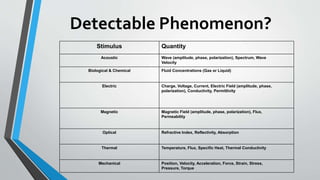
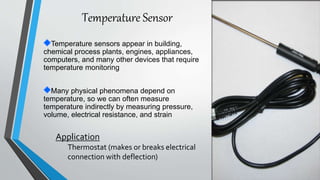
Sensors are devices that detect physical phenomena and convert them into signals that can be measured and processed. They are used to measure properties like temperature, light, motion, pressure, and more. Sensors are found in many applications to enable automation and monitoring, from industrial plants and medical devices to cars, phones, and home appliances. Common sensors include temperature sensors, accelerometers, light sensors, magnetic sensors, ultrasonic sensors, photogates, and gas sensors like CO2 sensors.