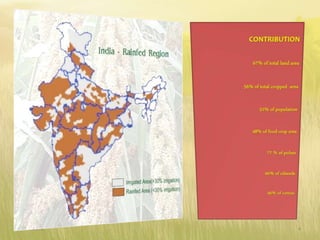
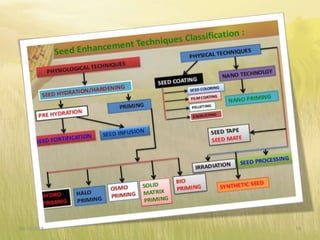
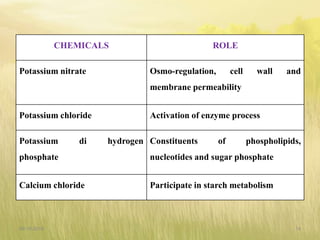
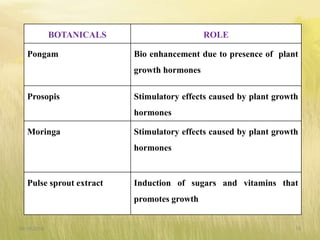
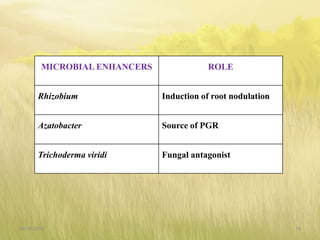
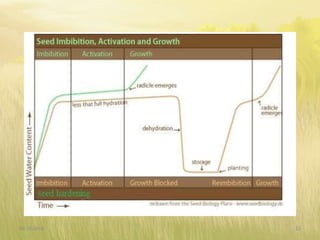
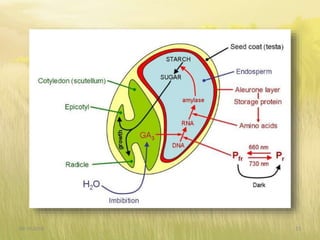
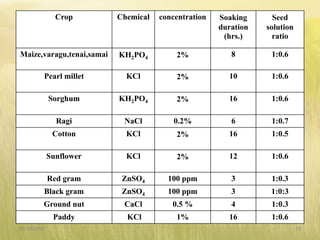
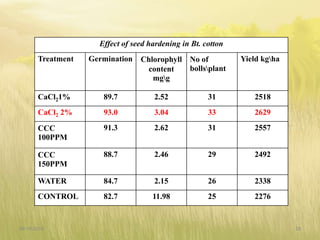
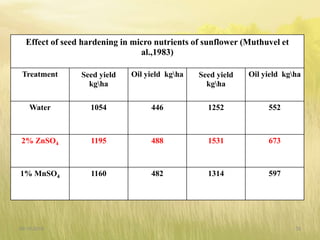
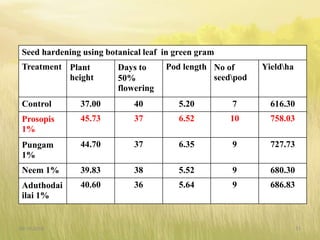
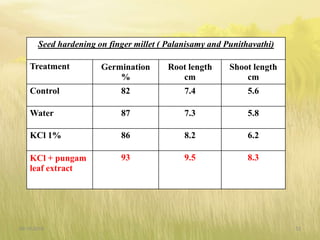
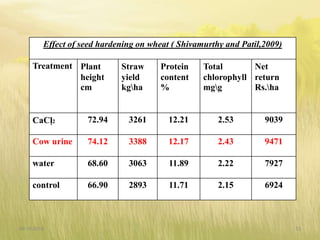
The document covers seed hardening, a technique to enhance seed quality and improve drought resistance through physiological preconditioning involving hydration. It outlines methods, including soaking dry seeds in water or chemical solutions, to facilitate rapid and uniform germination while detailing benefits such as quicker recovery from wilting and improved competitive ability against weeds. Various examples and treatments for different crops illustrate the application and effectiveness of seed hardening, while acknowledging limitations related to time and concentration.