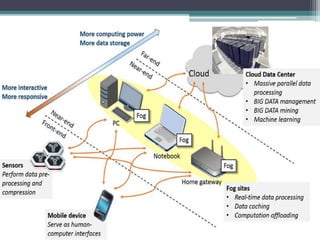
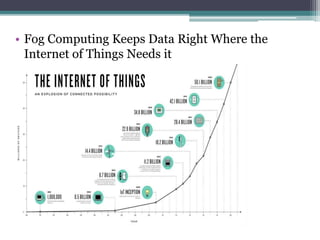
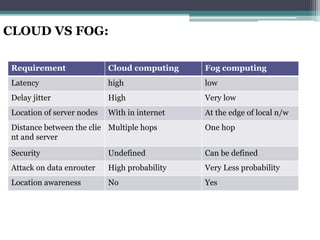
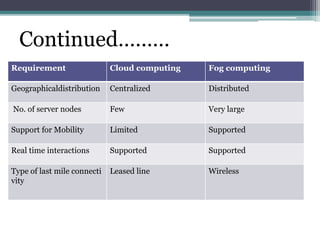
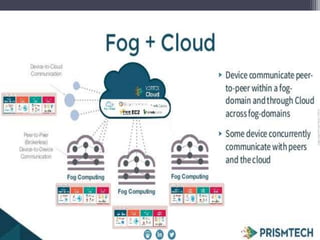
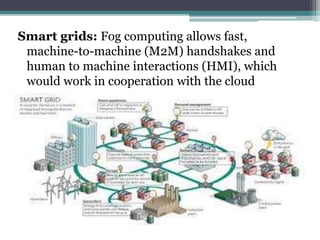
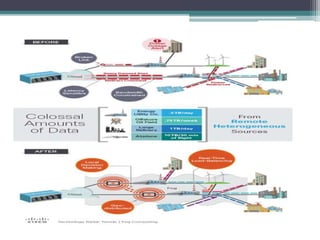
Fog computing is a model that processes data and applications at the edge of the network, rather than sending all data to the cloud. It helps address issues with IoT networks like high latency and bandwidth usage. Fog computing can overcome cloud limitations by keeping data local, reducing congestion and improving security. It is well-suited for applications that require real-time, localized processing like connected vehicles, smart grids, smart cities, and healthcare. Fog computing lowers costs and improves efficiencies compared to relying solely on cloud infrastructure.