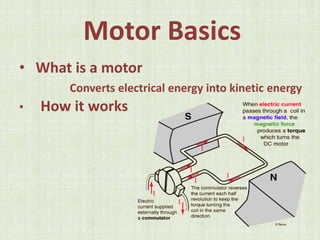
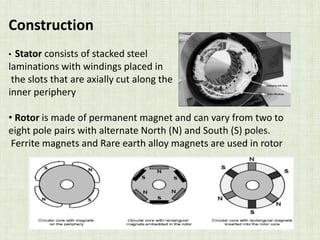
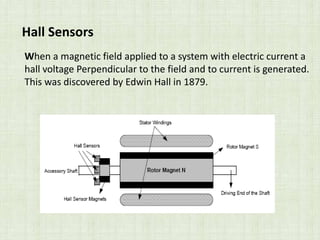
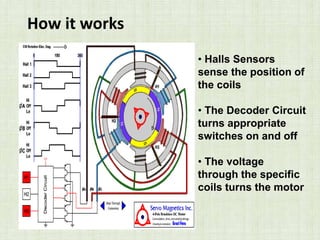
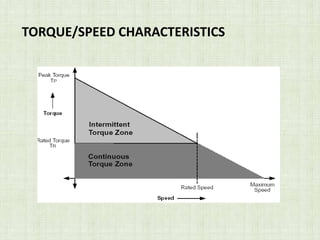
This document is a seminar paper on brushless DC motors submitted for a bachelor's degree. It includes sections on motor basics, the principles of BLDC motors, their construction including hall sensors, how BLDC motors work, torque/speed characteristics, advantages like increased efficiency over brushed DC motors, disadvantages like more complex circuitry, and applications in devices like hard drives, medical tools, and vehicles.