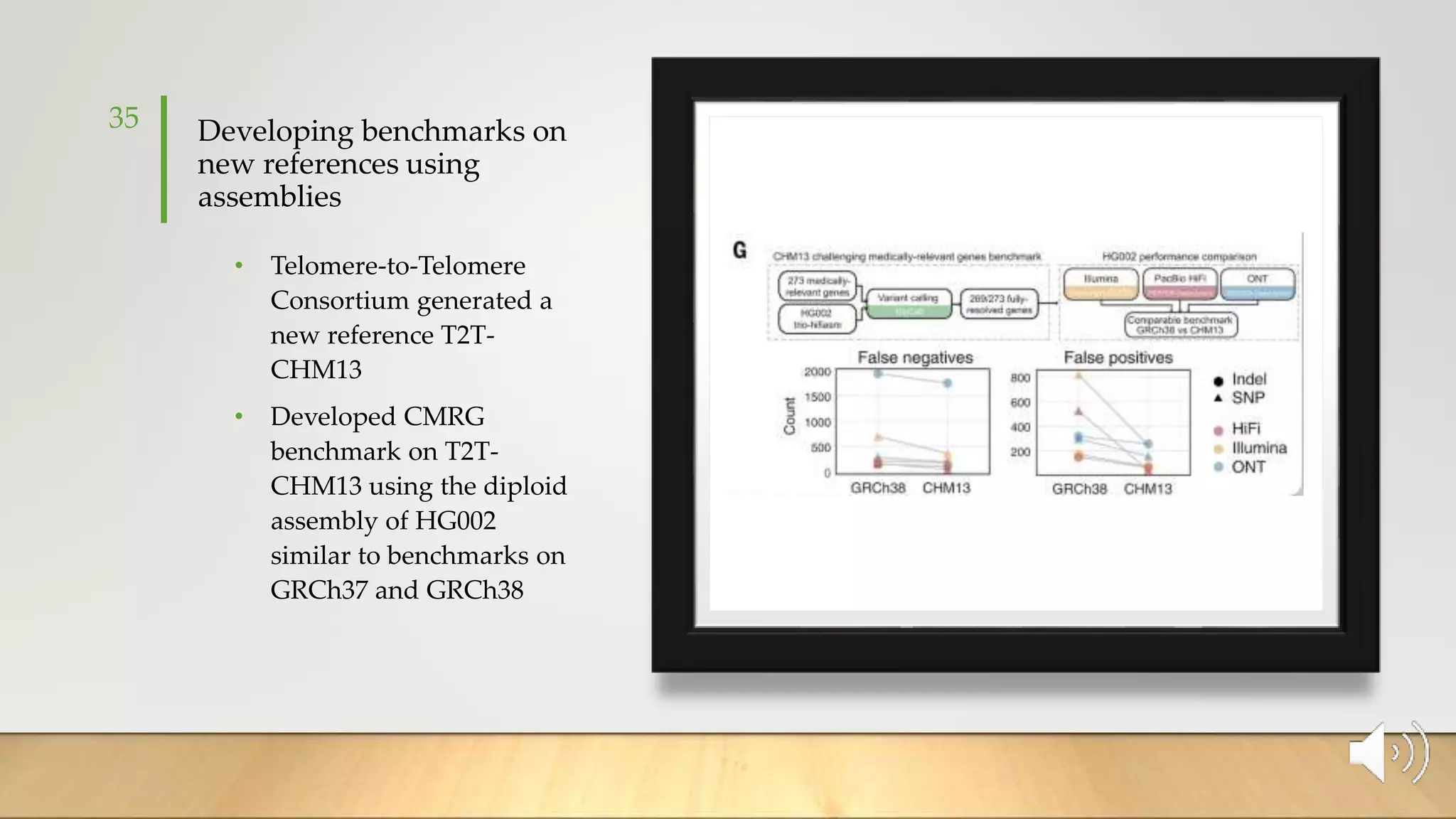
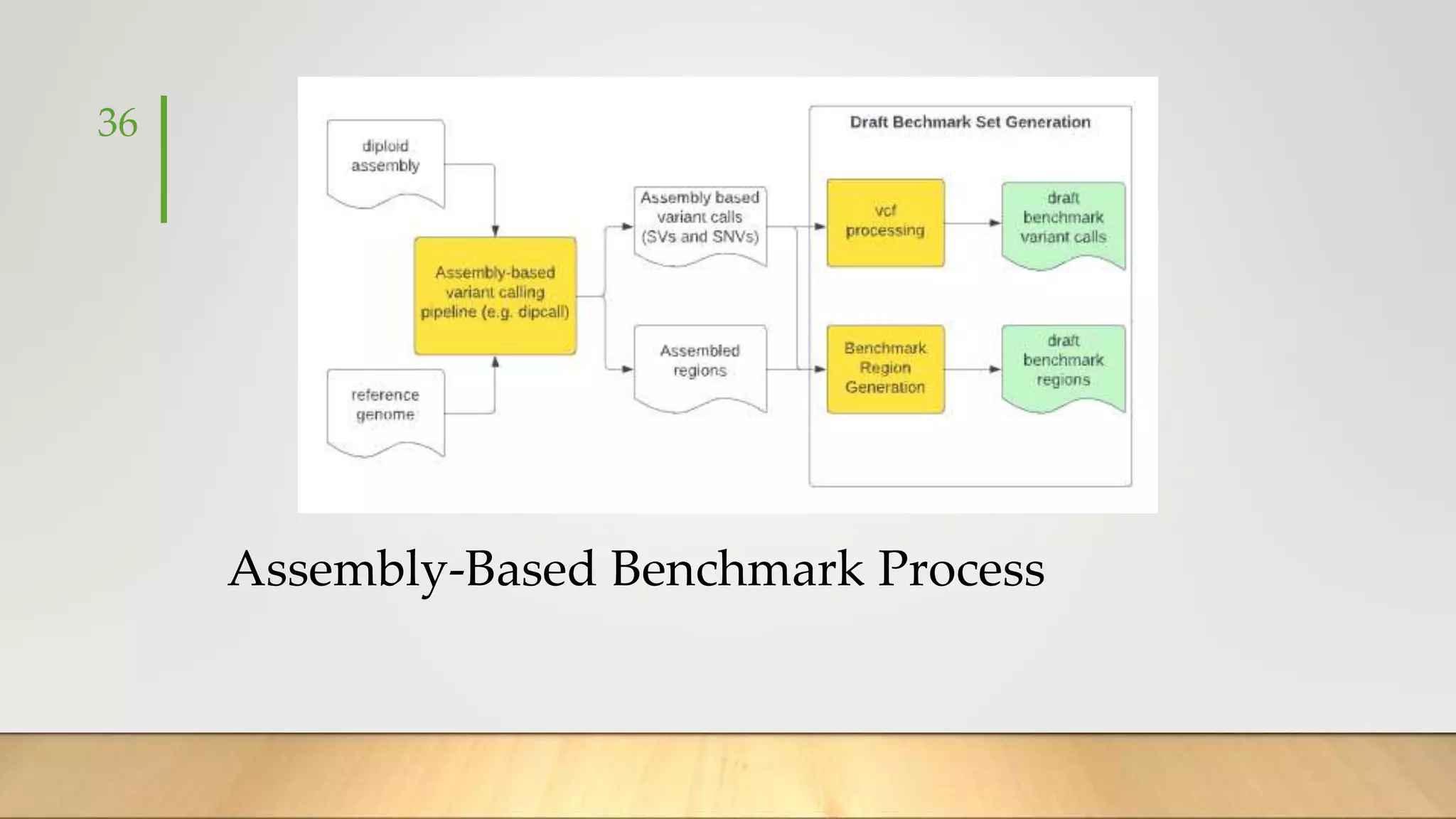
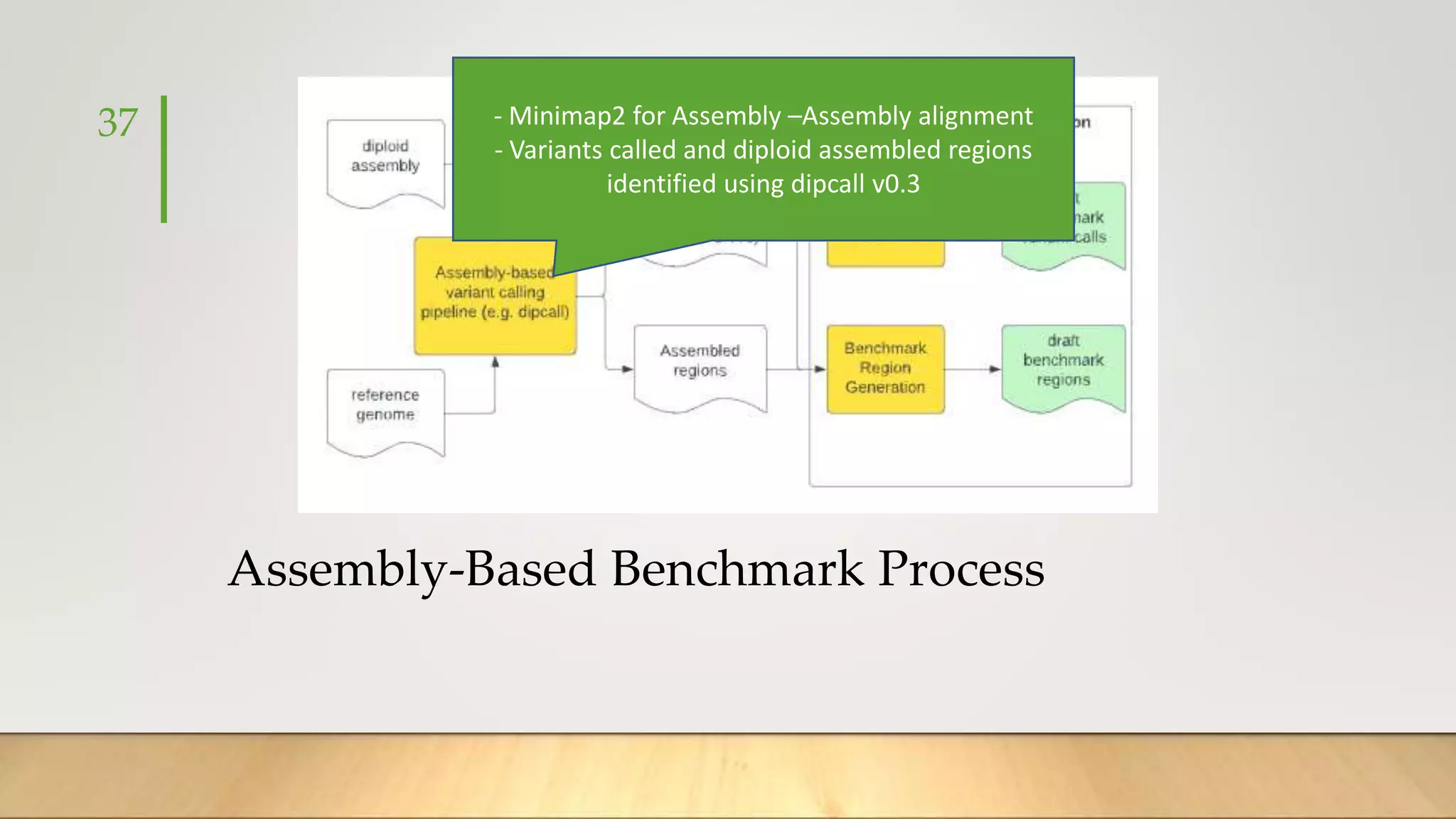
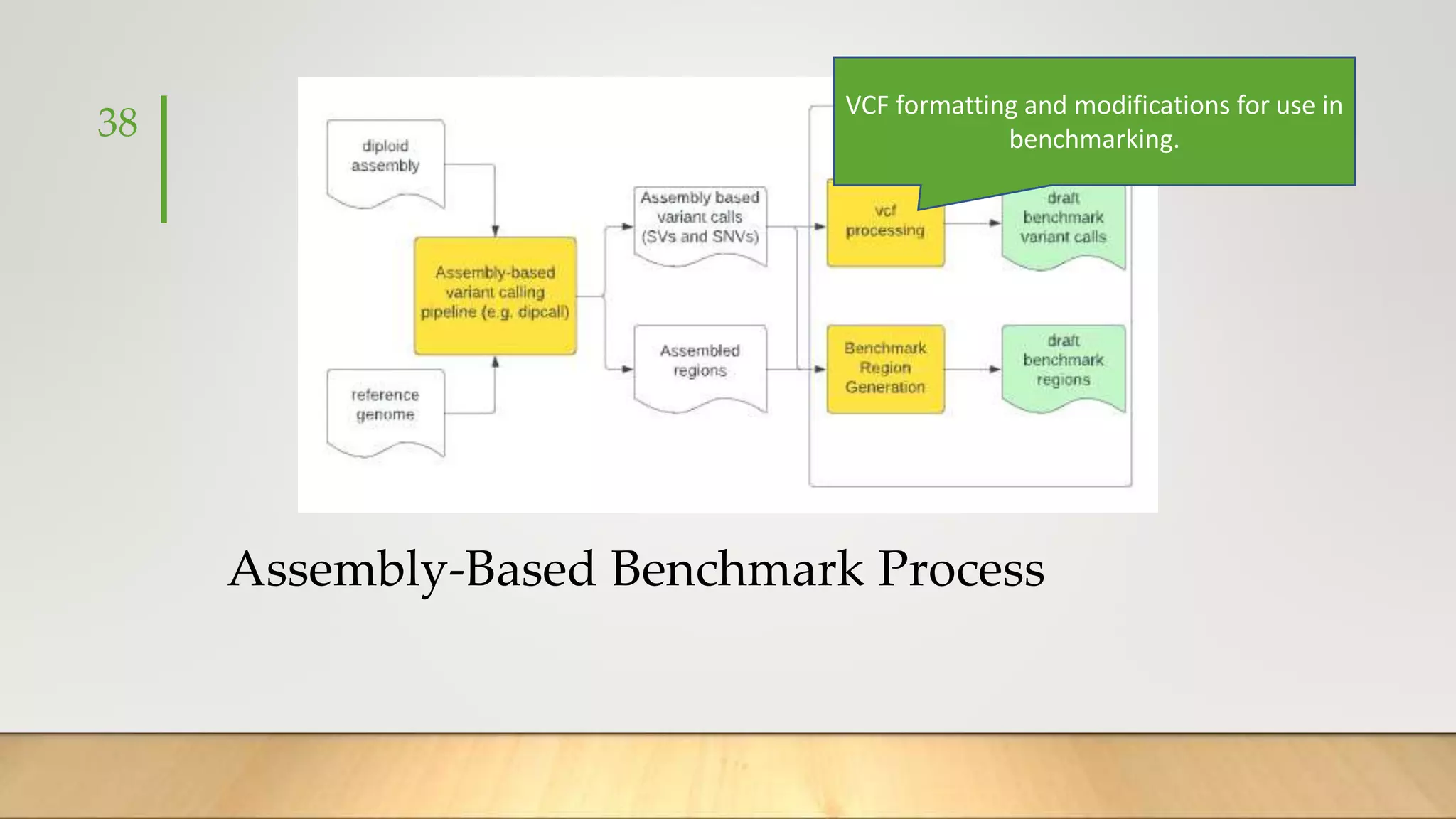
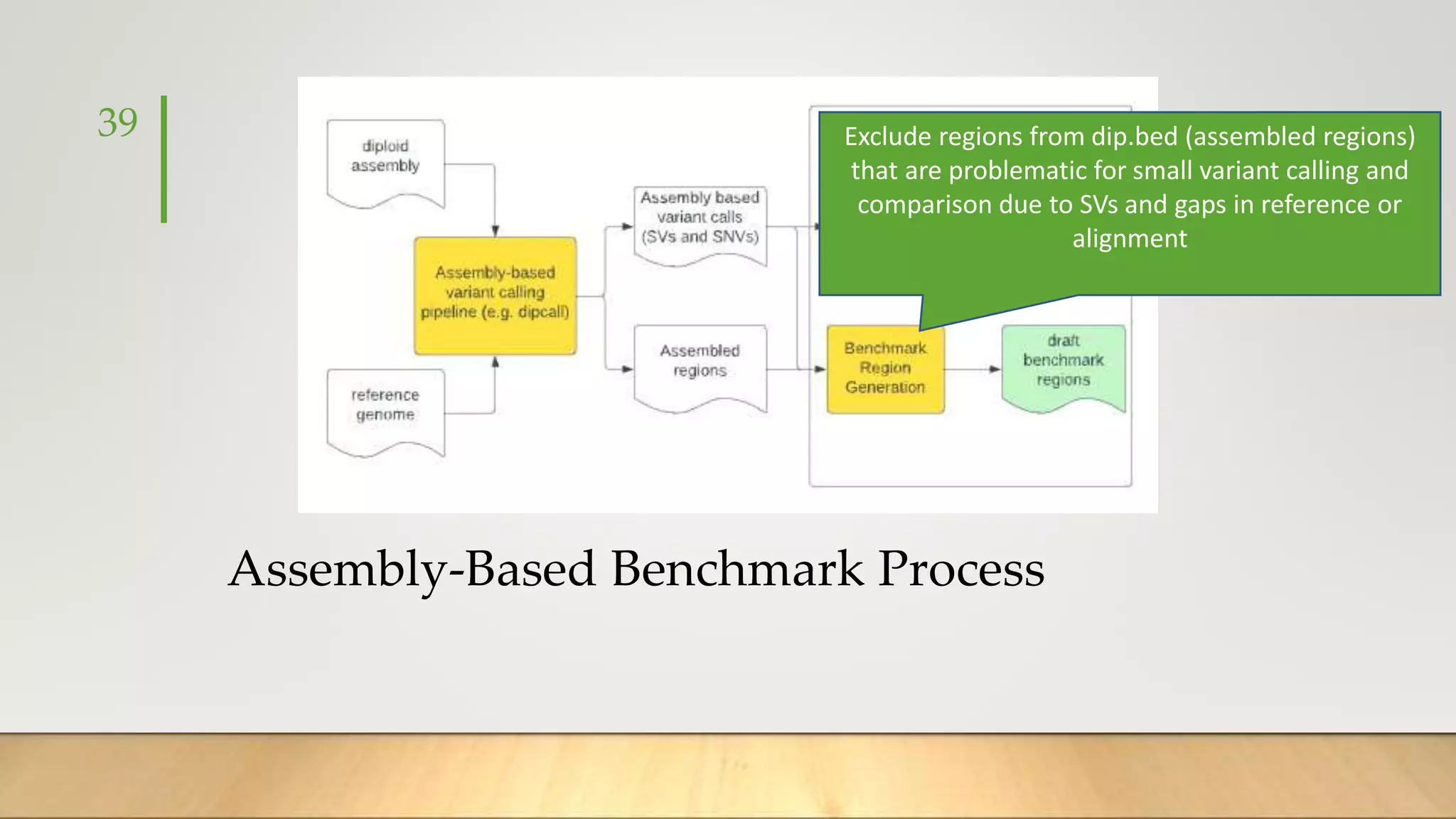
GIAB provides benchmark reference materials and datasets to improve confidence in genome sequencing and variant calling. It has characterized variants in 7 human genomes across different reference builds. Best practices for benchmarking include using appropriate stratifications, validation tools, and metrics interpretation to evaluate variant calling accuracy. Current efforts focus on developing benchmarks using diploid genome assemblies.