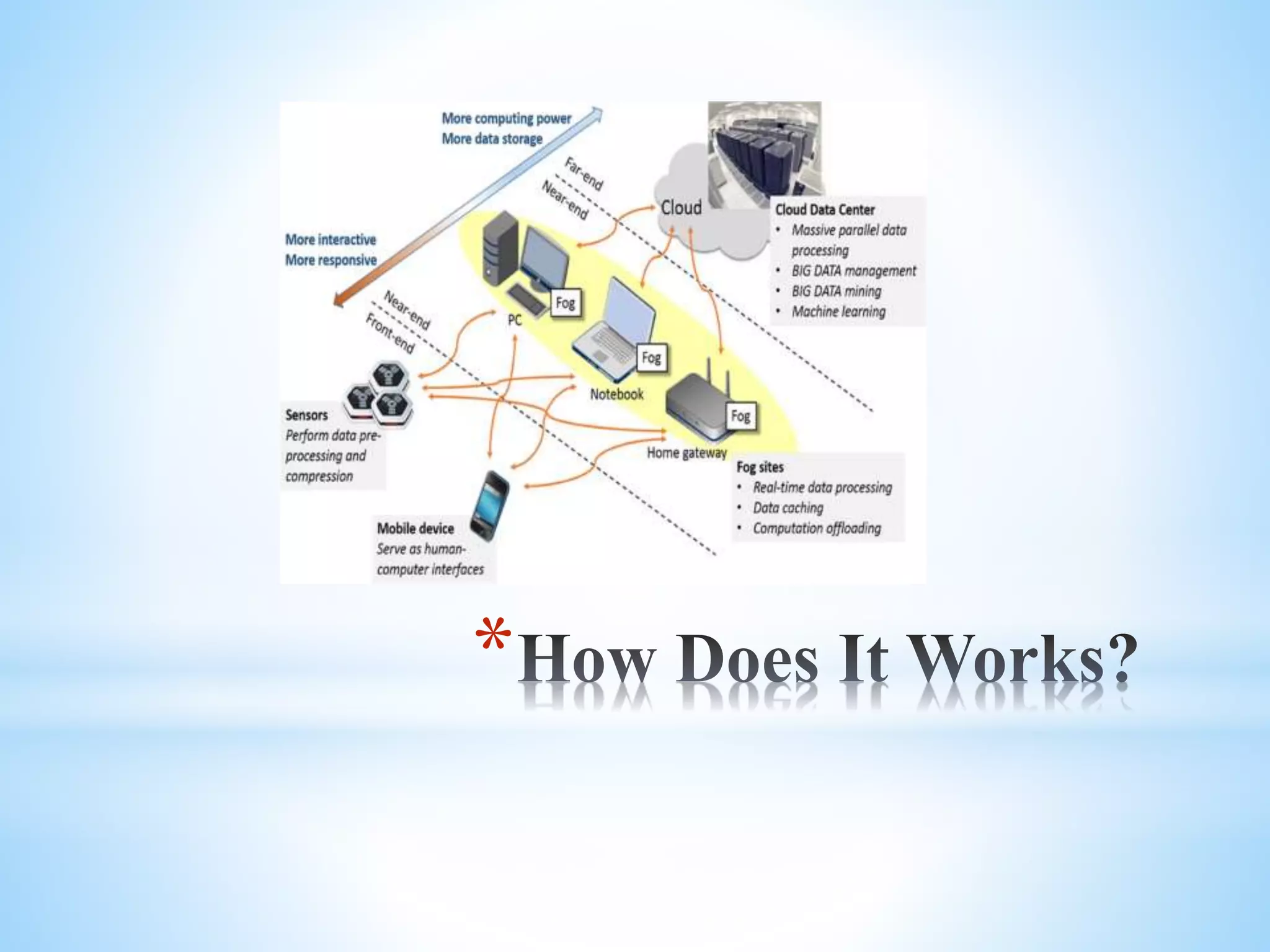
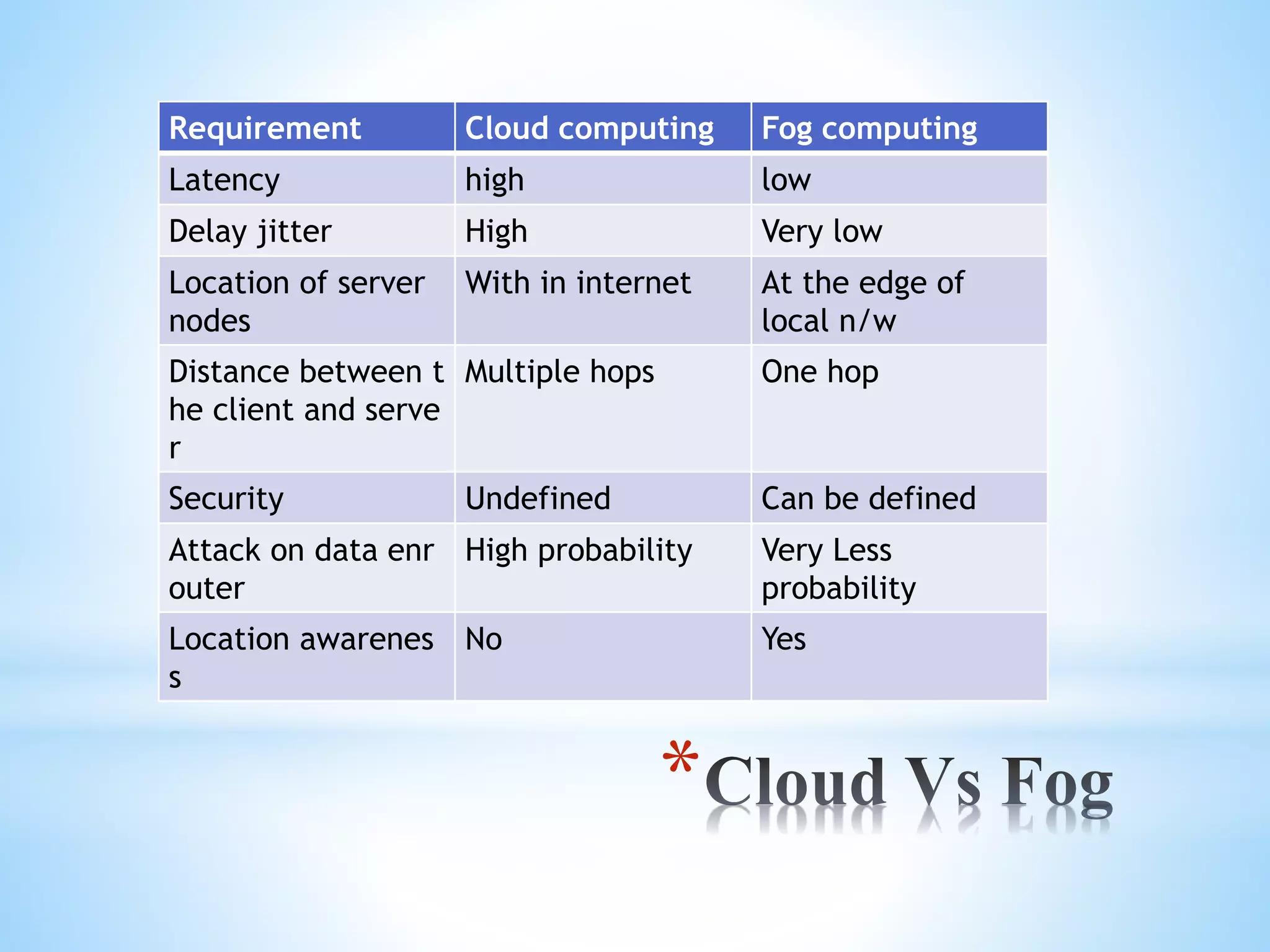
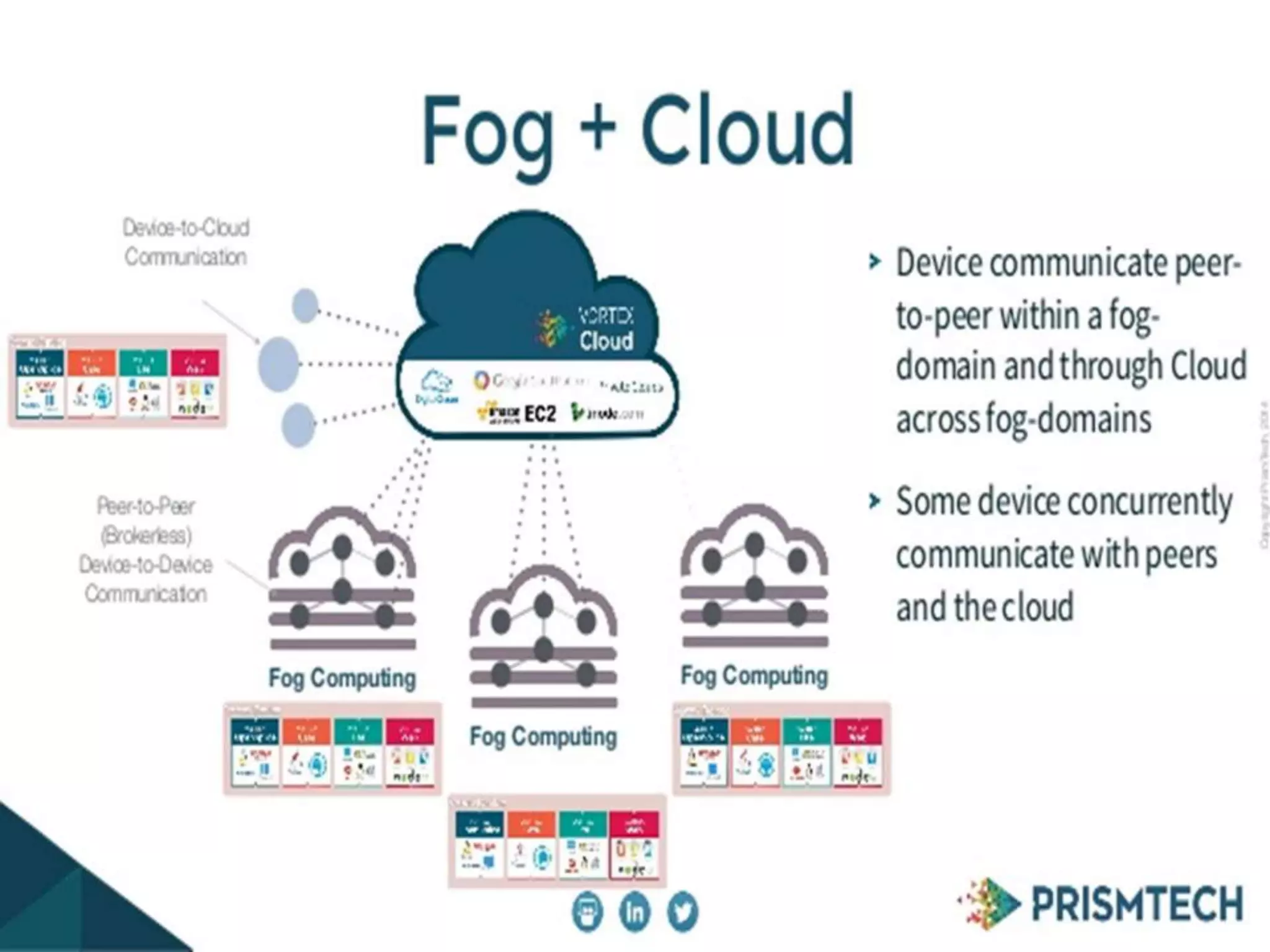
Fog computing extends cloud computing to the edge of a network, closer to IoT devices. It helps process data locally instead of sending everything to the cloud, reducing latency, bandwidth usage, and security risks. Fog computing can provide localized services for applications like healthcare that generate large amounts of data at the network edge. While it addresses some limitations of cloud computing, fog introduces its own security and privacy challenges that must be managed.