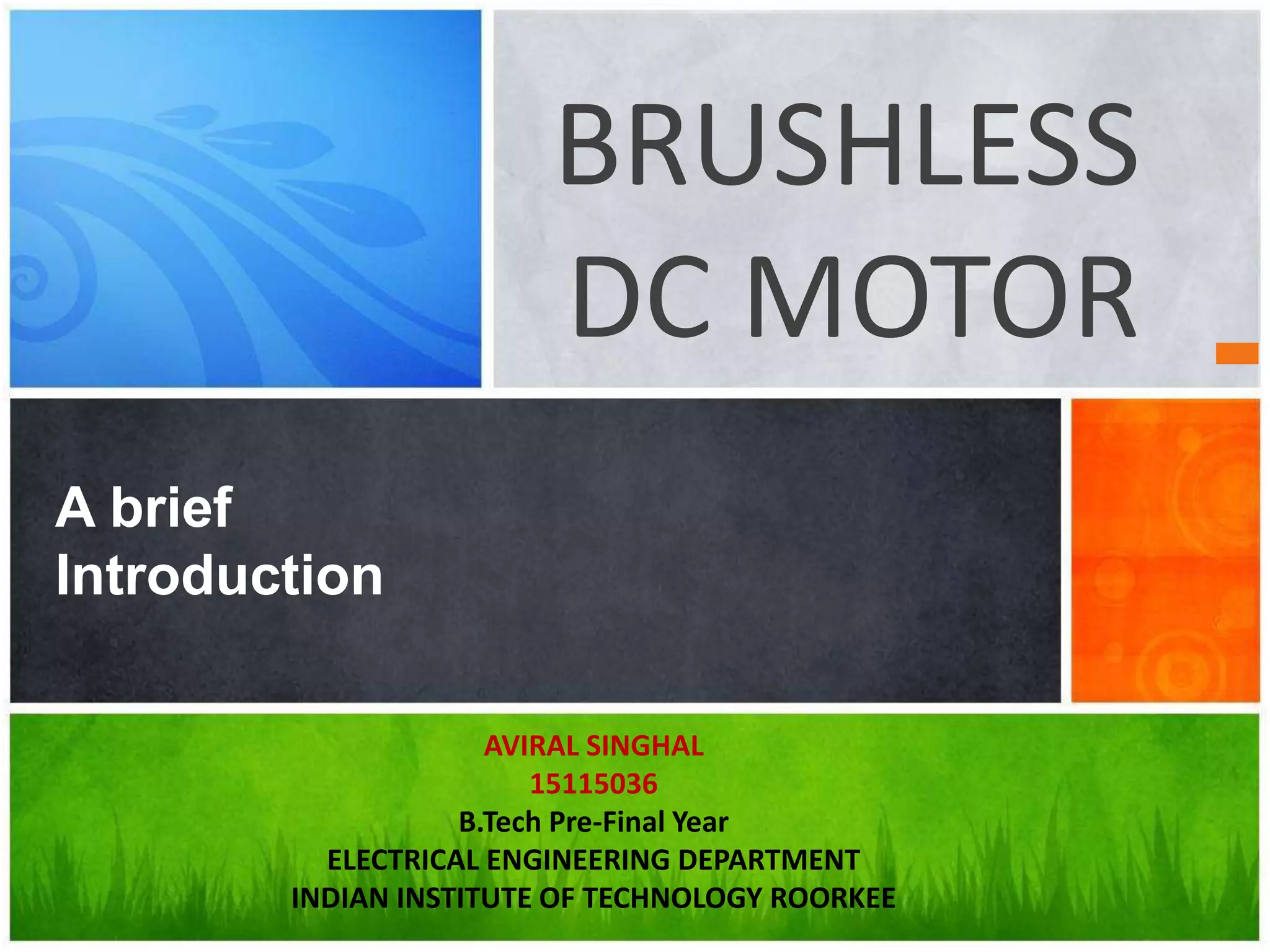
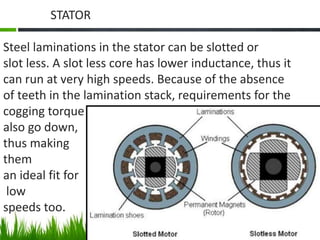
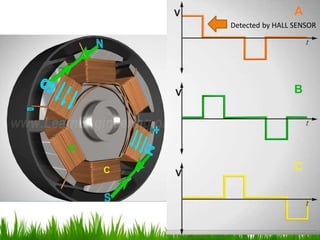
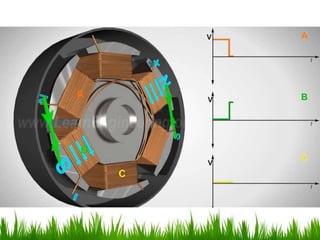
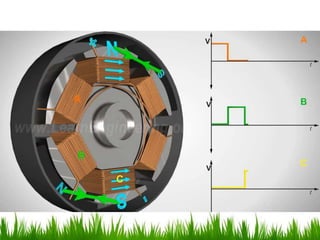
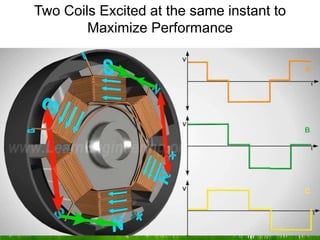
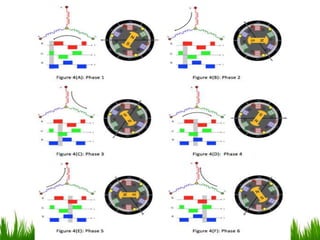
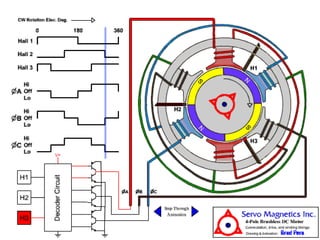
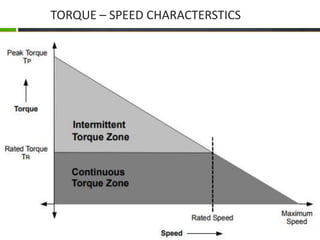
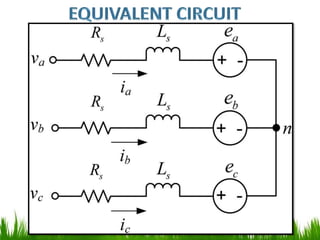
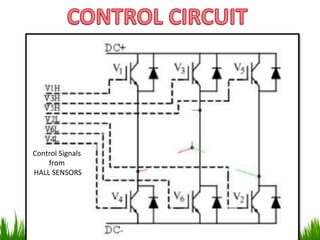
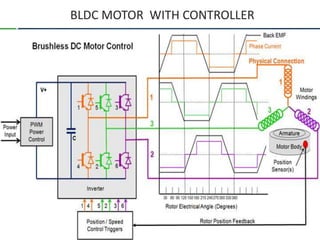
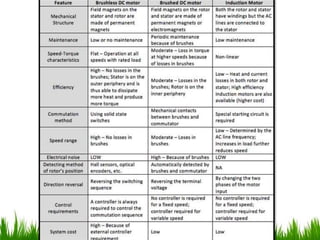
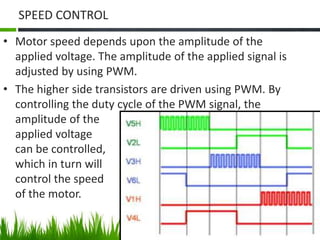
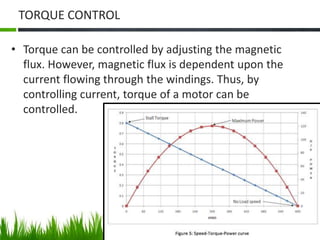
The document provides an overview of brushless DC (BLDC) motors, highlighting their construction, operation, and advantages over traditional motors. It explains the control of speed and torque, along with motor protection mechanisms, and discusses various applications in different fields such as medical instruments and vehicles. Additionally, it compares the benefits and drawbacks of BLDC motors and references various literature on the subject.