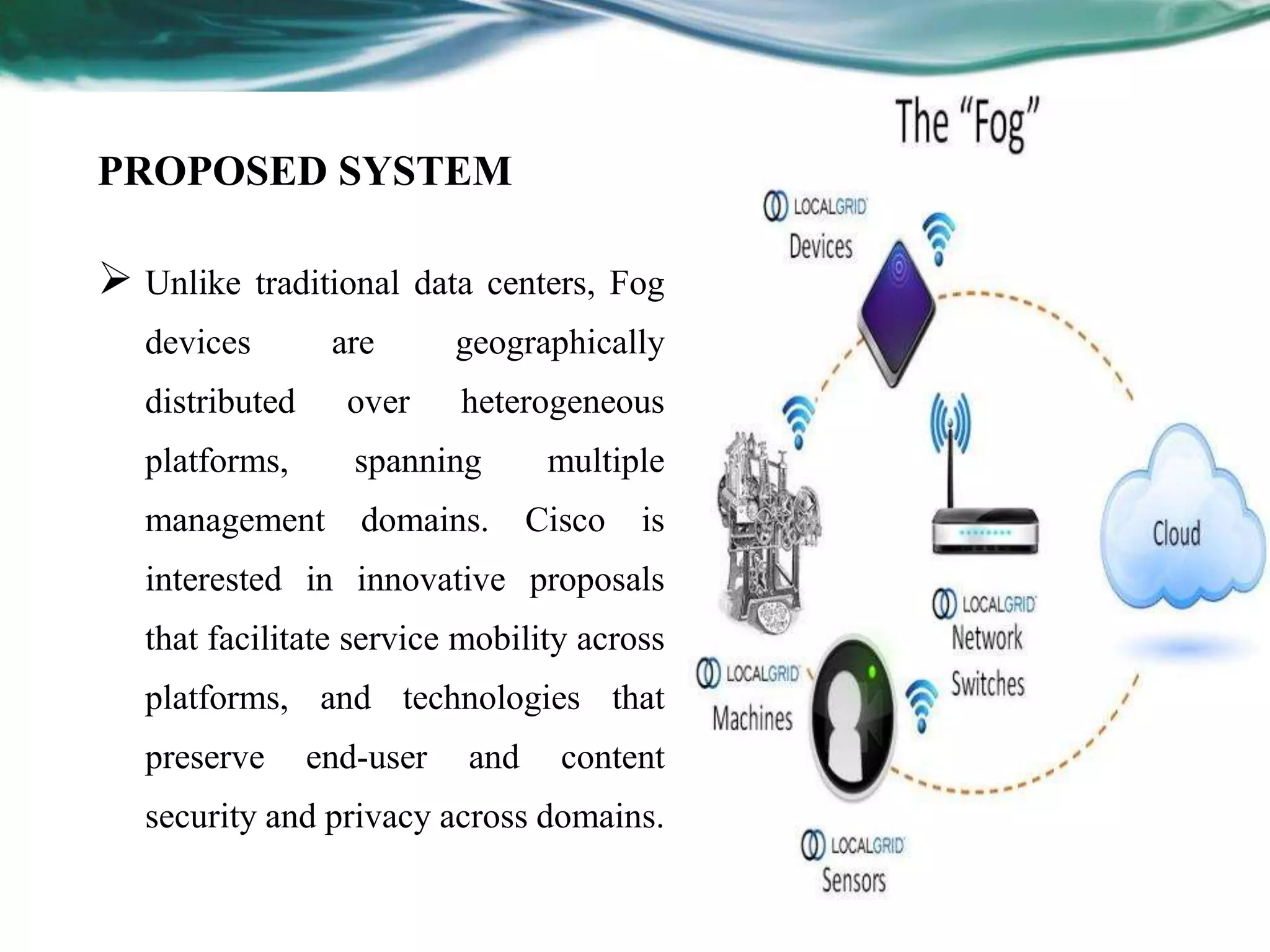
The document discusses fog computing, a technology that extends cloud computing services to the edge of networks, enhancing performance for Internet of Things applications. It covers existing limitations of cloud computing, proposes a distributed fog architecture for improved security and efficiency, and addresses security and privacy issues, particularly in smart grids. The conclusion emphasizes the potential of fog computing to provide greater security for user data and reduce insider threats.



















![REFERENCES
[1] F. Bonomi, “Connected vehicles, the internet of things, and fog com-
puting,” in The Eighth ACM International Workshop on Vehicular Inter-
Networking (VANET), Las Vegas, USA, 2011.
[2] F. Bonomi, R. Milito, J. Zhu, and S. Addepalli, “Fog computing and its
role in the internet of things,” in Proceedings of the First Edition of the MCC
Workshop on Mobile Cloud Computing, ser. MCC’12. ACM,2012, pp. 13–16.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarpptfogcomp-170420185314/75/Seminar-ppt-fog-comp-21-2048.jpg)
