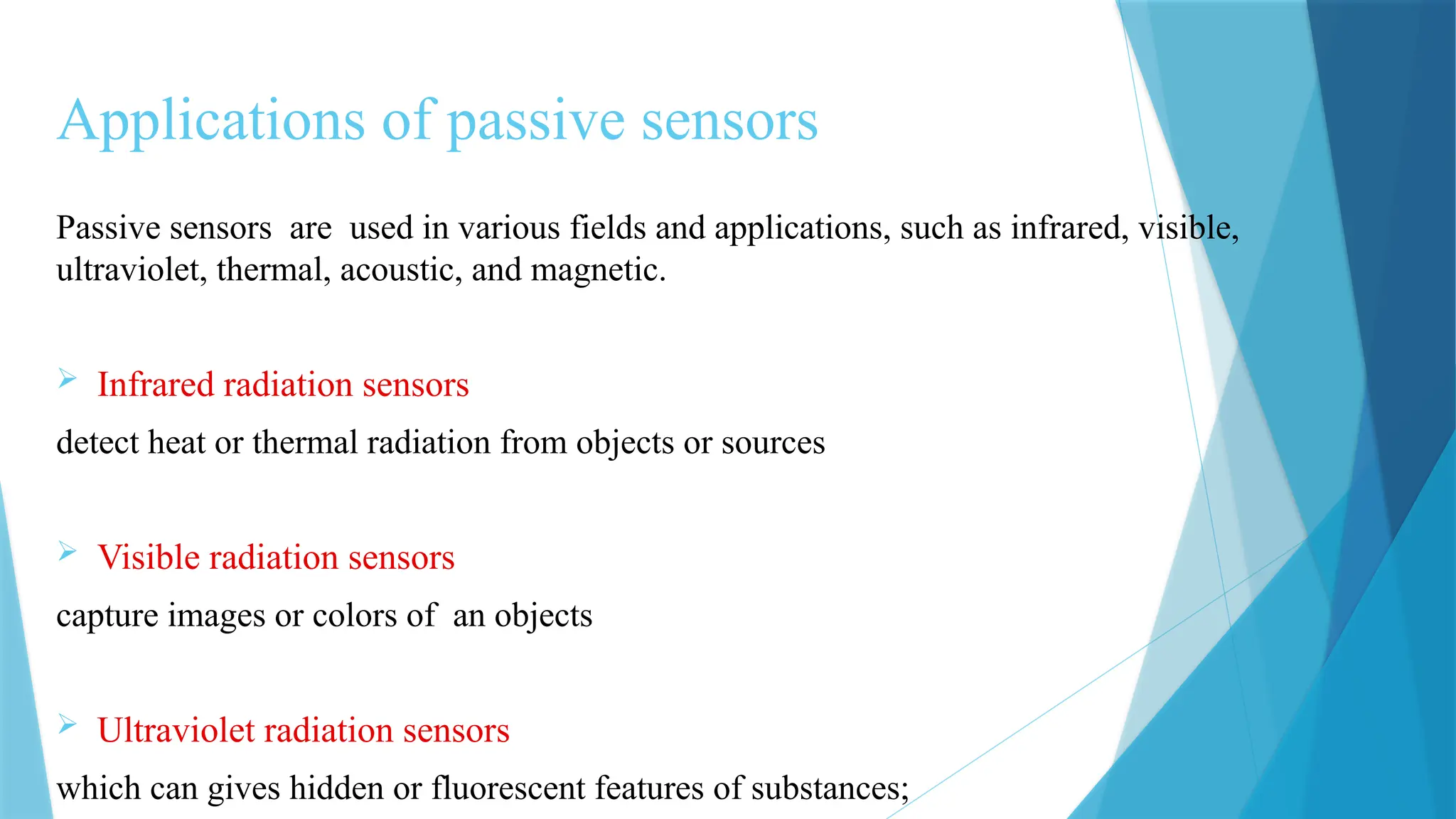
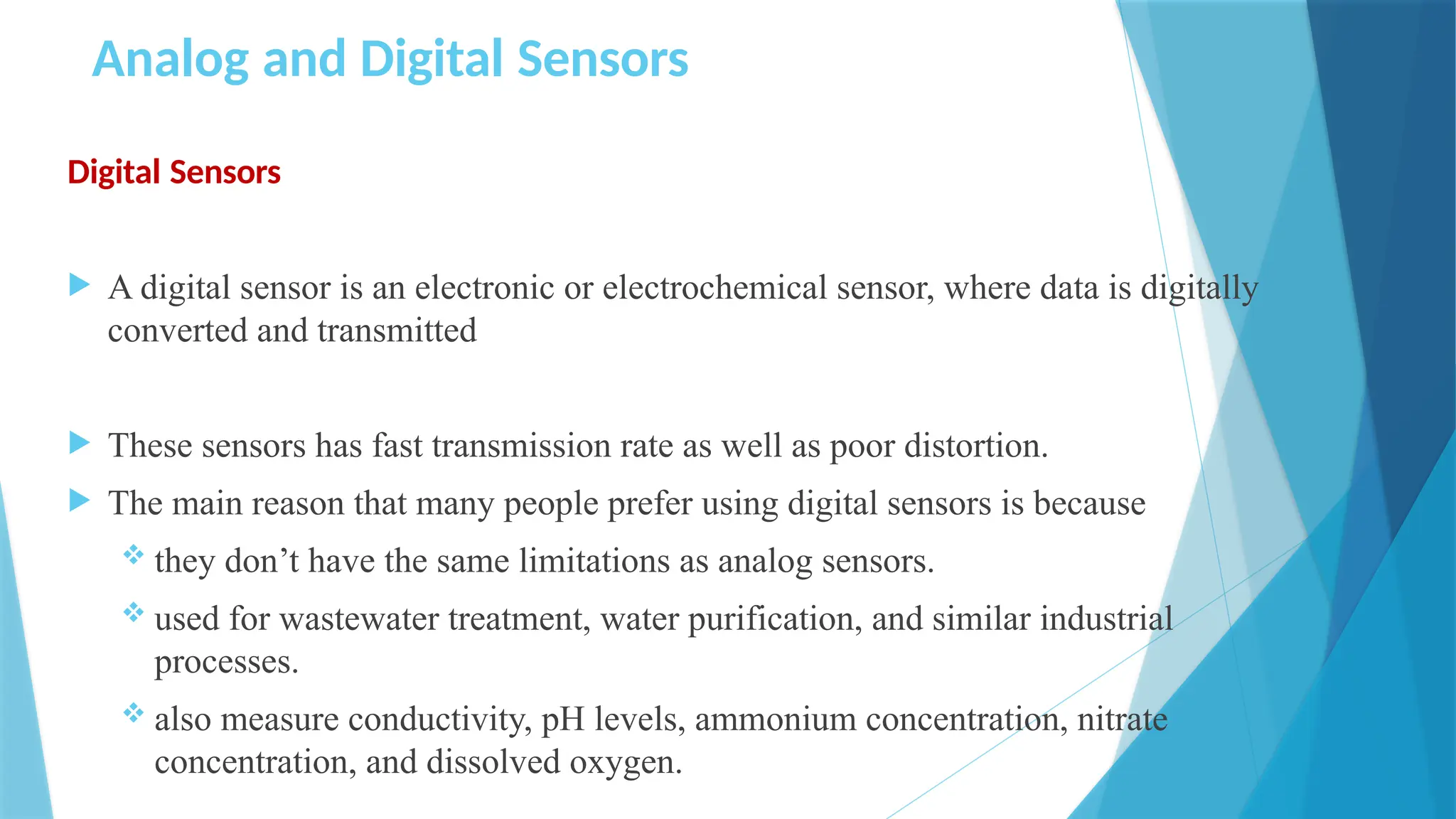
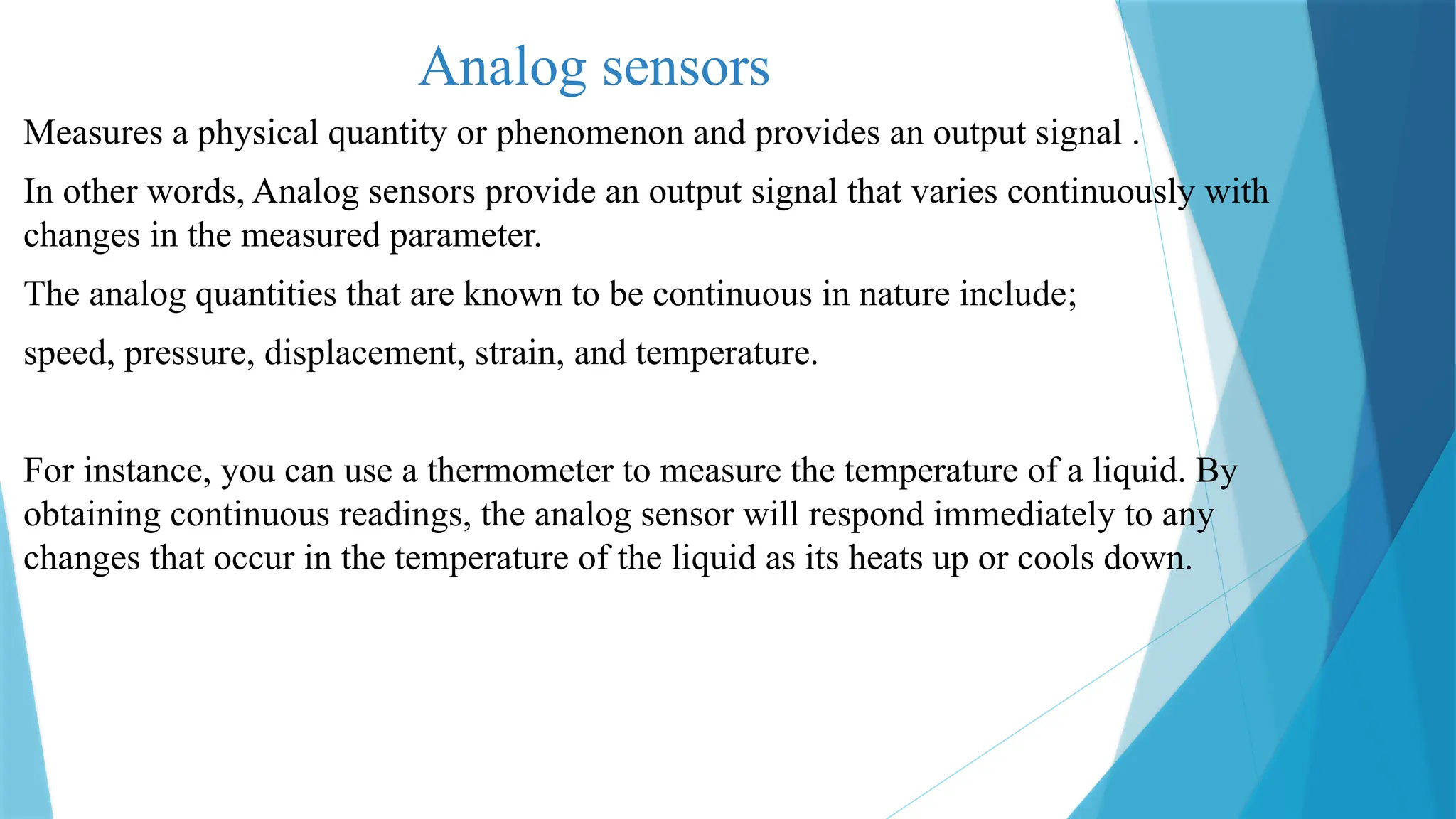
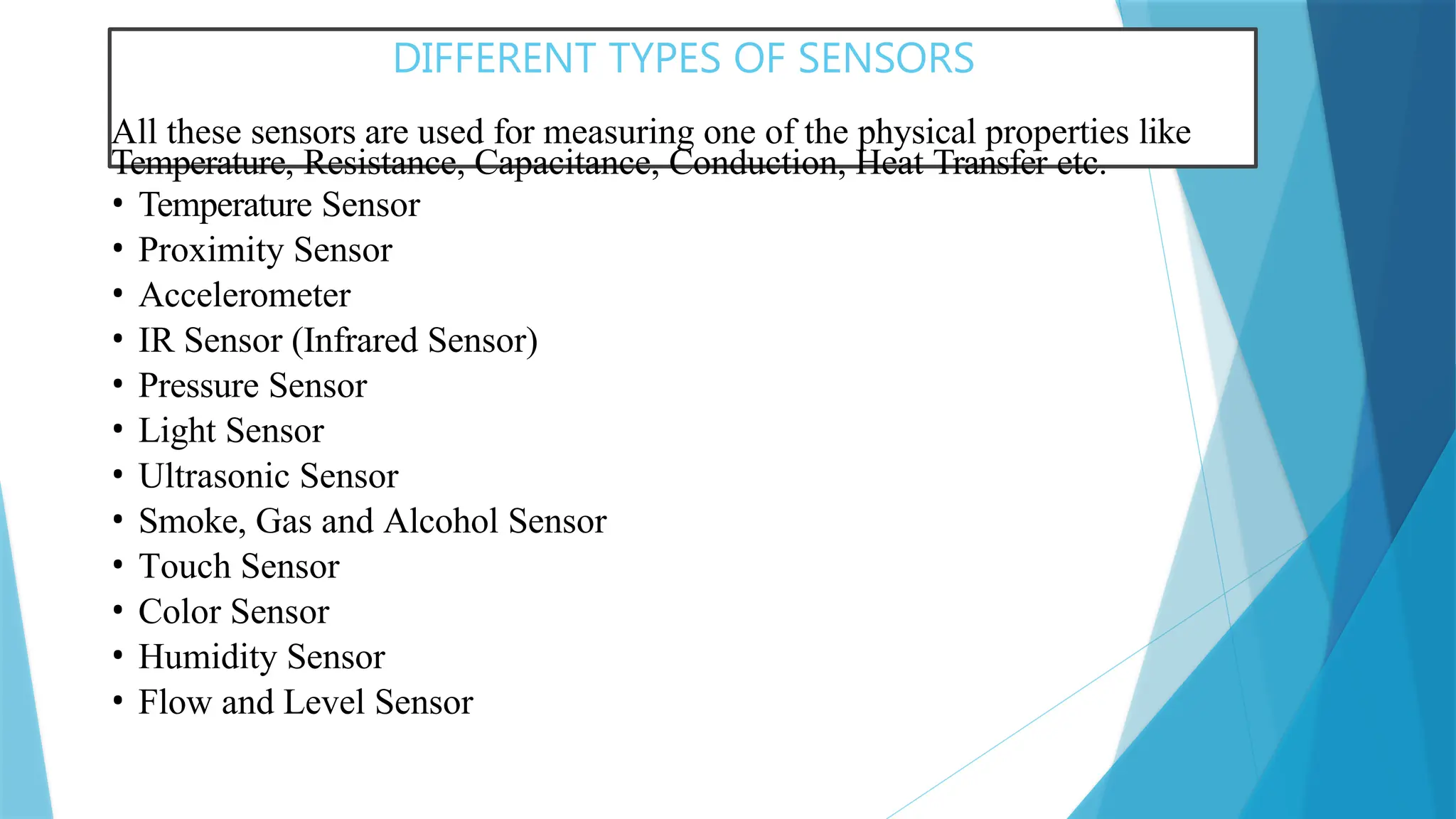
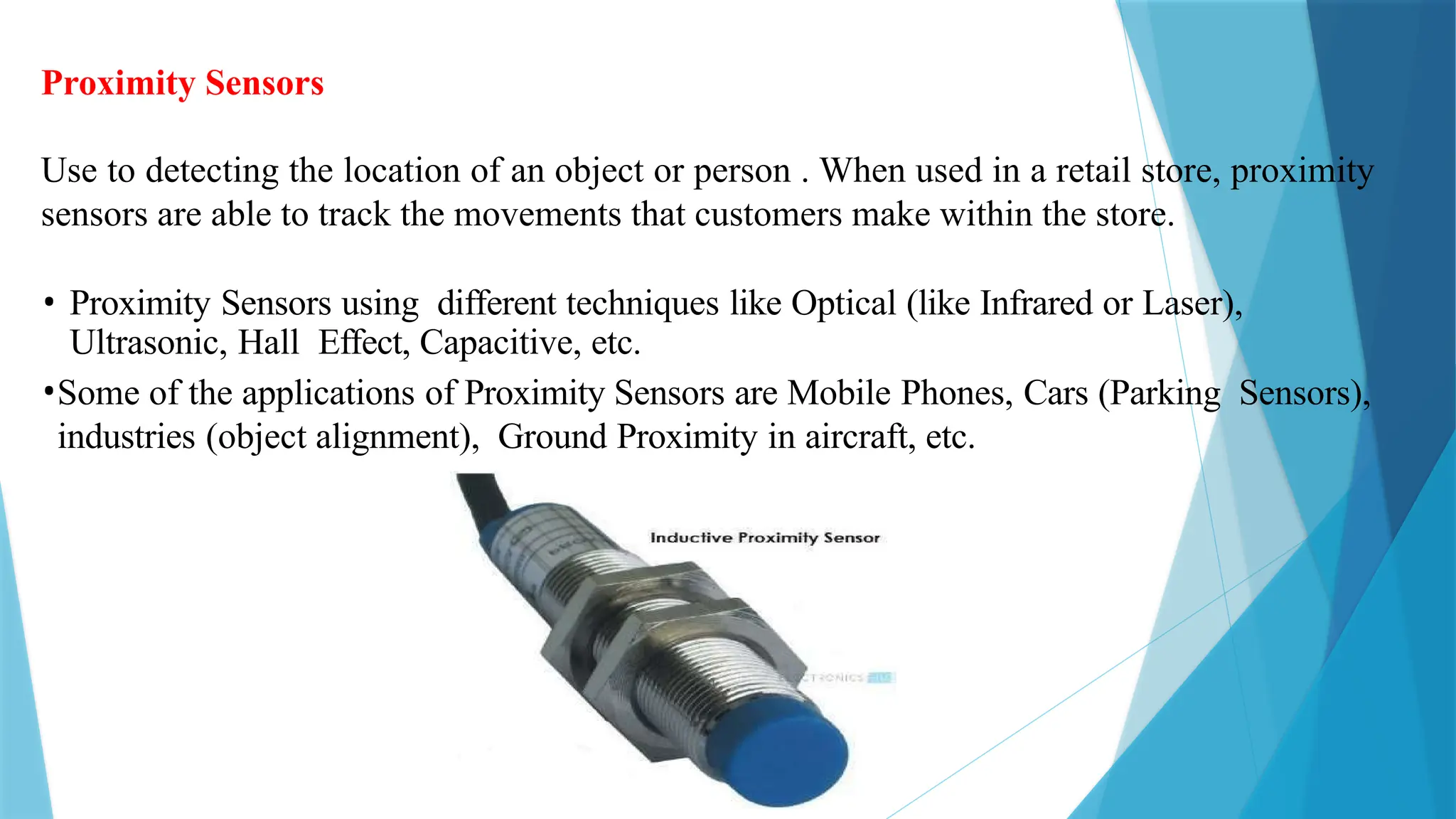
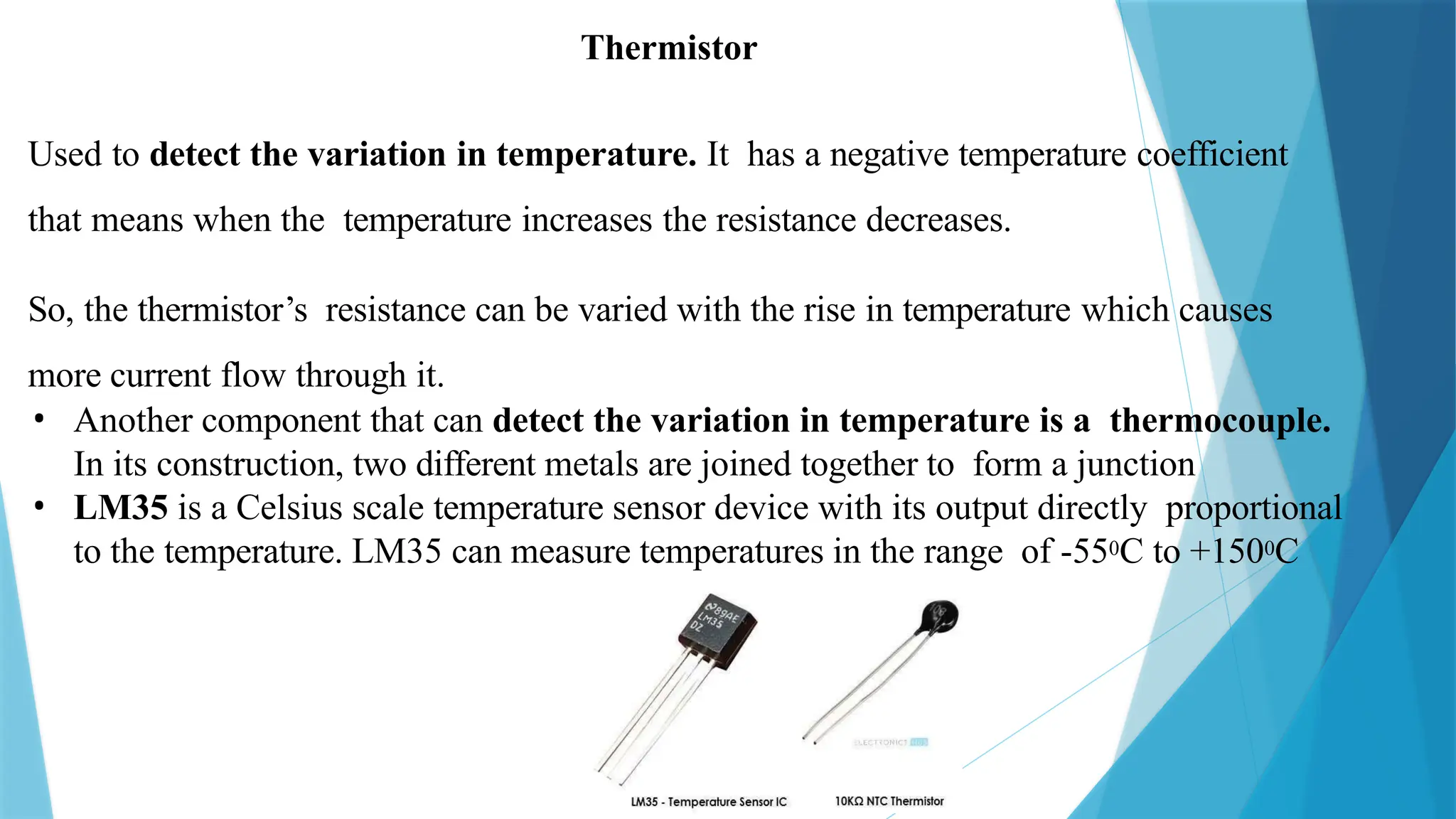
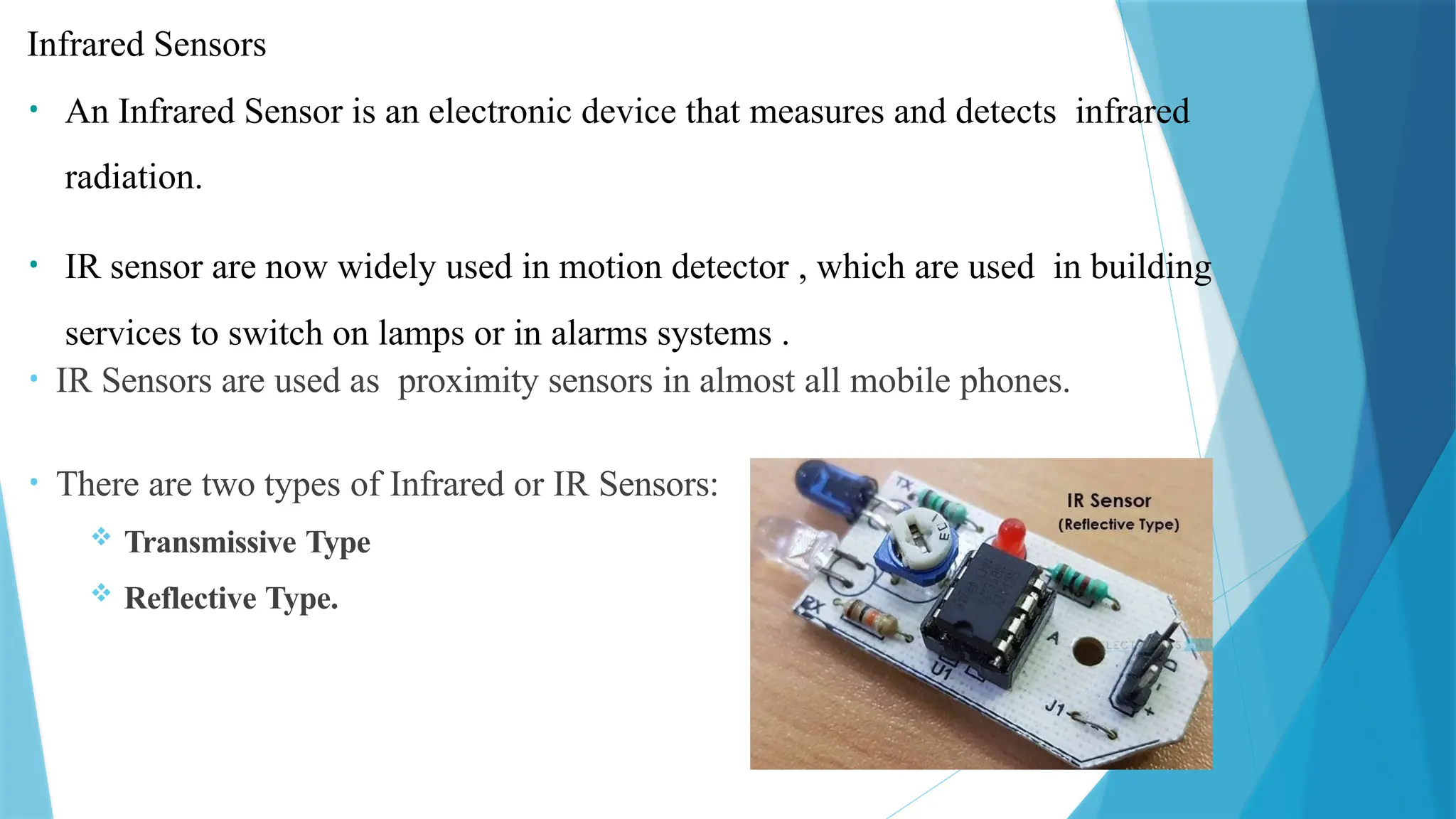
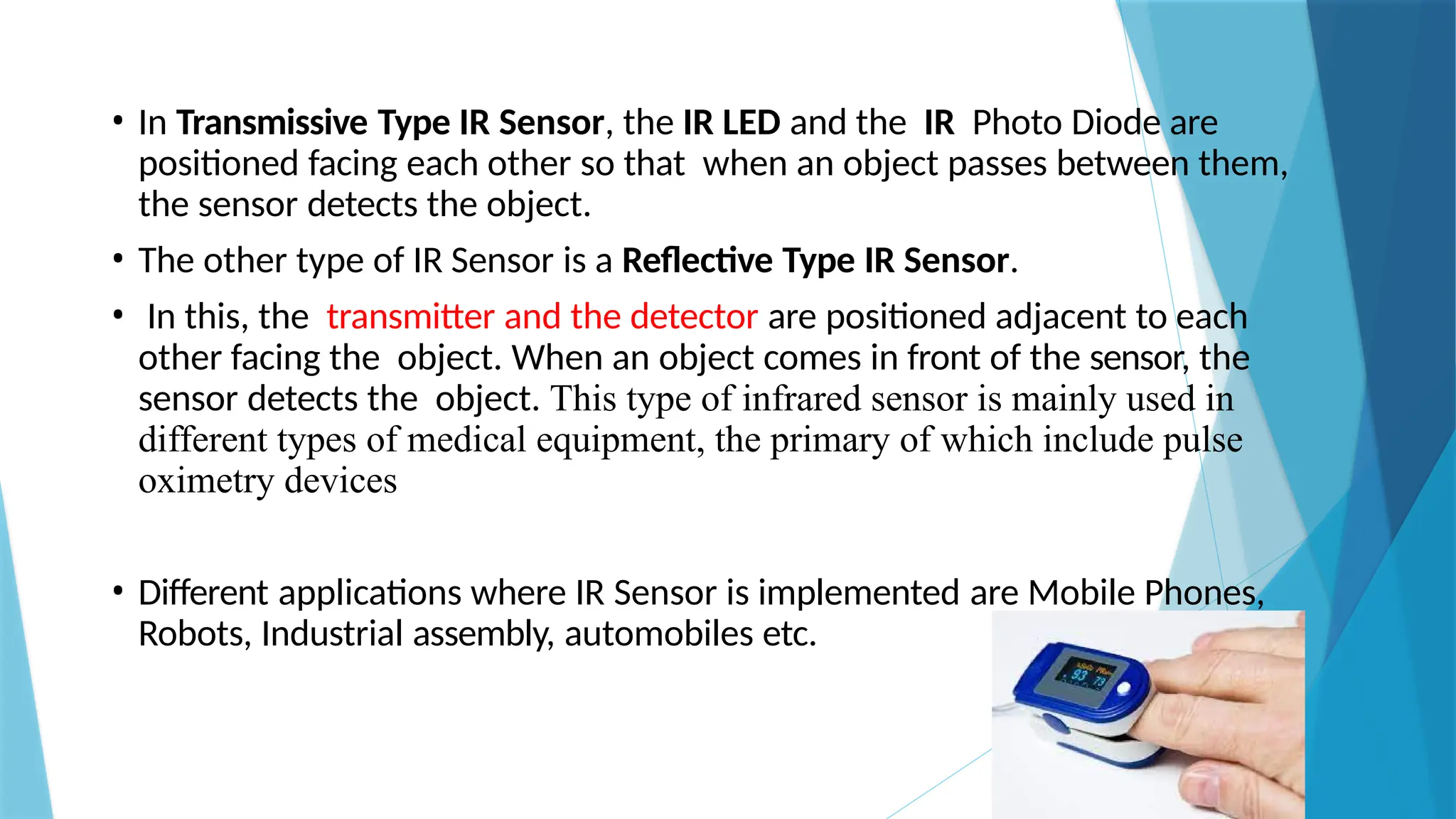
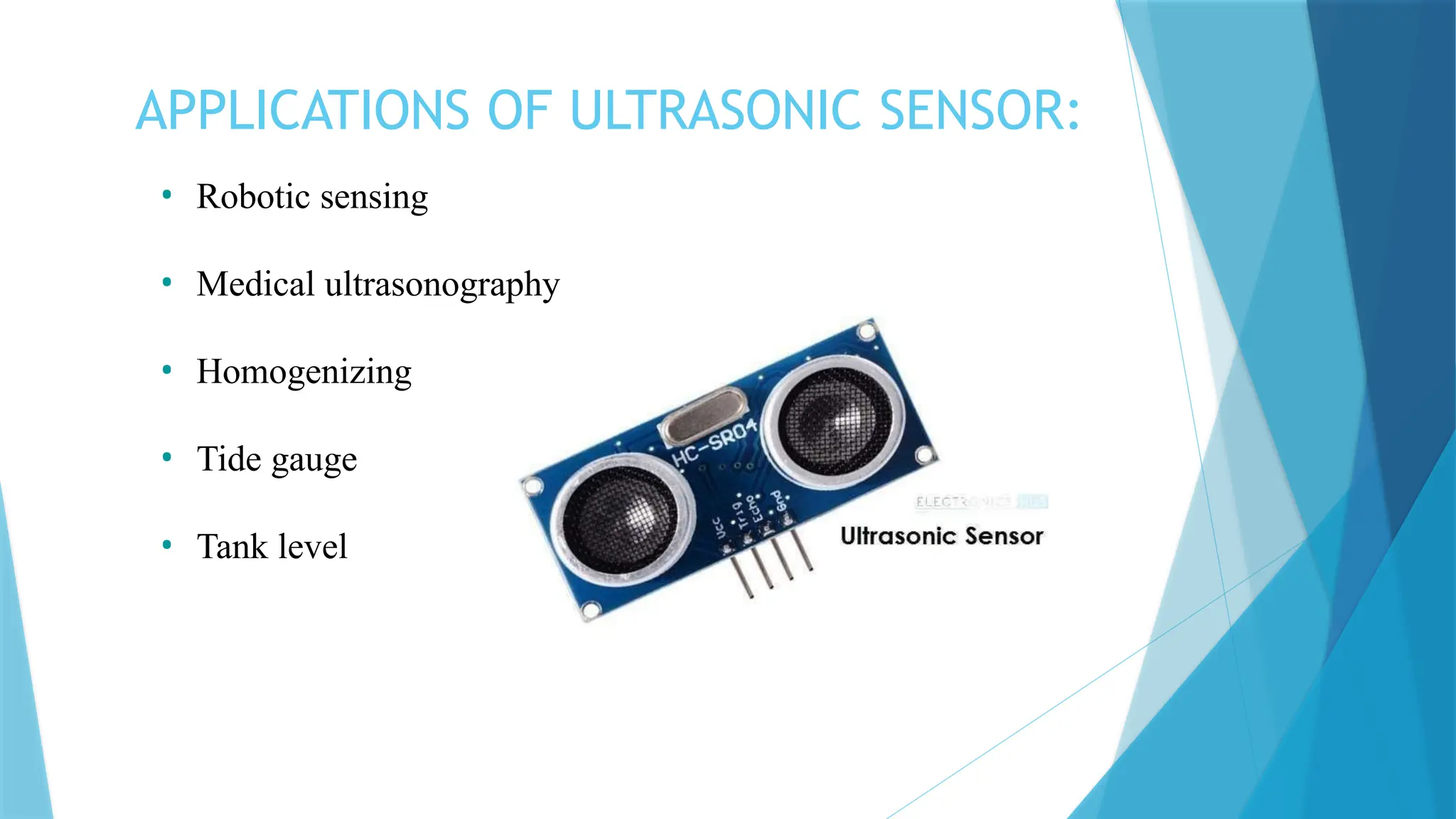
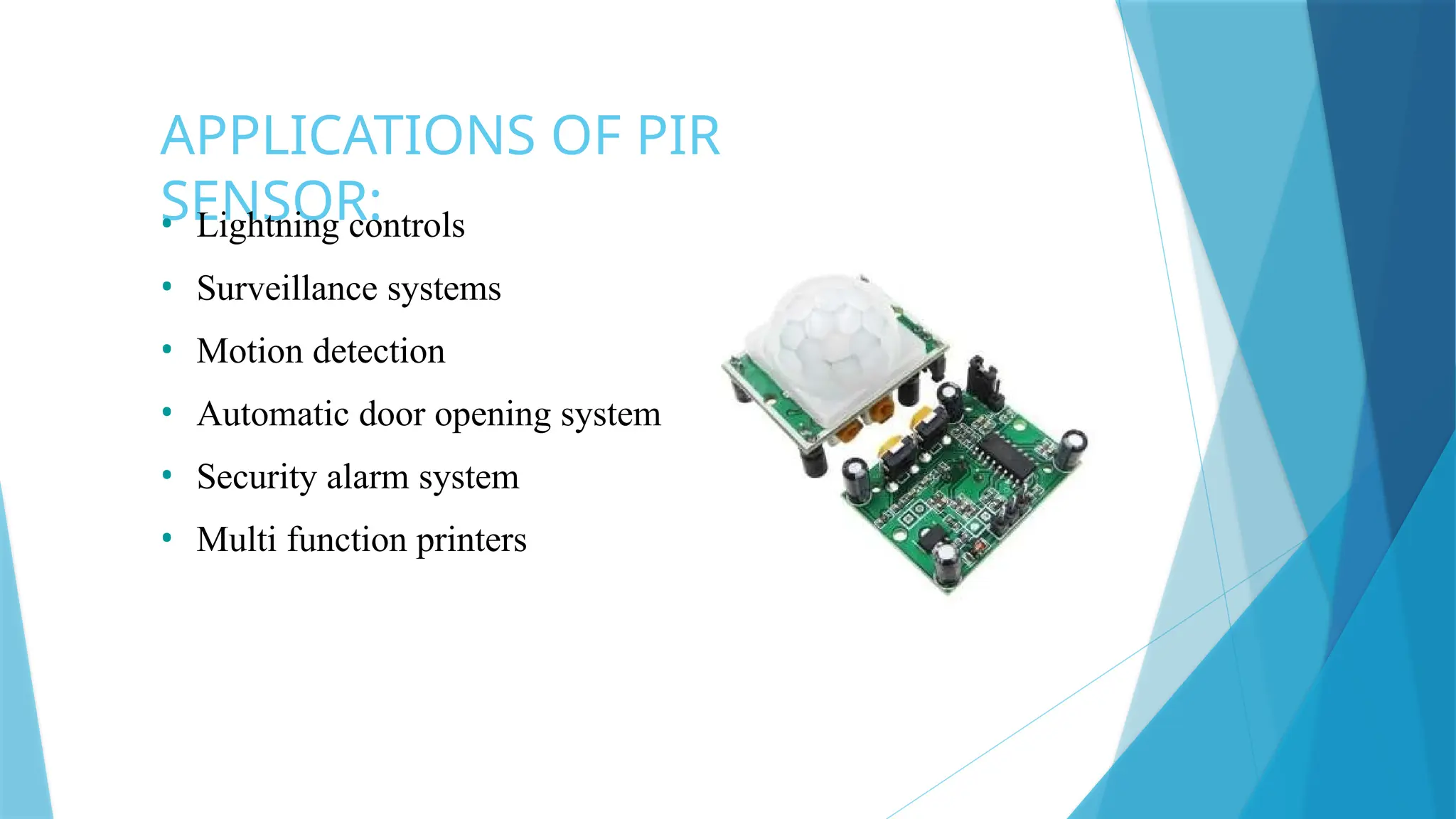
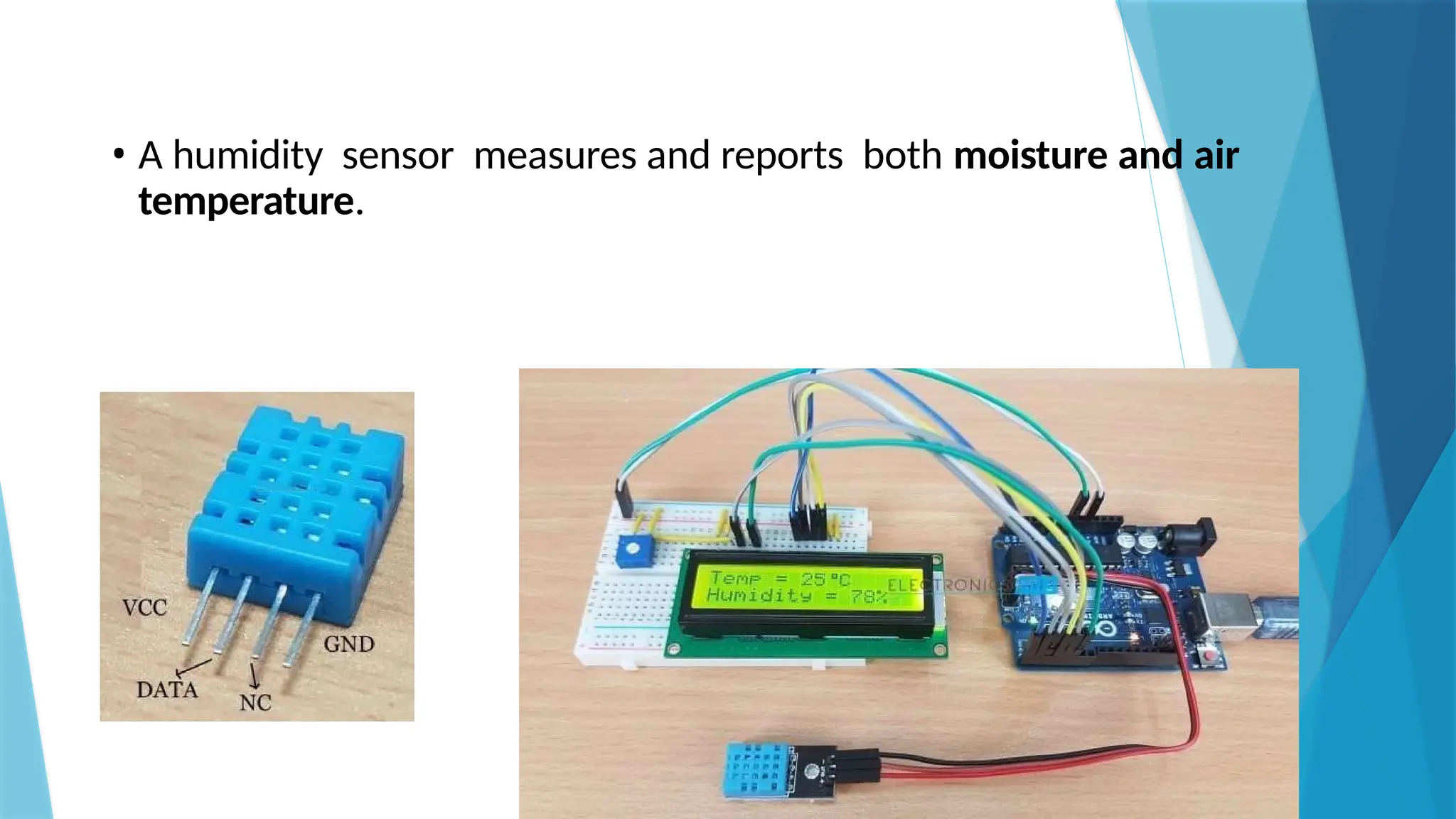
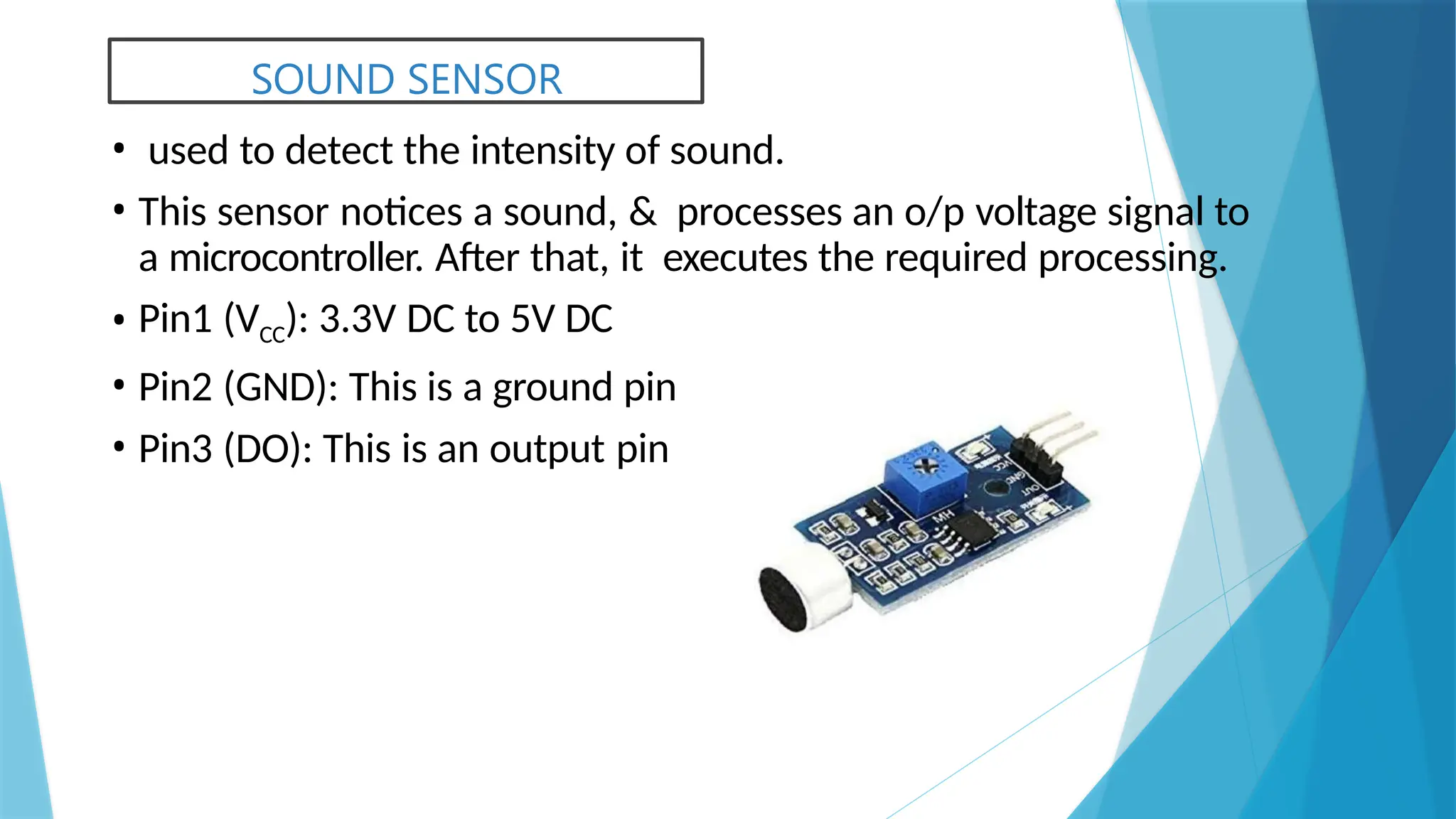
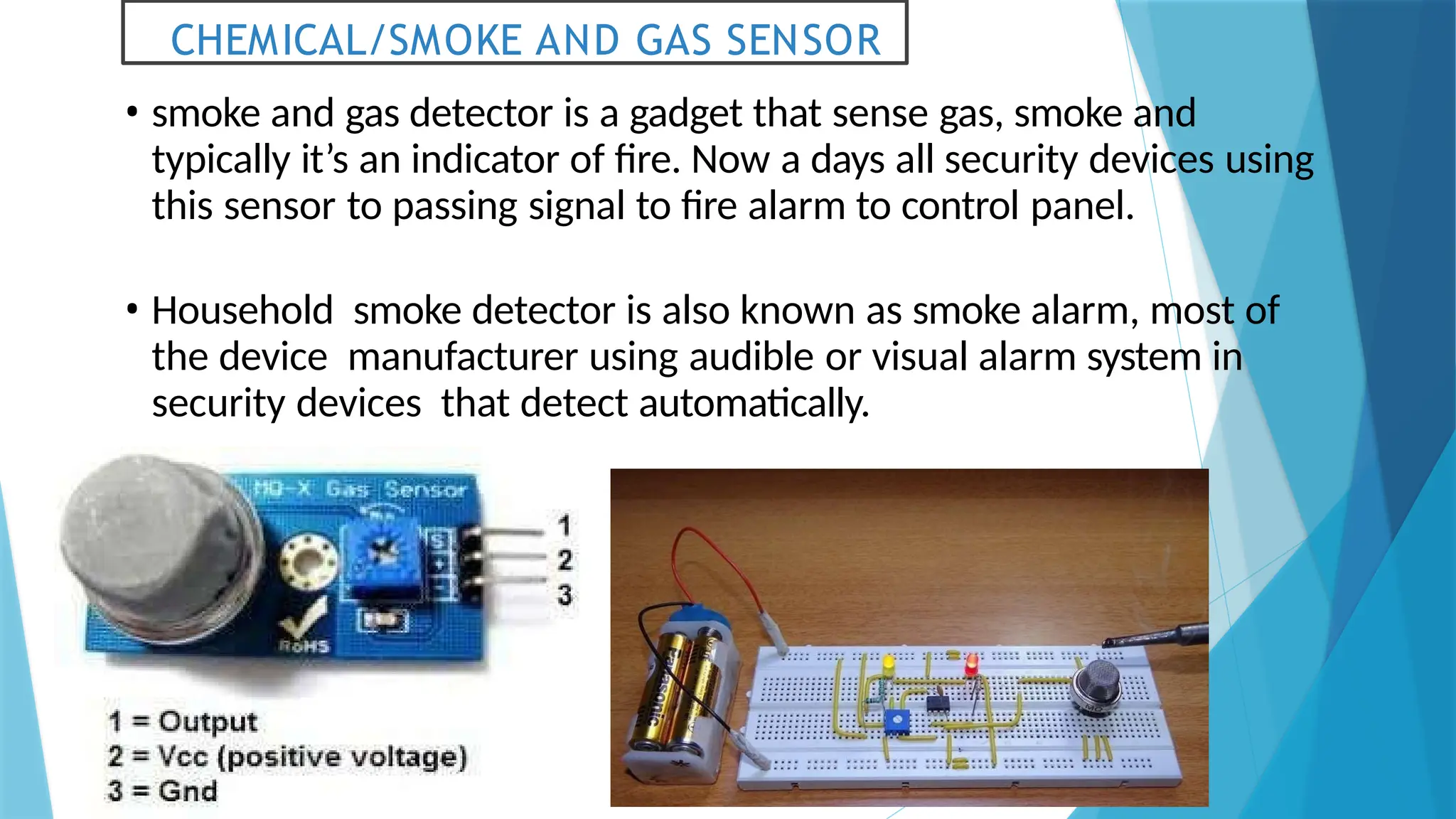
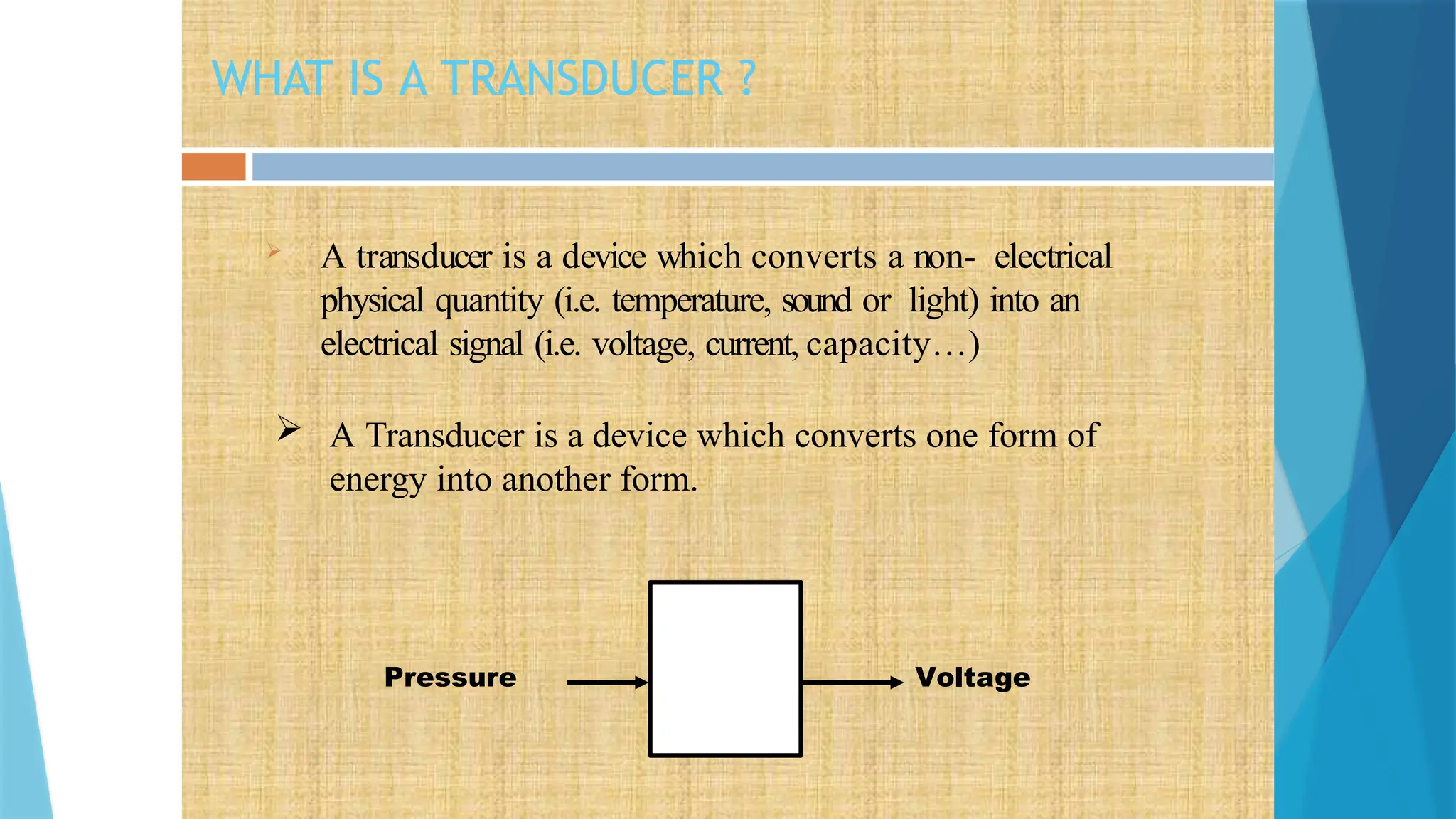
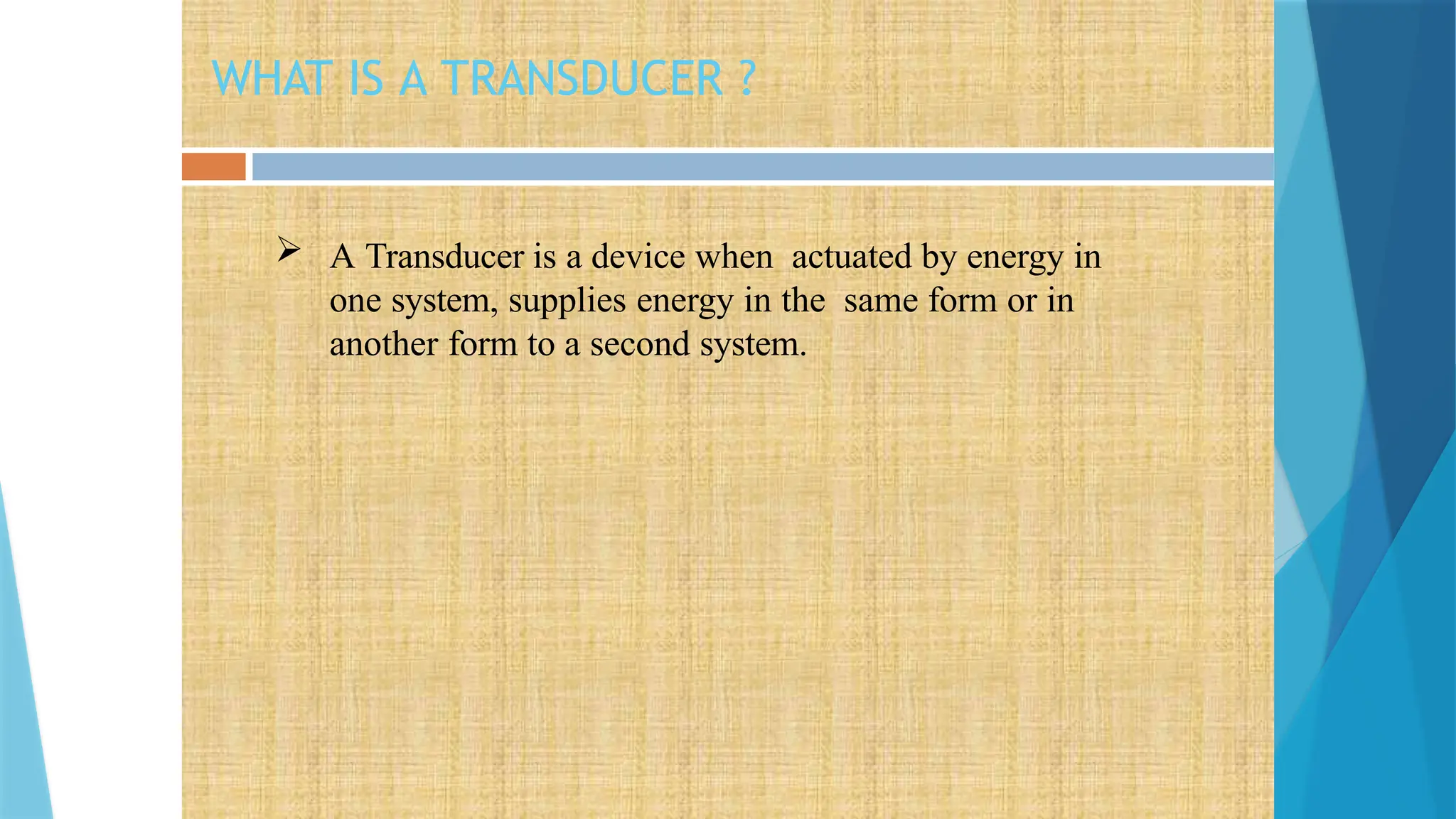
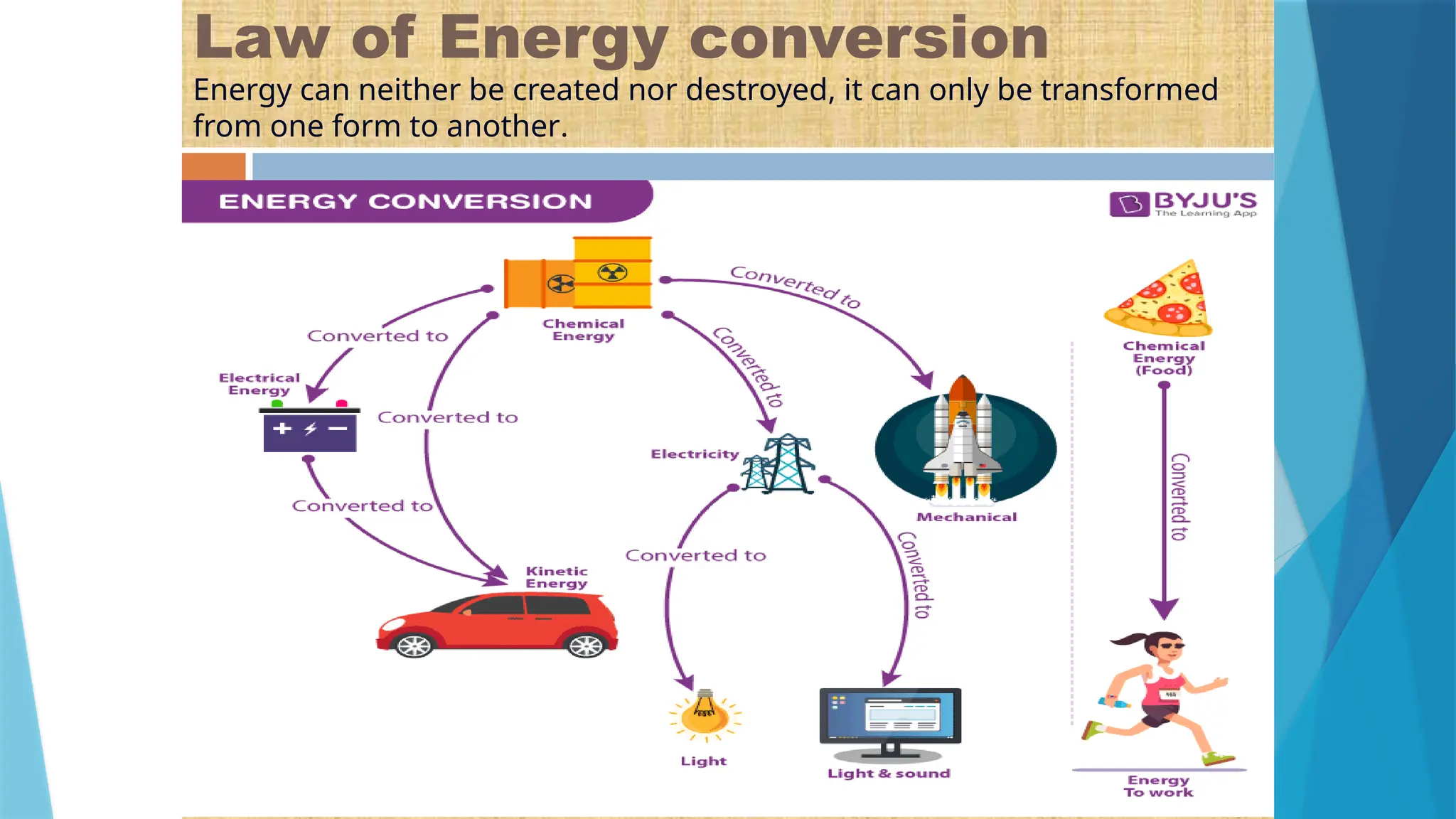
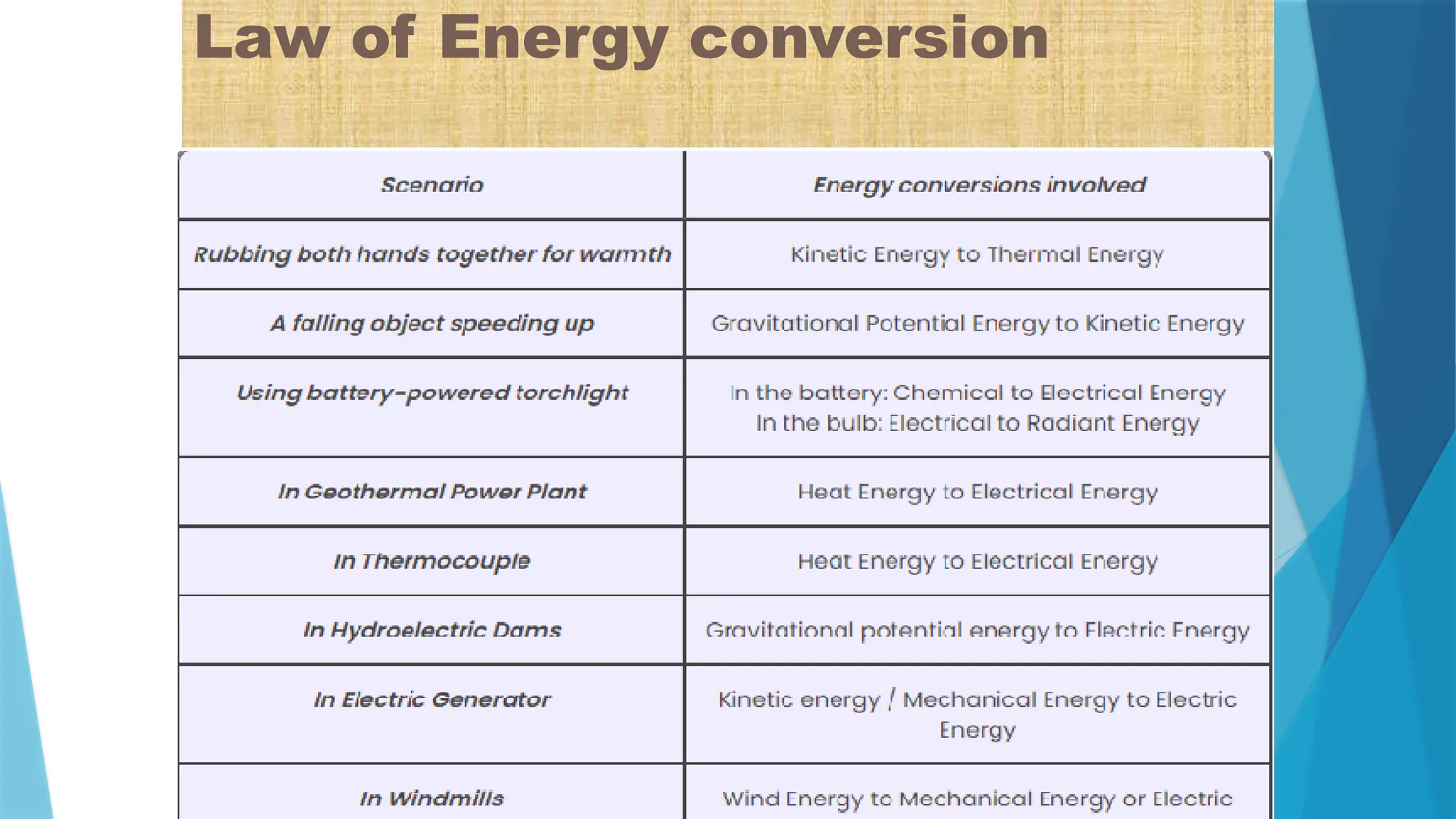
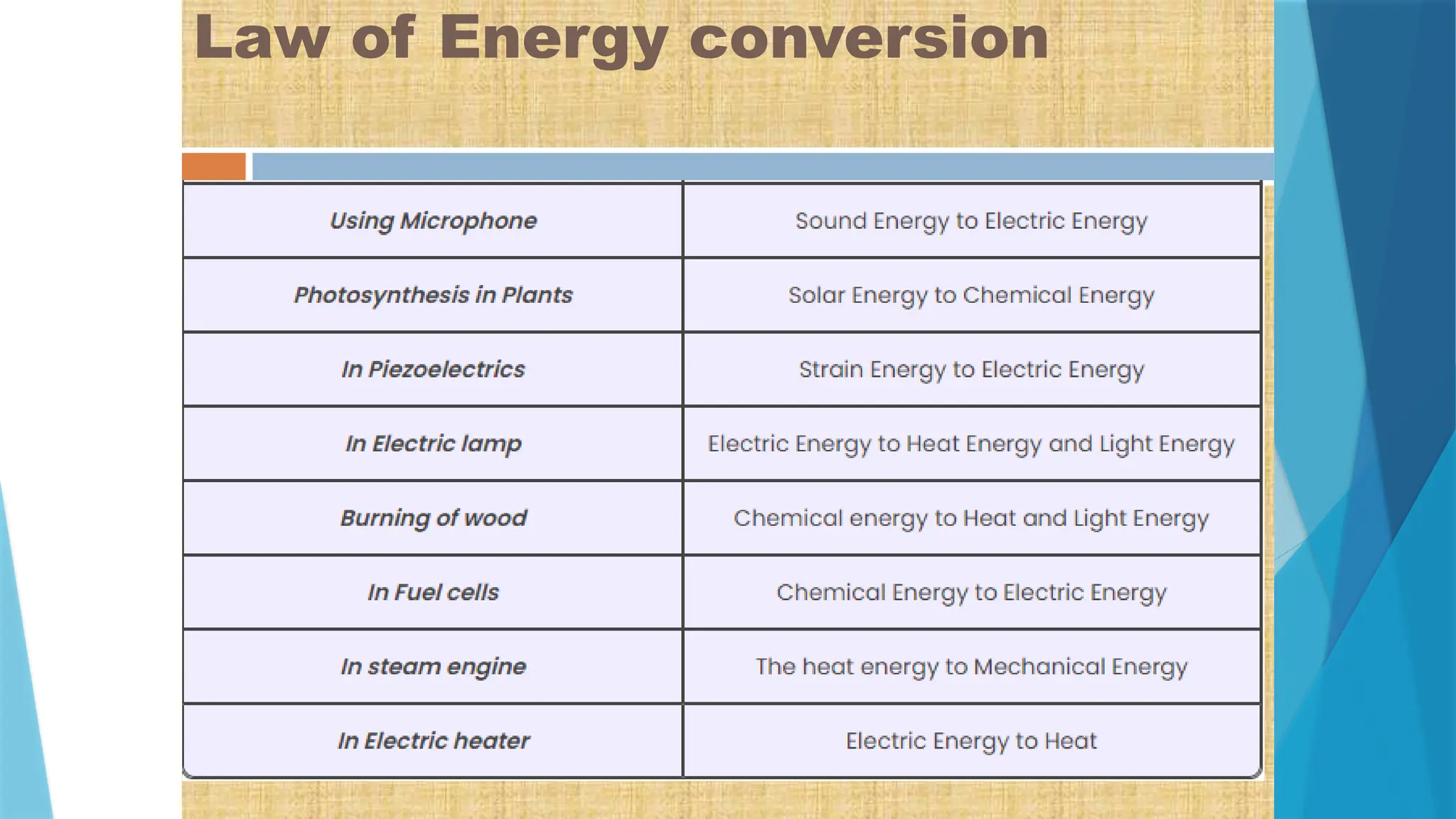
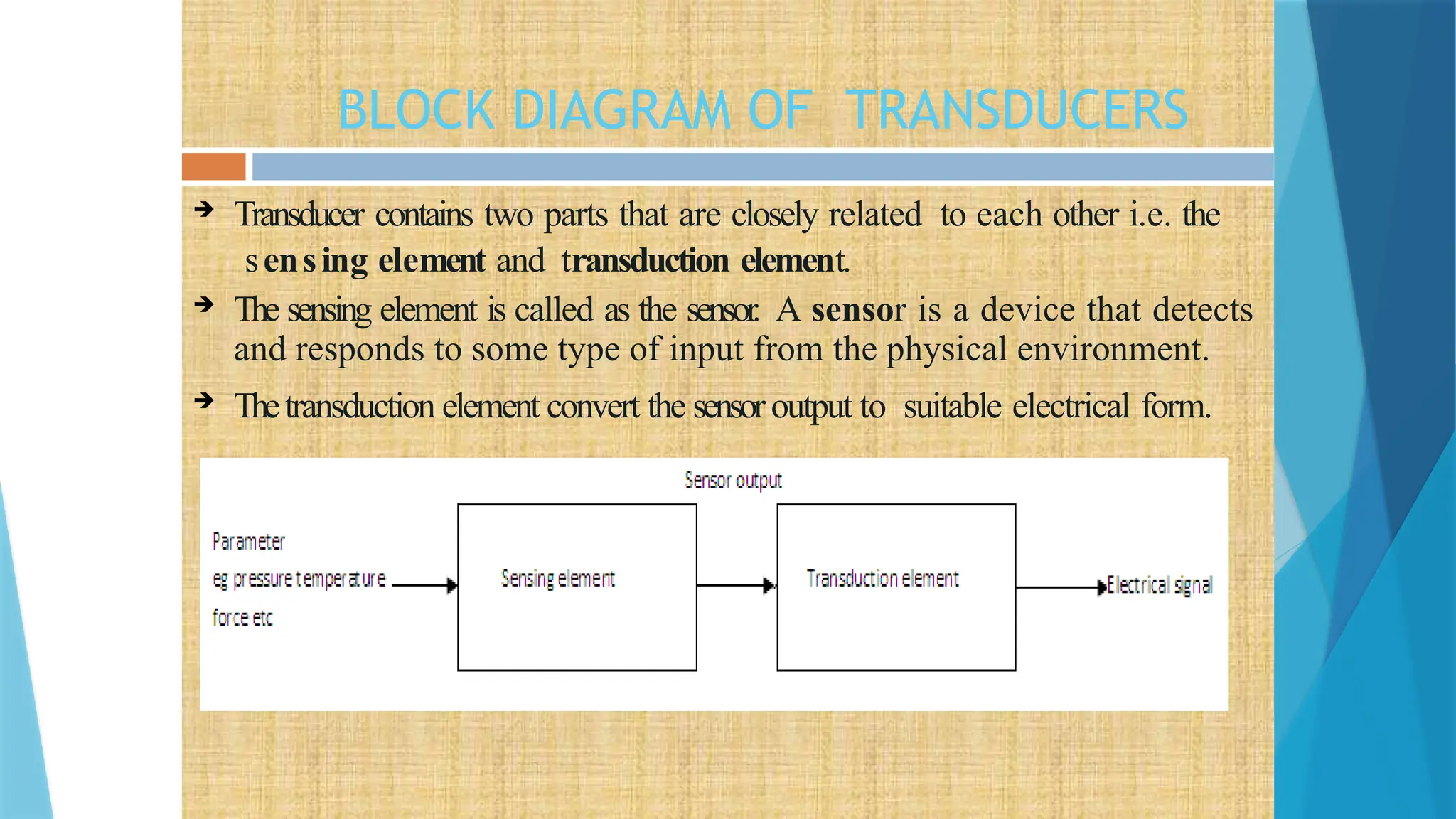
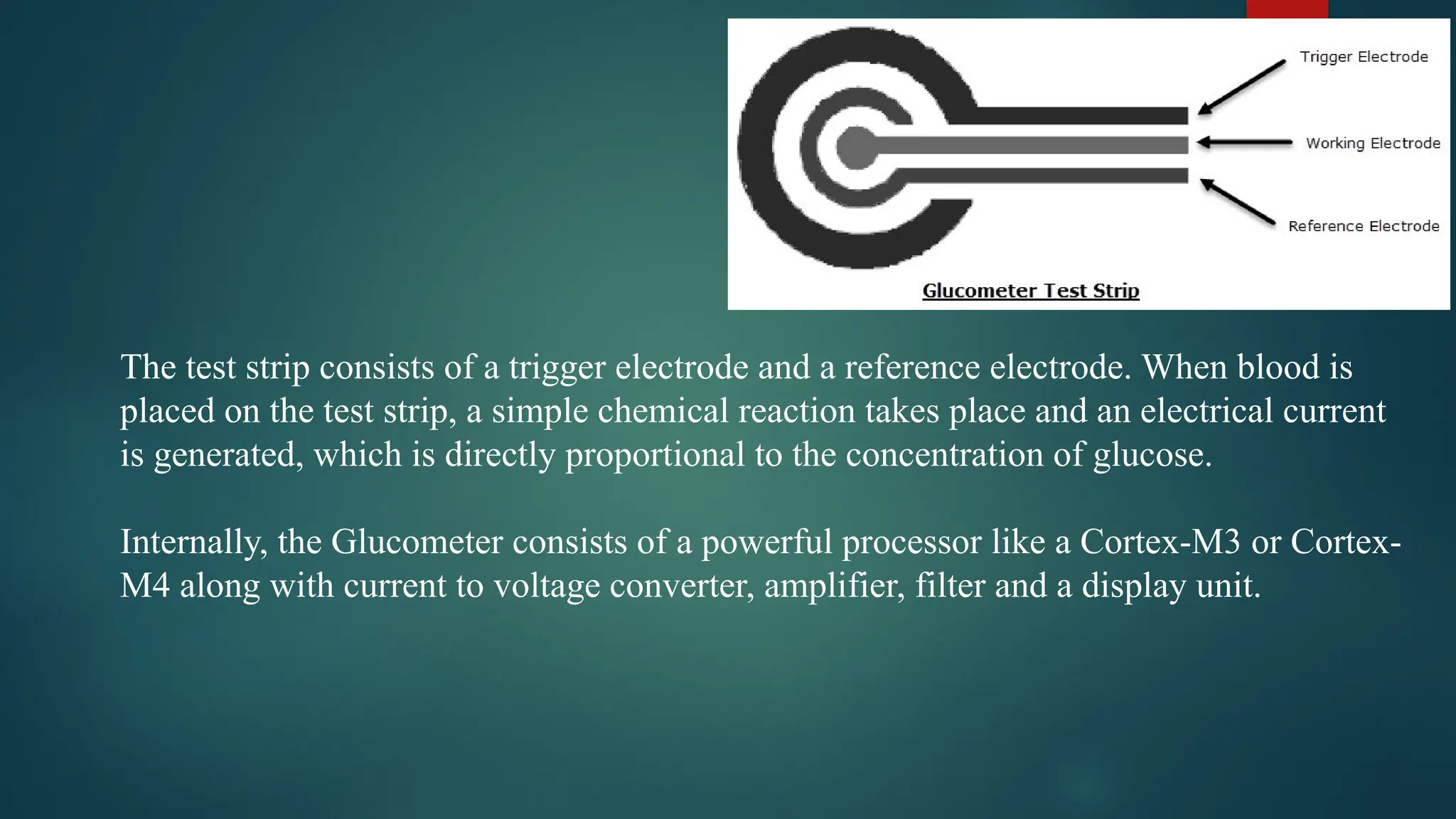
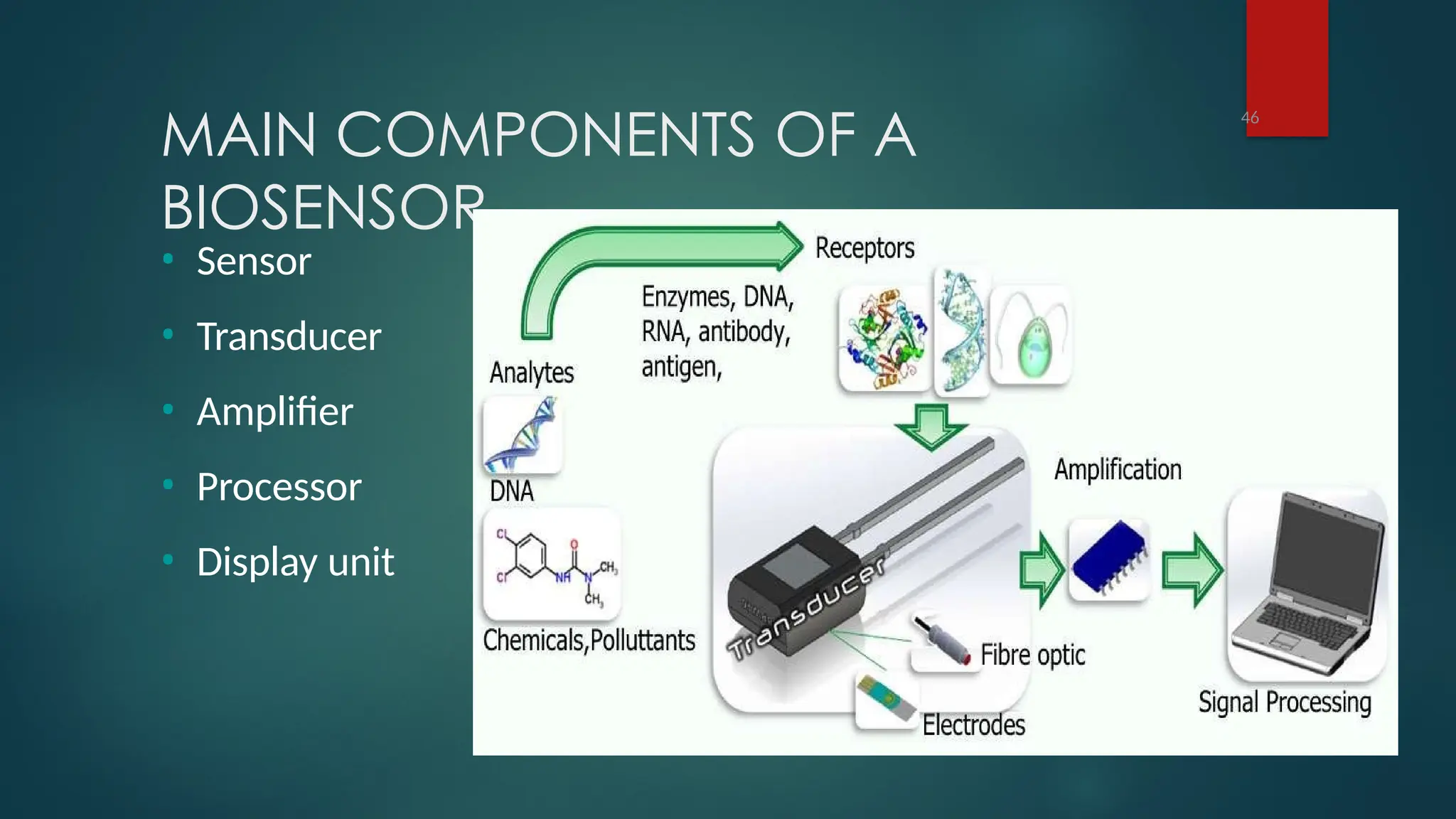
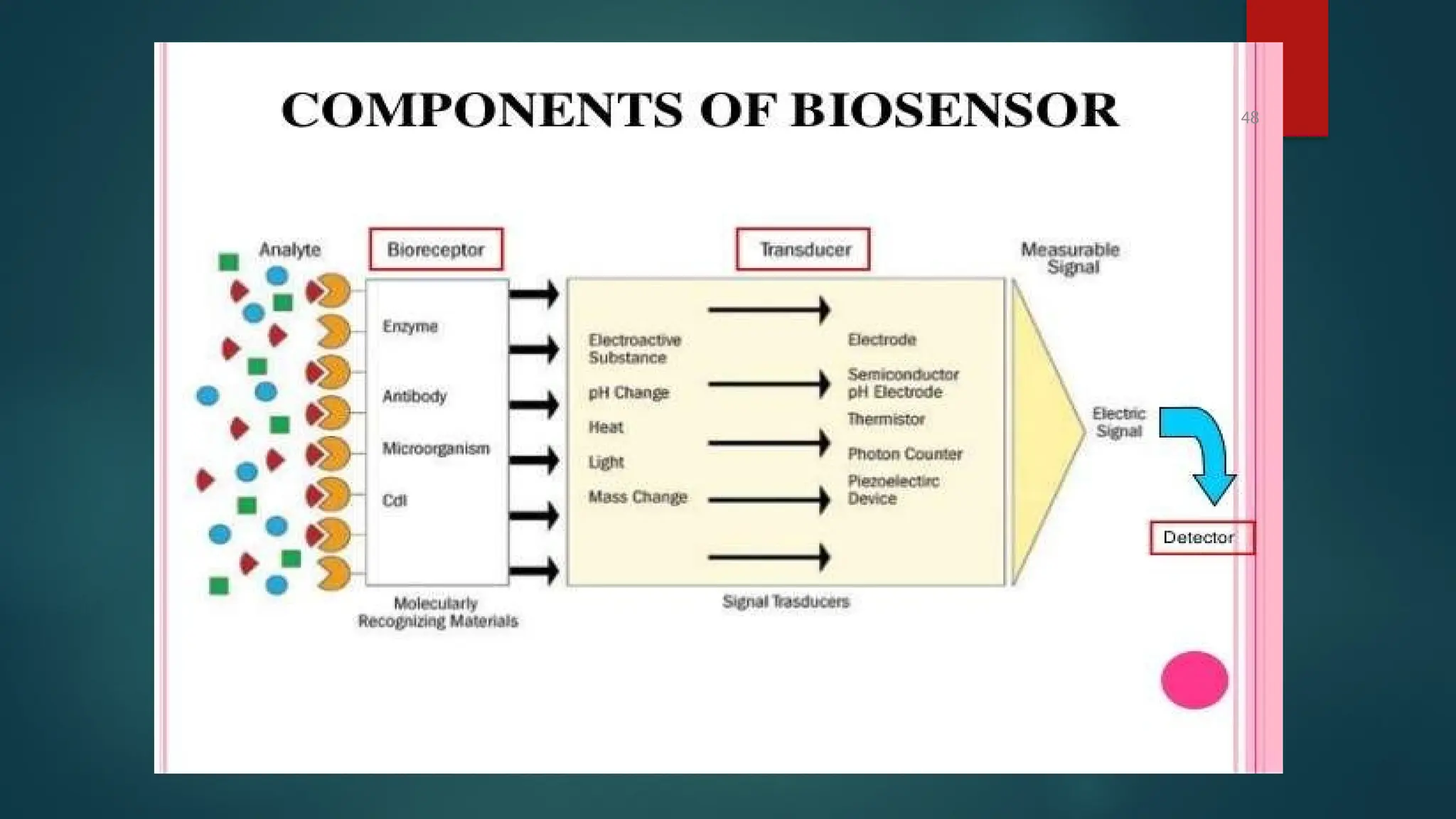
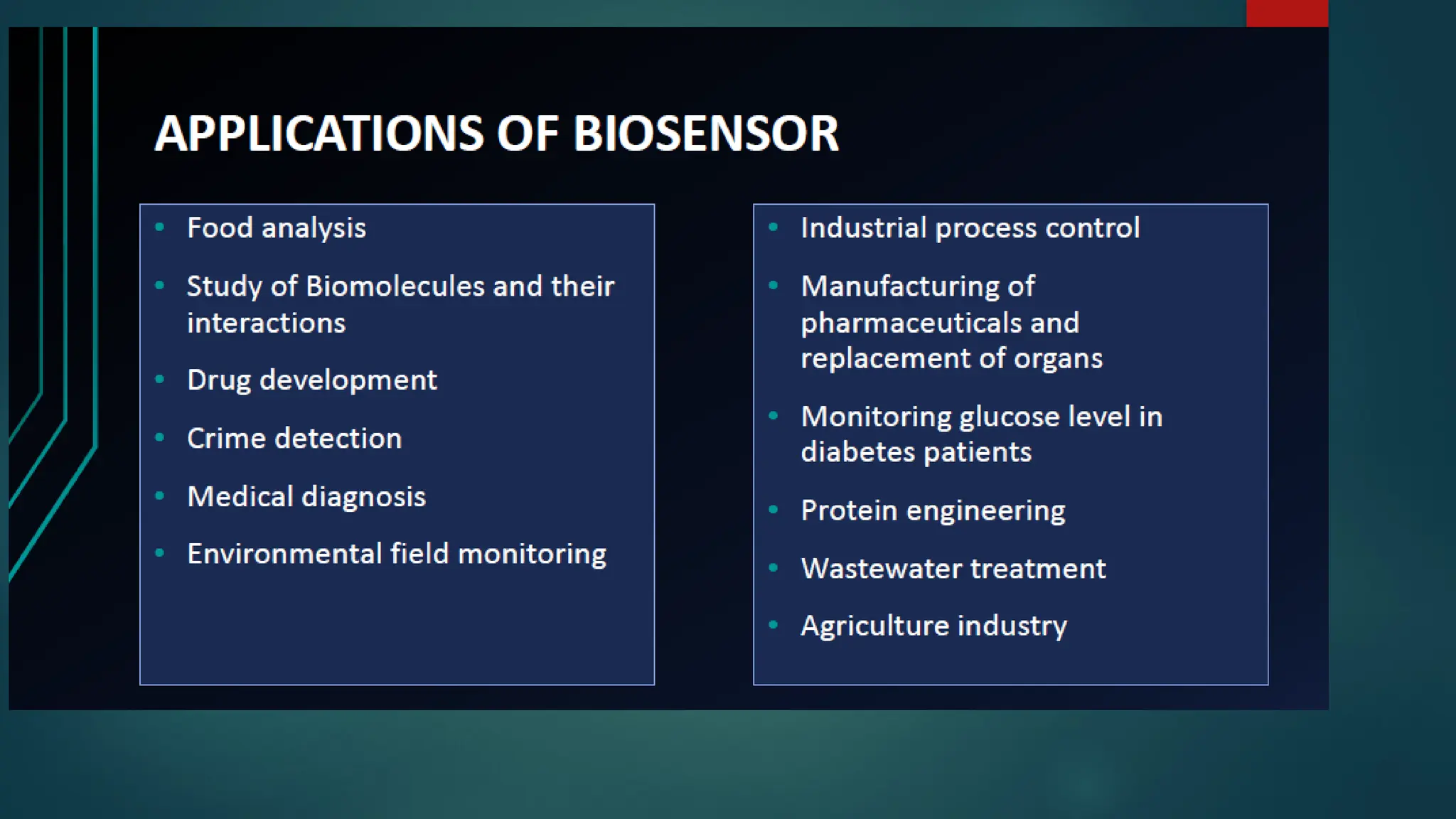
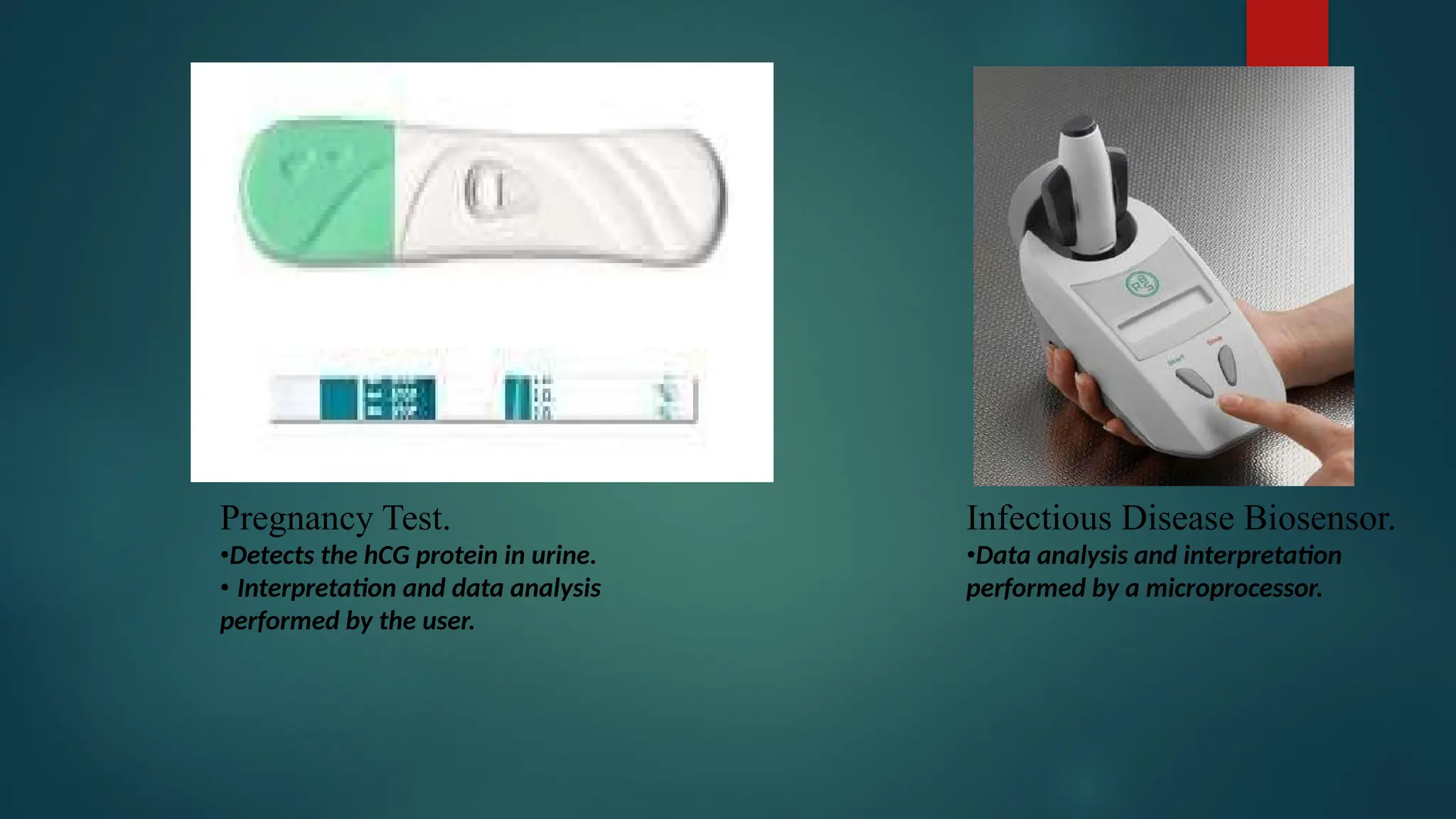
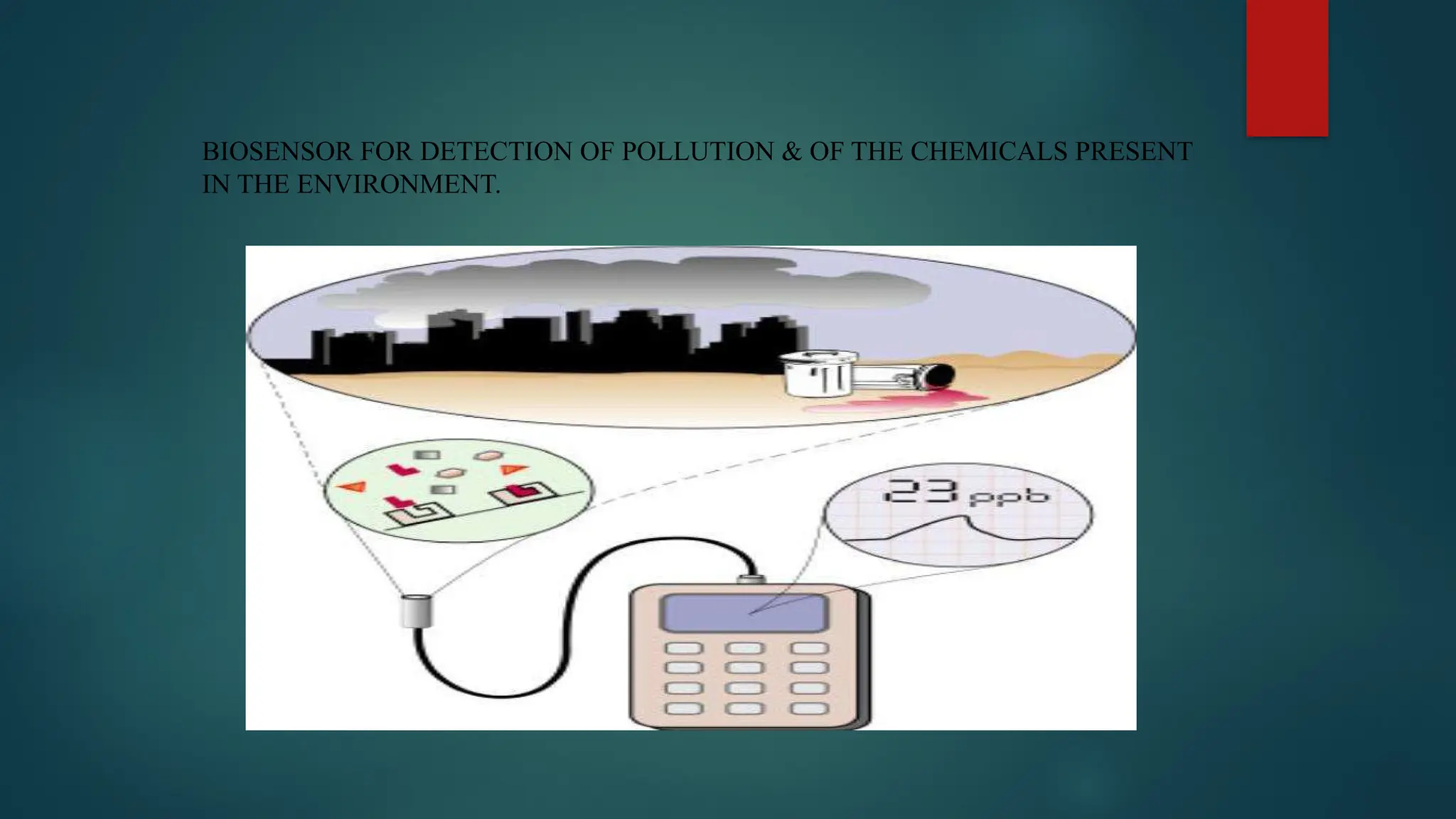
The document provides a comprehensive overview of sensors, describing their classifications into active and passive types, applications, and specific kinds like analog and digital sensors. It details various sensor applications including temperature, humidity, pressure, and smoke detection, as well as advanced technologies such as biosensors and nanosensors. Additionally, it explains concepts related to transducers, energy transformation, and total energy conservation.