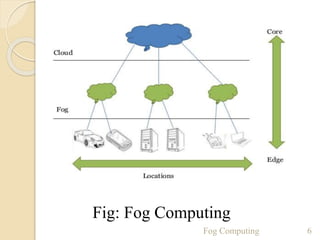
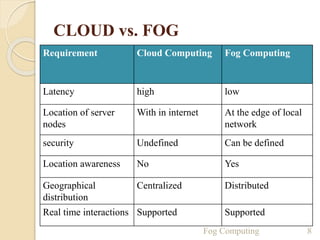
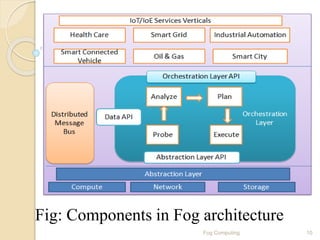
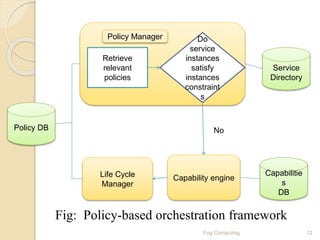
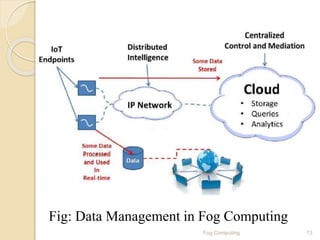
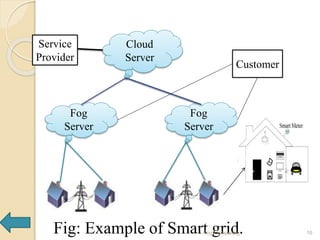
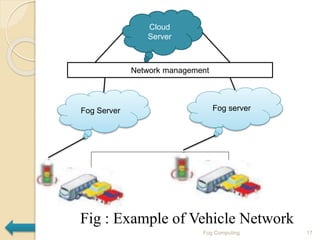
The seminar presentation introduced fog computing, which extends cloud computing and services to the edge of the network. Fog computing provides data, compute, and application services to end-users. It was developed to address limitations of cloud computing like high latency and lack of location awareness. Fog computing improves efficiency, latency, security, and supports real-time interactions through geographical distribution of resources at the edge of the network. The presentation covered fog computing characteristics, architecture, applications in areas like smart grids and vehicle networks, and concluded that fog computing will grow in helping network paradigms requiring fast processing.