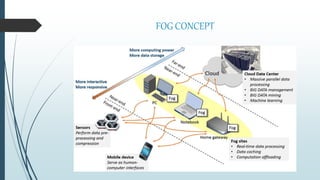
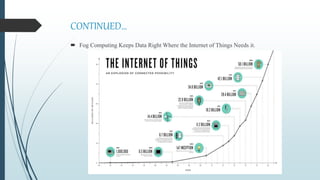
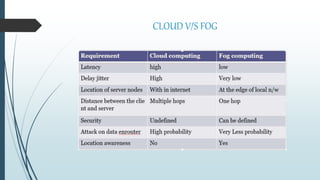
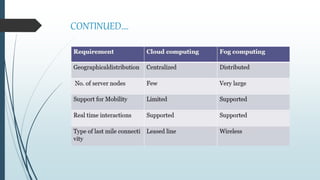
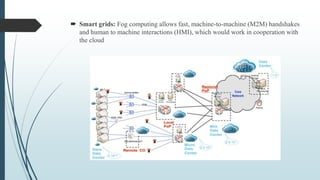
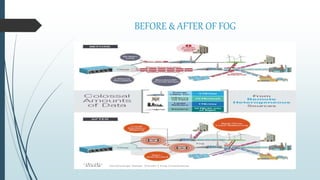
This document provides an overview of fog computing, including its origins at Cisco, its advantages over cloud computing for applications with low latency requirements like IoT, and examples of applications that could benefit like smart cities and healthcare. Fog computing processes data locally at the edge of the network rather than sending all data to the cloud, helping address issues of bandwidth constraints, network congestion, and latency for real-time applications. Security challenges also exist with protecting data and devices at the edge of the network in fog computing environments.