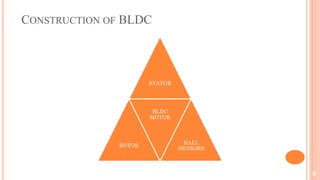
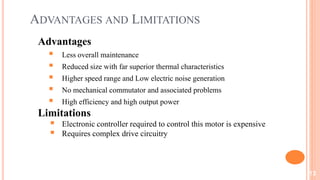
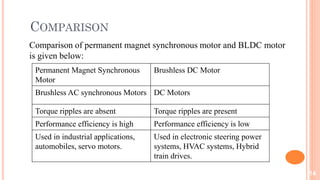
The document discusses brushless DC motors (BLDC). It explains that a BLDC motor is a permanent magnet synchronous electric motor driven by DC electricity with electronic commutation. It has a stationary stator with coils and a rotating permanent magnet rotor. Hall sensors detect the rotor position to synchronize switching of the stator coils and generate torque electronically rather than using brushes. BLDC motors are highly efficient and capable of high speeds. Common applications include computer hard drives, vehicles, industrial robots, and appliances.