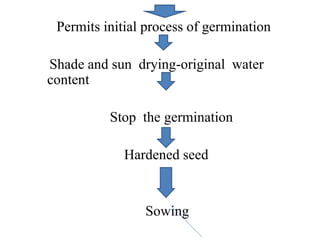
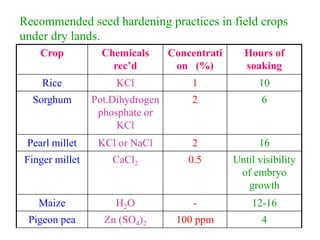
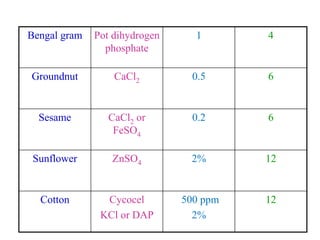
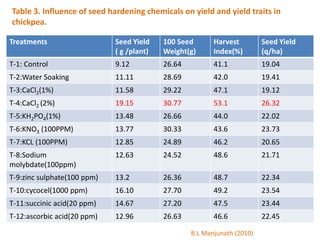
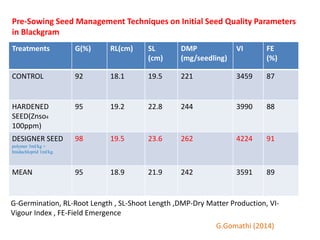
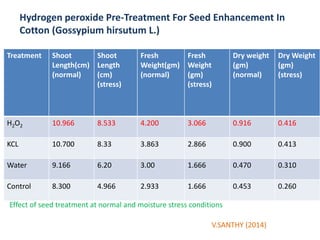
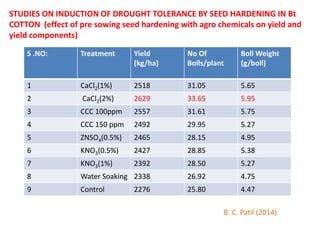
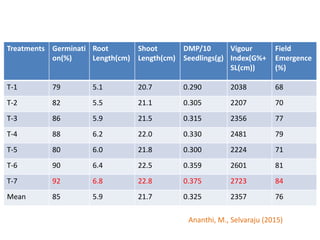
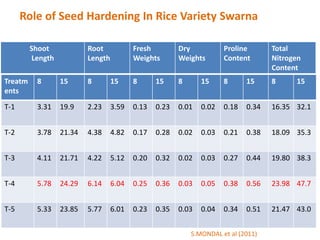
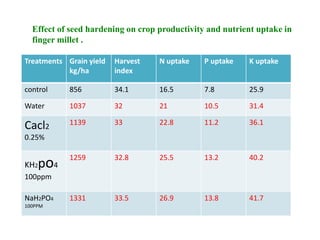
This document discusses seed hardening techniques for improving crop yields in dryland conditions. It defines seed hardening as hydrating seeds to initiate pre-germination metabolism followed by dehydration to fix biochemical events and impart stress resistance. Methods discussed include water soaking, chemical treatments with salts, growth regulators, and vitamins. Recommended treatments for various crops aim to increase germination rate, seedling vigor, and ultimately crop yields. Tables show seed hardening chemicals improving chickpea yield traits and cotton growth under normal and drought conditions. The document concludes by stating seed hardening benefits seedling establishment and crop productivity in dry areas.