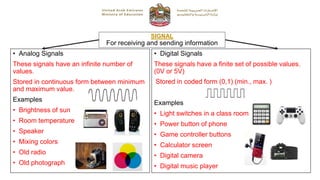
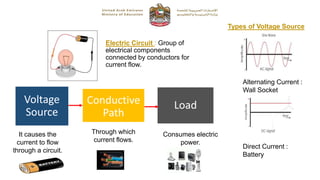
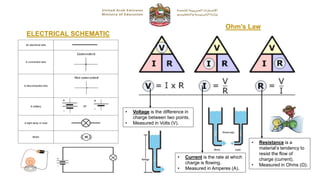
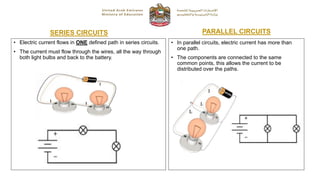
The document provides instructions for a Grade 10 General examination on Fundamentals of Electronics. It outlines 4 sections covering electrical circuits, resistors, electronic calculations, and embedded systems. Students must have a blue ink pen, pencil, ruler, and calculator (if required) and are not allowed electronic devices. The exam consists of multiple choice, true/false, short answer, and matching questions worth a total of 50 marks over 35 minutes.