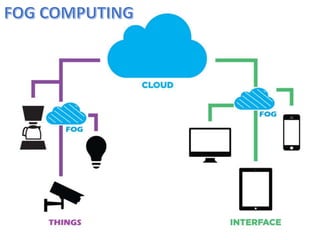
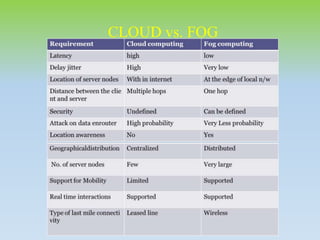
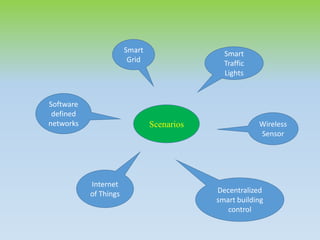
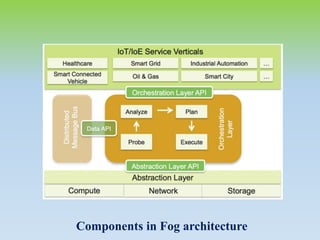
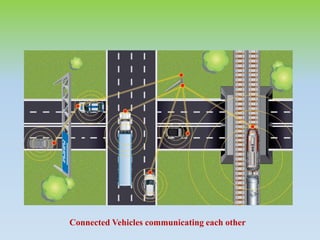
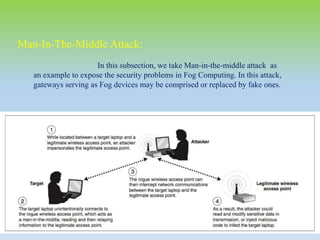
This document provides an overview of fog computing, including its characteristics, architecture, applications, examples, advantages, and disadvantages. Fog computing extends cloud computing by performing computing tasks closer to end users at the edge of the network to reduce latency. It has a dense geographical distribution and supports mobility and real-time interactions better than cloud computing. The document outlines the key components of fog architecture and discusses scenarios where fog computing can be applied, such as smart grids, smart buildings, and connected vehicles.