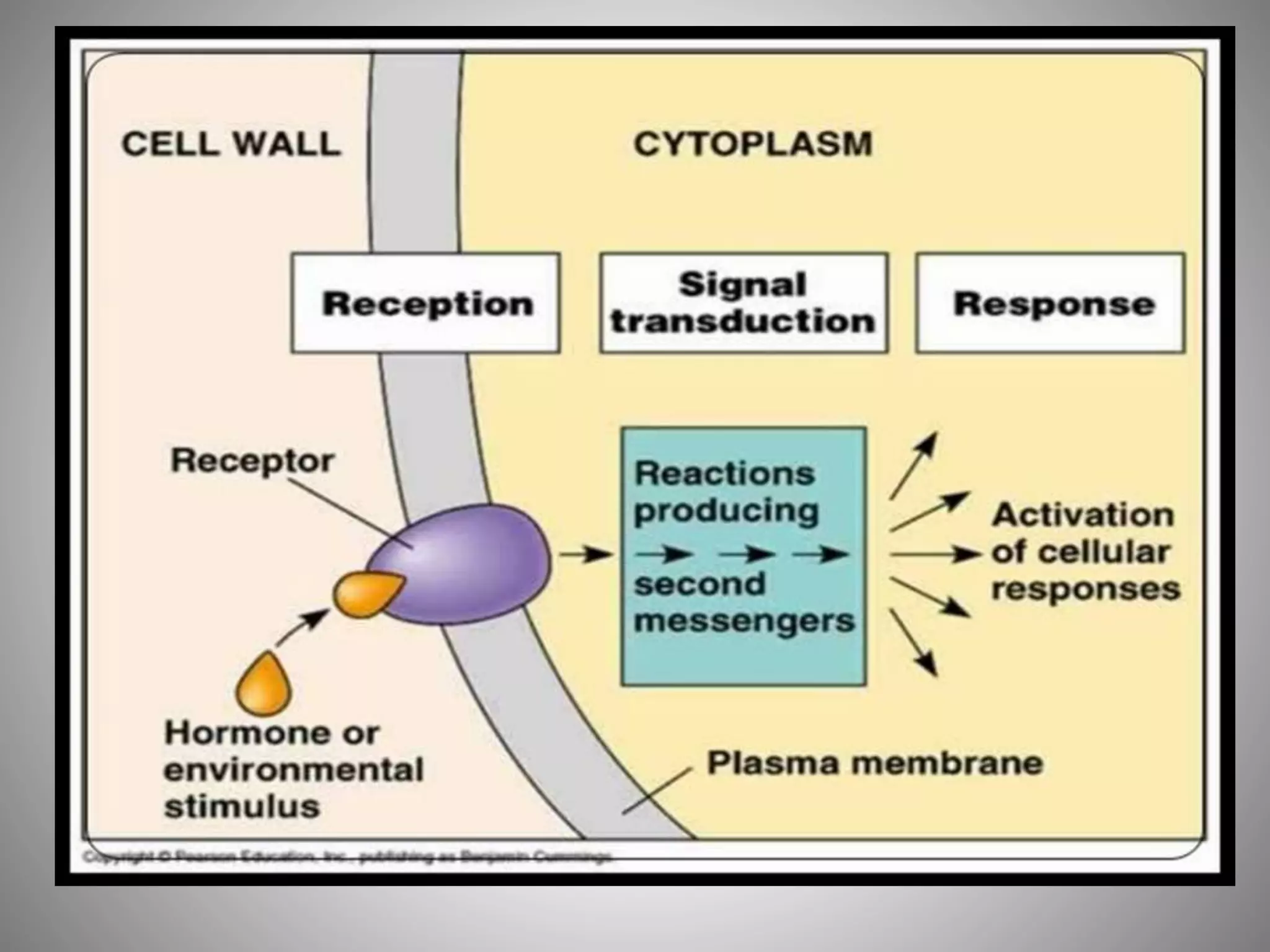
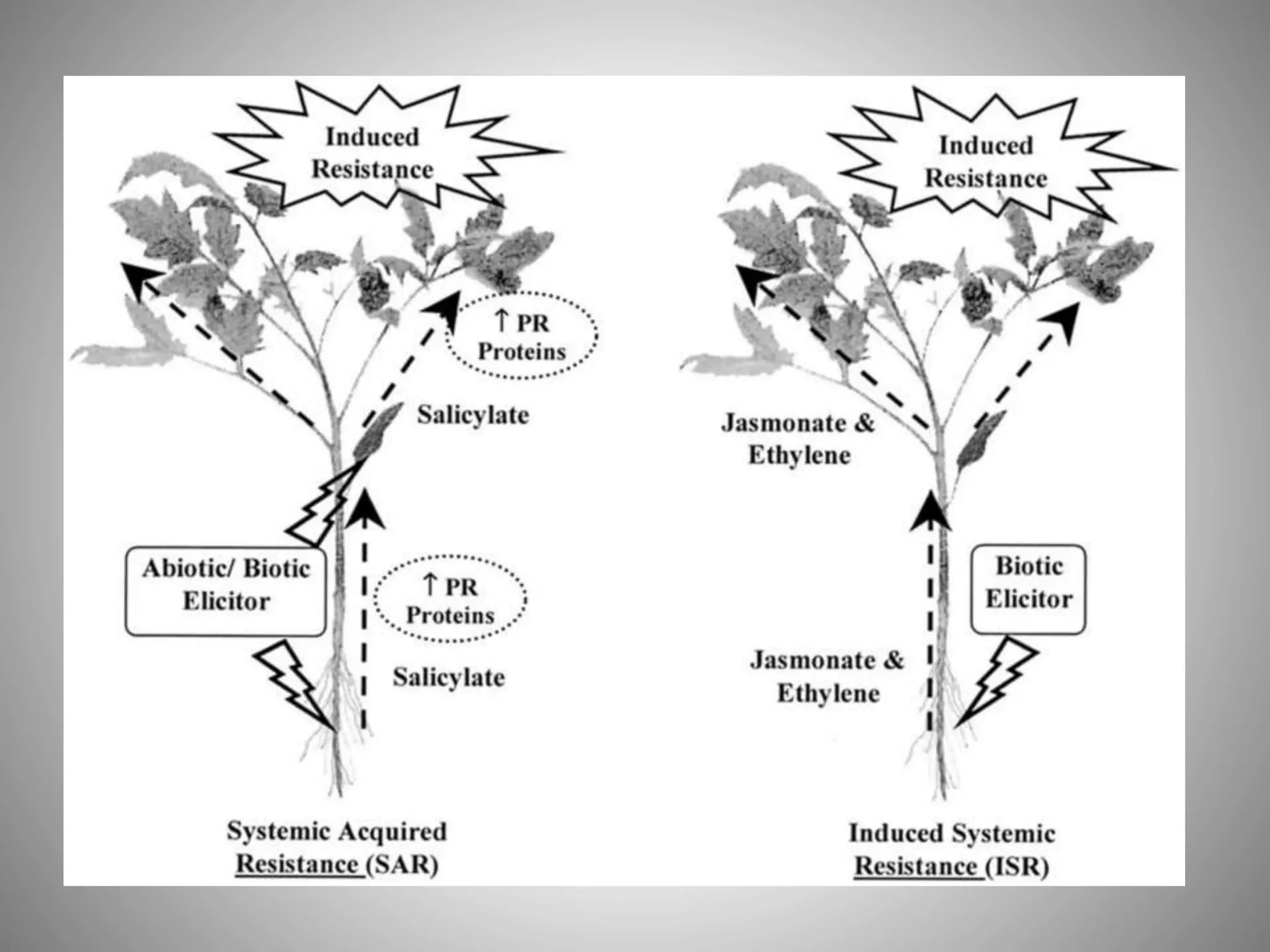
This document summarizes induced plant resistance against pathogens. It discusses the historical background of induced resistance being first observed over 100 years ago. It describes different types of induced resistance including systemic acquired resistance (SAR) and induced systemic resistance (ISR). SAR is mediated by salicylic acid and involves pathogenesis-related proteins, while ISR is mediated by jasmonic acid and ethylene. Biological agents like PGPR bacteria and plant extracts can also induce resistance. Signal transduction pathways underlying these responses are triggered upon pathogen recognition. While induced resistance offers opportunities for crop protection, practical applications are currently limited to some plants.