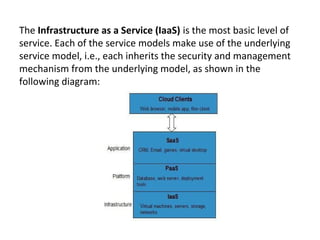
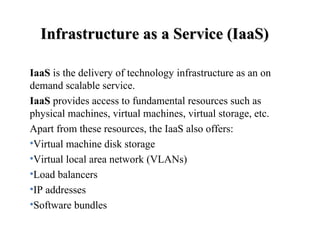
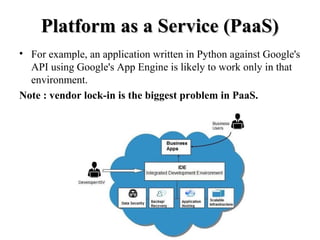
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like applications and storage over the internet. It works based on deployment models (public, private, hybrid, community clouds) and service models (Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS)). IaaS provides basic computing and storage resources, PaaS provides platforms for building applications, and SaaS provides ready-to-use software applications delivered over the internet. The main advantages of cloud computing include lower costs, improved performance, unlimited storage, and device independence while disadvantages include reliance on internet and potential security and control issues.