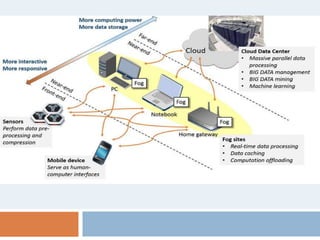
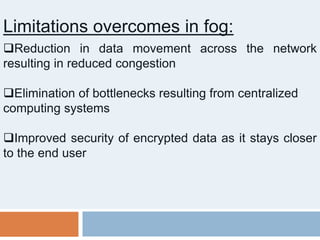
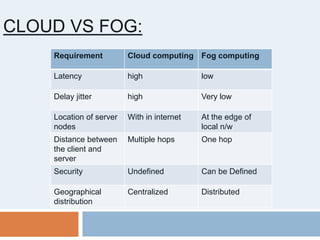
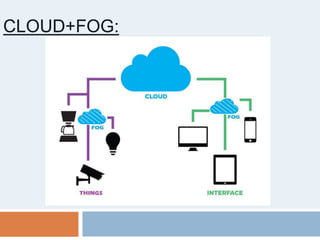
This document provides an introduction to fog computing. Fog computing is a model where data processing and applications occur at the edge of networks rather than solely in the cloud. This helps address limitations of cloud computing like high latency and bandwidth usage. Key characteristics of fog computing include low latency, geographical distribution, mobility support, and real-time interactions. Potential applications discussed are connected cars, smart grids, and smart traffic lights, which can benefit from fog computing's low latency and location awareness.