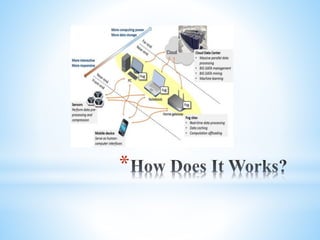
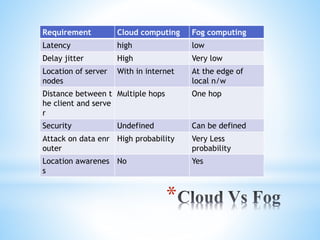
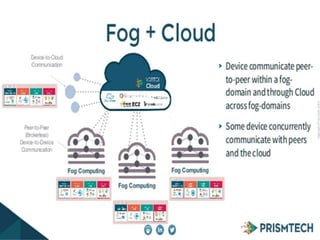
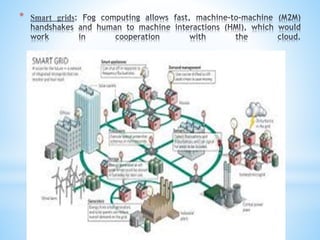
Fog computing extends cloud computing to the edge of a network, closer to IoT devices. It helps process data locally instead of sending everything to the cloud, reducing latency, bandwidth usage, and security risks. Fog computing can provide localized services for applications like healthcare and smart grids, improving response times, privacy, and insights while lowering costs compared to relying solely on cloud infrastructure. The main challenges involve authentication across gateways and devices, and protecting privacy while still obtaining useful aggregate data.