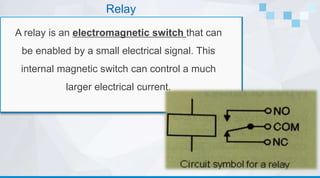
This document provides an overview of relays, 555 timers, and operational amplifiers. It defines each component and identifies their basic functions and applications. Relays are electromagnetic switches that control electrical current using a small input signal. 555 timers produce oscillating outputs that can be used for timing functions. Operational amplifiers are integrated circuits that amplify signals and can be used as comparators by comparing inputs. The document includes diagrams of each component and examples of their uses.