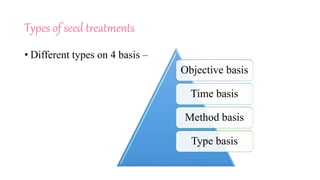
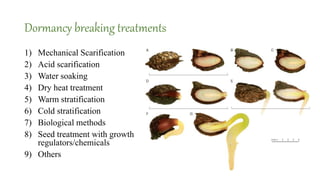
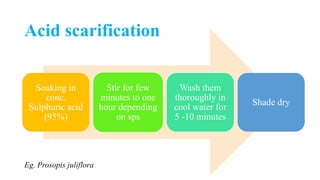
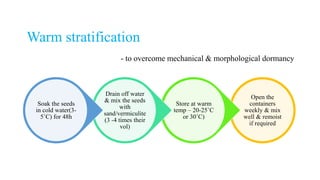
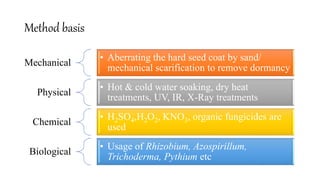
The document outlines various seed treatment methods aimed at breaking dormancy, enhancing germination, and protecting seeds from pests and diseases. It categorizes these treatments based on objectives, timing, methods, and types, detailing specific techniques such as mechanical scarification, chemical applications, and seed coating. Additionally, it discusses the use of growth regulators and innovative methods like magnetic treatment and infrared radiation to improve seed viability and growth.