This document summarizes a research paper presentation on cloud and fog computing. The presentation discusses:
1) The security issues in cloud computing and how fog computing can address them through techniques like user profiling and decoy documents.
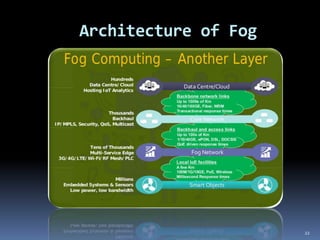
2) The characteristics, architecture, applications and advantages of fog computing, which extends cloud services to the edge of the network.
3) How fog computing helps improve cloud computing security by processing and analyzing data locally, reducing traffic to the cloud and misleading attackers through decoy documents.