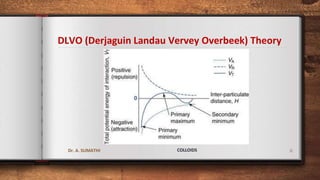
The document discusses the stability of colloidal systems. It explains that lyophilic sols are stabilized by electrostatic repulsion between charged colloidal particles, while lyophobic sols are thermodynamically unstable but can be stabilized by imparting a small charge to particles. The DLVO theory describes the electrostatic repulsive and van der Waals attractive forces acting on particles. Addition of electrolytes can reduce repulsion and cause coagulation. Protective colloids can stabilize hydrophobic colloids through adsorption. The gold number test measures the minimum amount of protective colloid needed to prevent coagulation of a gold sol.