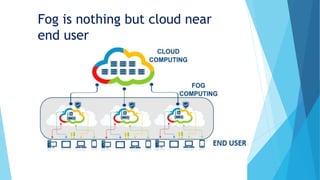
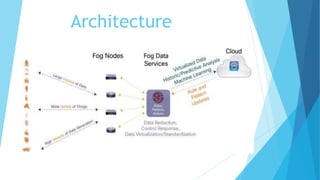
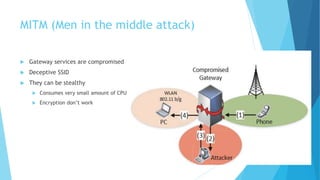
Fog computing, introduced by Cisco in 2014, decentralizes computing, networking, and storage resources closer to end users to reduce bandwidth usage and lower latency. It consists of a hierarchical framework with fog nodes at the edge, facilitates resource management, load balancing, and addresses significant security and privacy concerns, including mitigation strategies for attacks like MITM. The future includes new service models like fog-as-a-service (FaaS) and expanded applications in various industries.