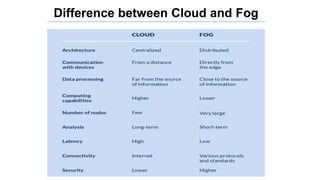
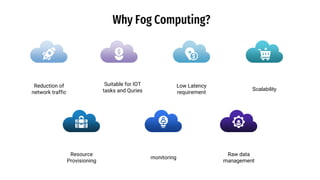
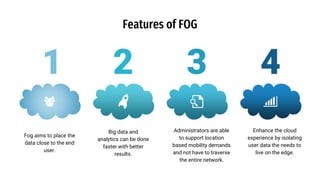
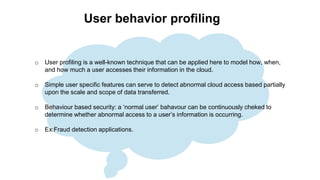
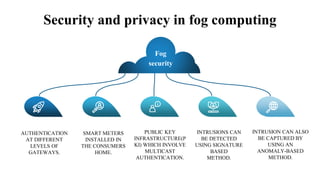
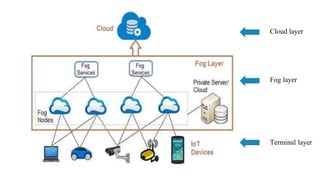
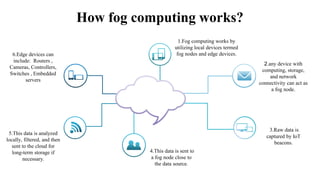
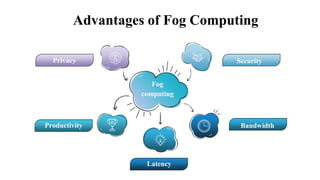
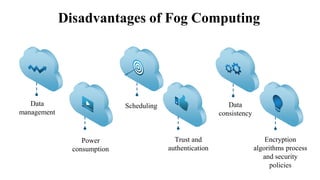
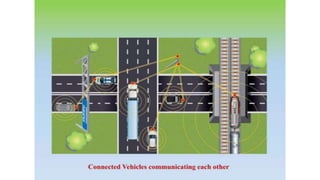
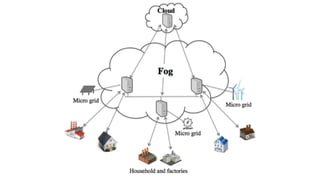
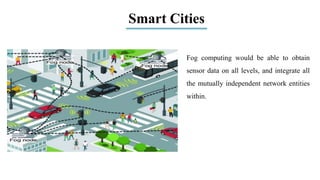
The document discusses fog computing as a technology that extends cloud computing to the edge of the network, focusing on its importance for the Internet of Things (IoT). It highlights the advantages of fog computing, such as reduced latency, real-time data processing, and improved data security, while also addressing its disadvantages and various applications in smart cities, connected vehicles, and smart grids. Lastly, it emphasizes the future potential of fog computing in enhancing cloud services and managing increasing IoT demands.

















![References
1. Bonomi, Flavio (September 19–23, 2011). "Connected Vehicles, the Internet of Things,
and Fog Computing, The 8th ACM International Workshop on VehiculAr Inter-
NETworking (VANET 2011), Las Vegas, NV, USA". www.sigmobile.org.
Retrieved 2019-08-07.
2. "What Is Fog Computing? Webopedia Definition". www.webopedia.com.
Retrieved 2017-04-07.
3. Bonomi, F., Milito, R., Zhu, J., and Addepalli, S. Fog Computing and its Role in the
Internet of Things. In Proc of MCC (2012), pp. 13-16.[4].
4. "Fog brings the cloud closer to the ground: Cisco innovates in fog
computing". newsroom.cisco.com. Retrieved 2019-01-24.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semppt-221029072737-0a9e46f4/85/semppt-pptx-29-320.jpg)