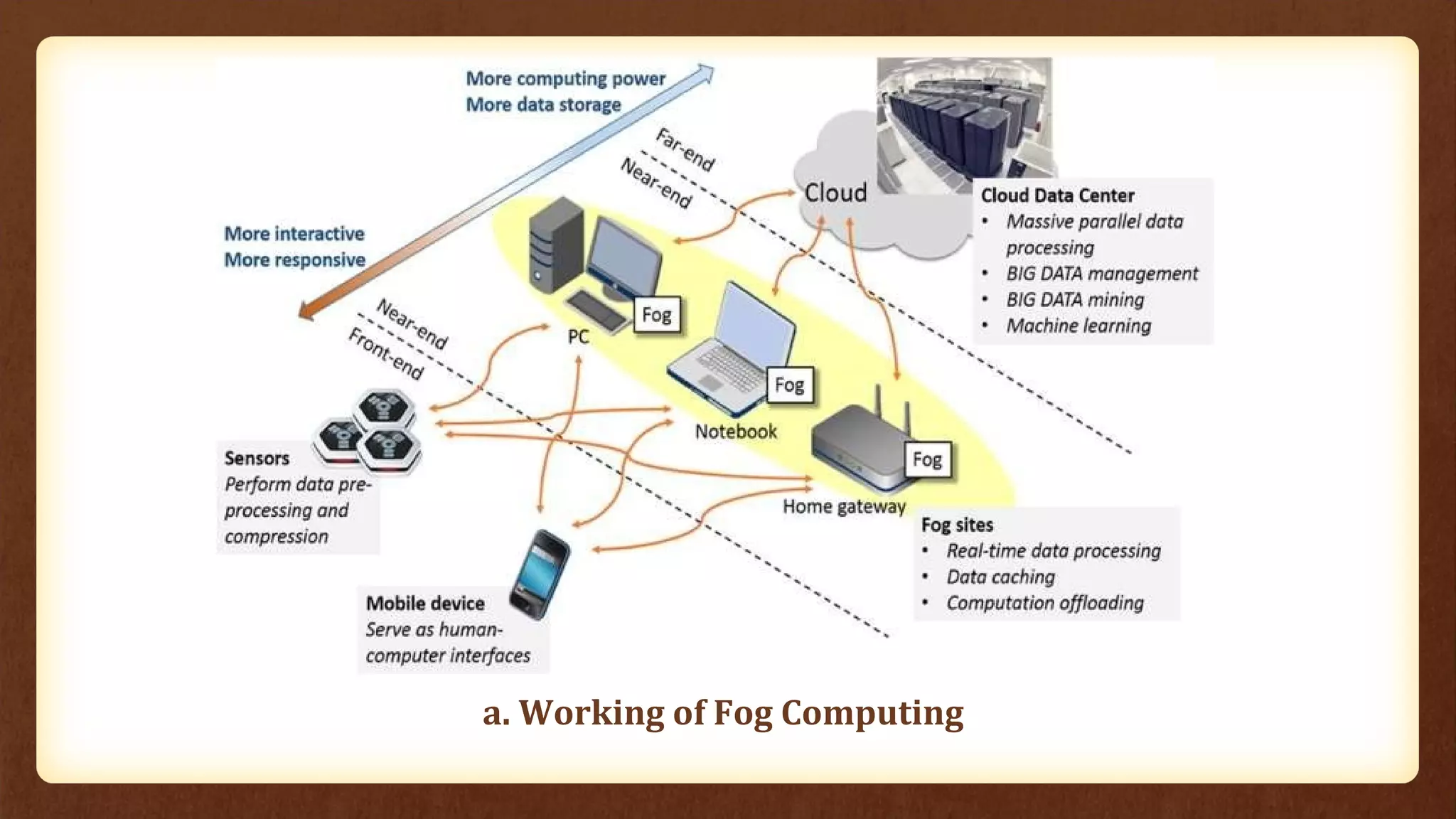
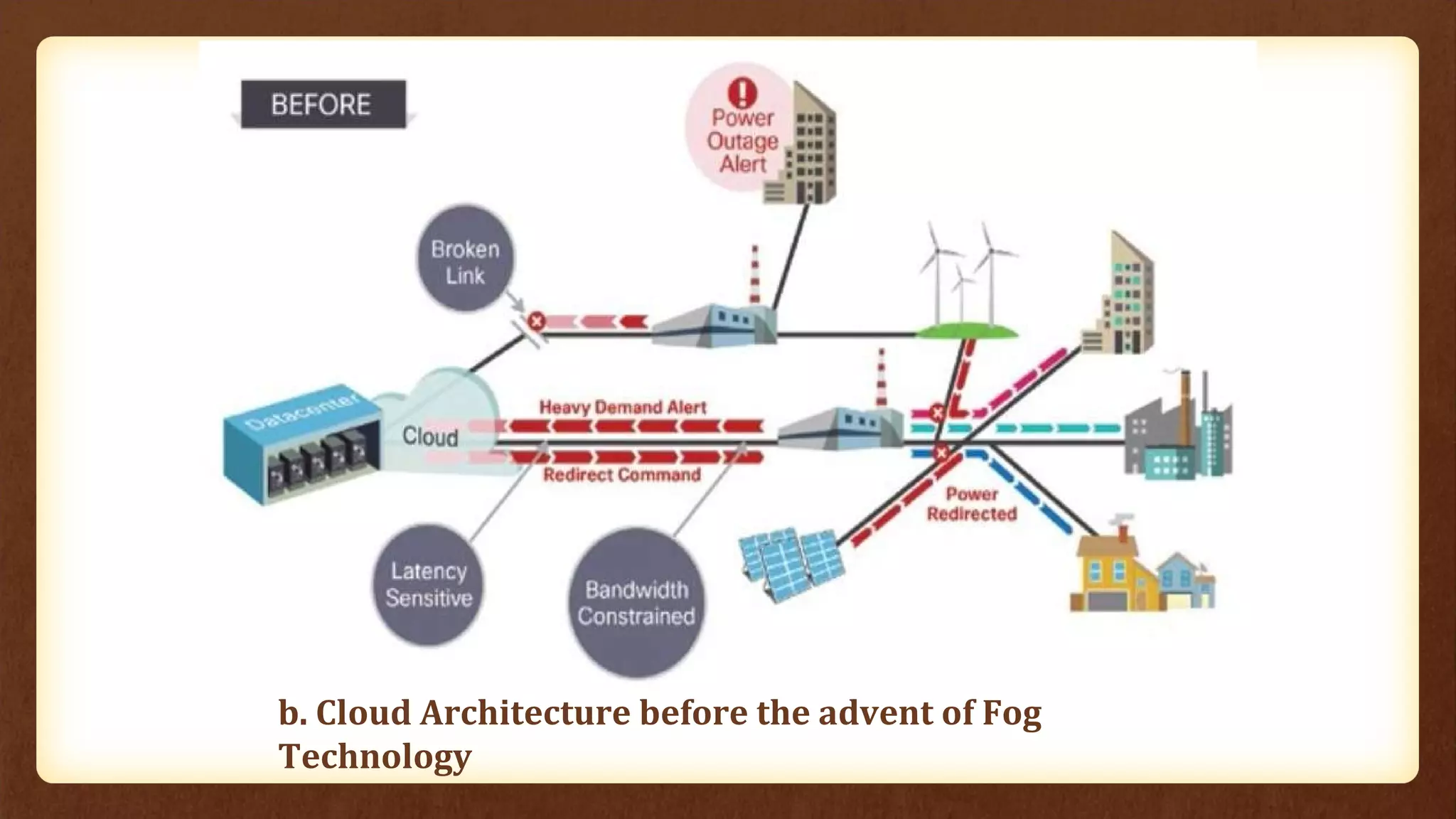
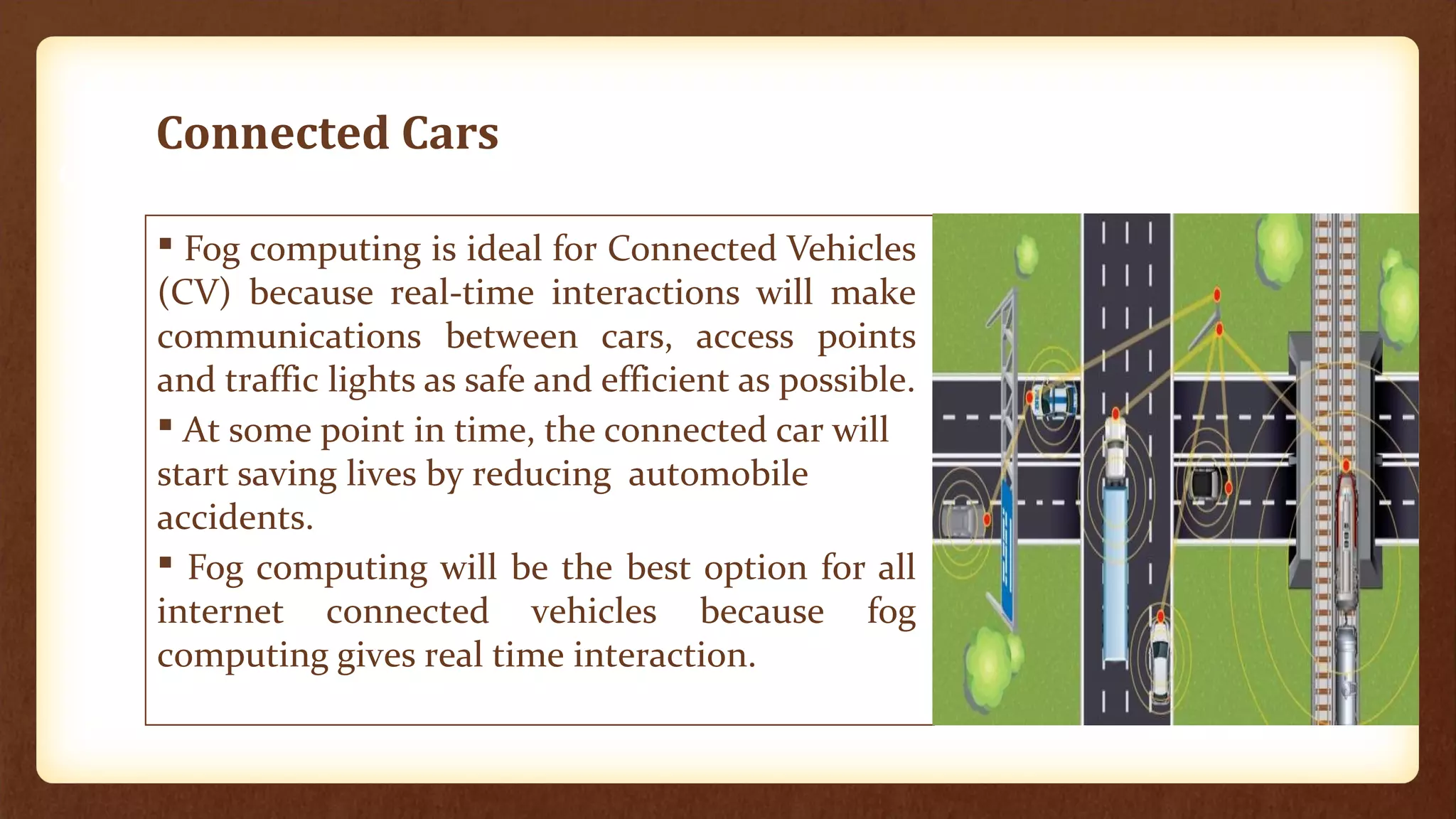
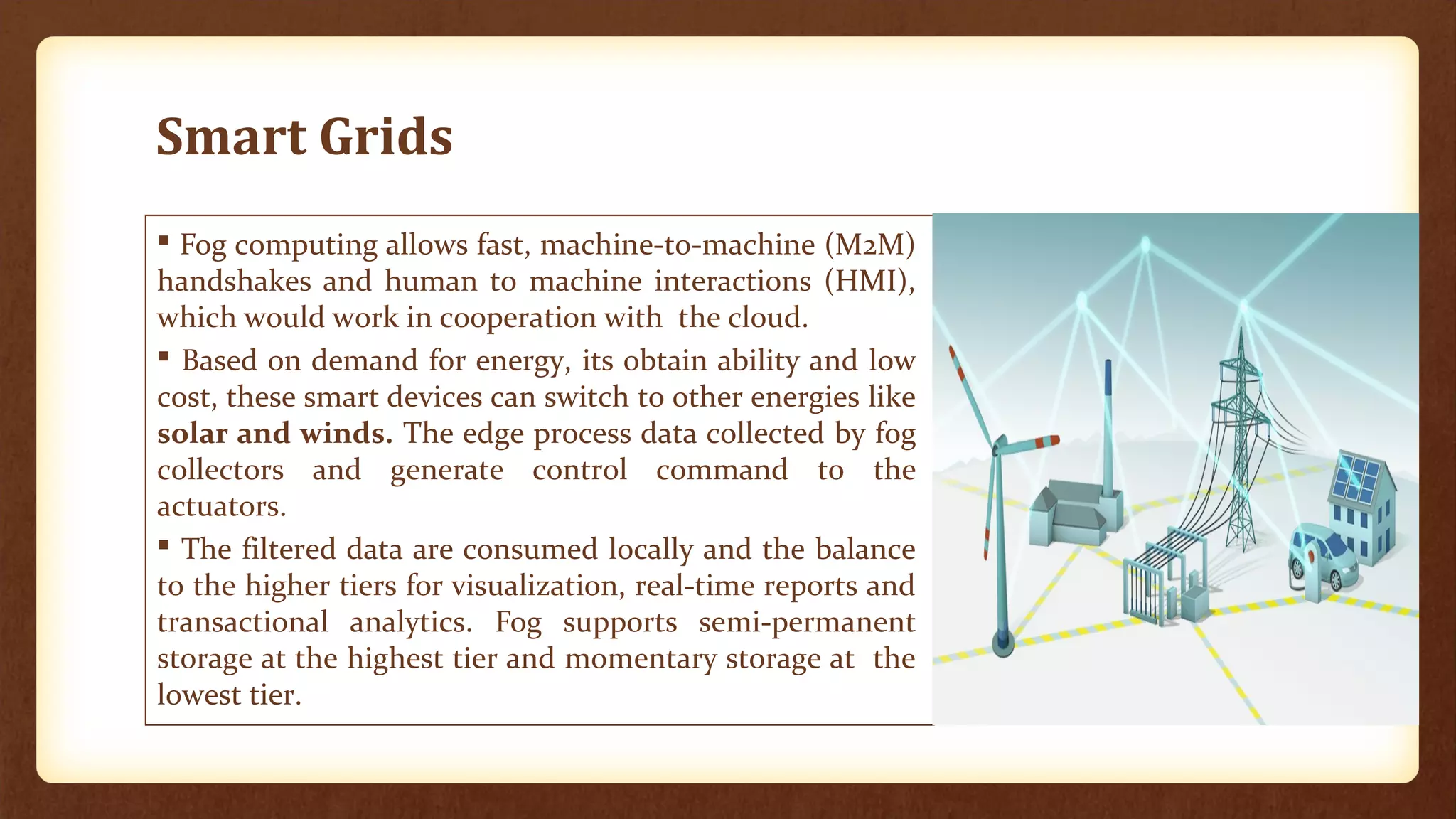
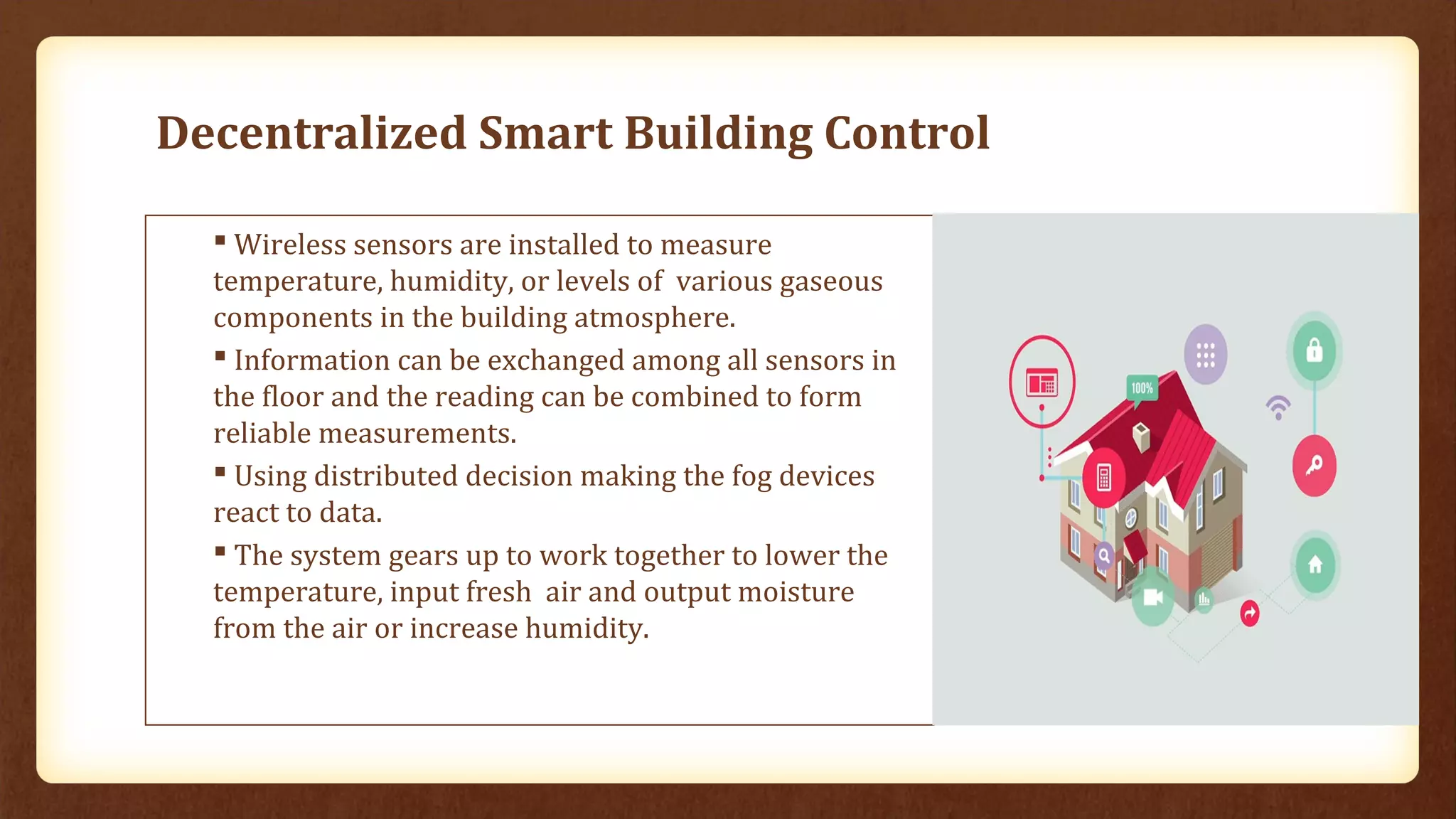
Fog computing extends cloud services to the network edge, enabling data processing and application services closer to end users, which addresses the limitations of traditional cloud computing, such as high latency and security concerns. It is particularly beneficial for applications in the Internet of Things (IoT), including connected vehicles, smart grids, smart buildings, and healthcare, as it facilitates real-time interactions and improved data management. The architecture of fog computing includes heterogeneous resources and a service orchestration layer, making it an effective solution for modern technology needs.