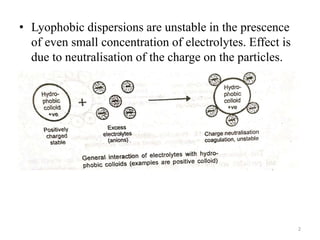
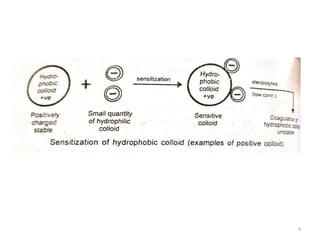
Lyophobic dispersions are unstable in the presence of electrolytes due to the neutralization of particle charges. Sensitization can occur when a small amount of hydrophilic colloid is added, making the hydrophobic sol more sensitive to precipitation from electrolytes through adsorption of oppositely charged particles. Protective colloidal action results from the adsorption of a large amount of hydrophilic colloids carrying opposite charges onto hydrophobic particles, forming a protective layer that prevents coagulation by ions. Colloids that stabilize other colloids through this process are called protective colloids.