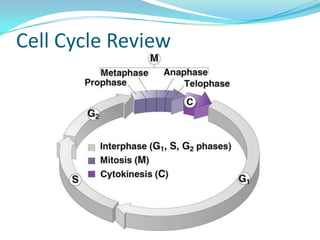
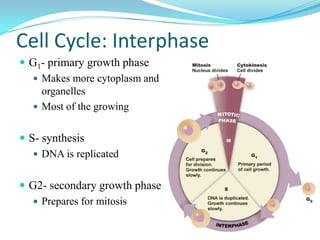
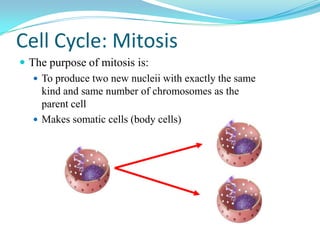
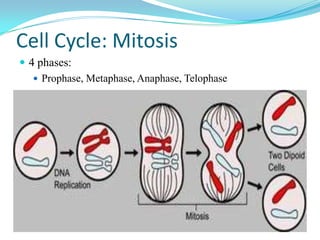
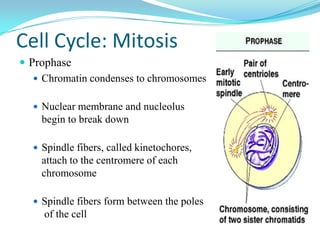
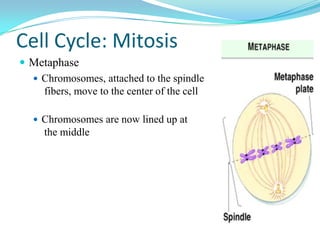
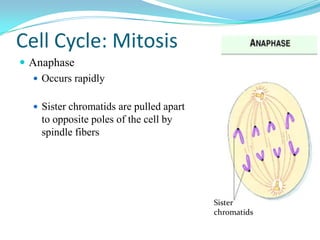
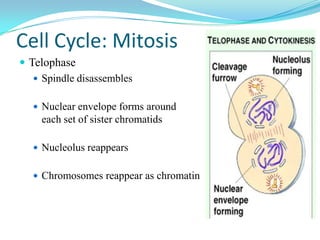
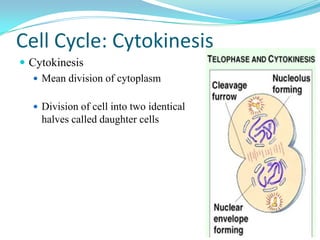
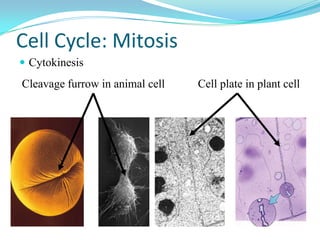
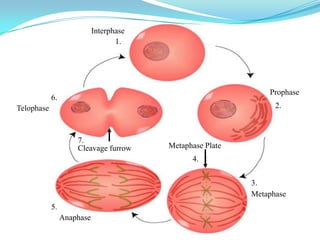
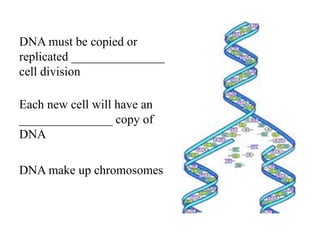
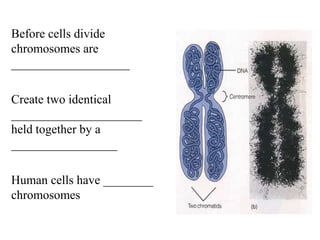
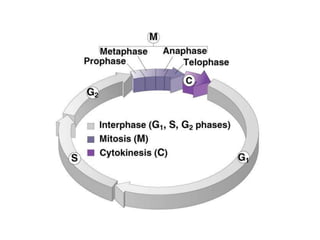
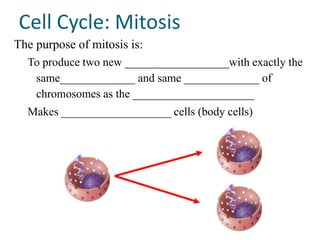
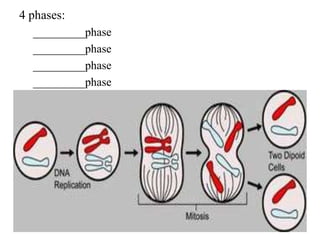
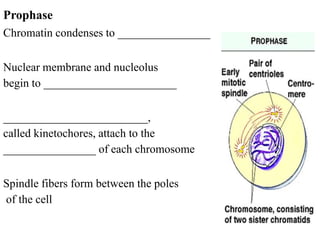
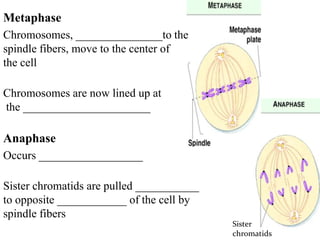
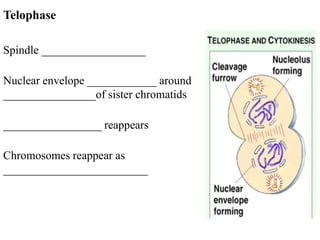
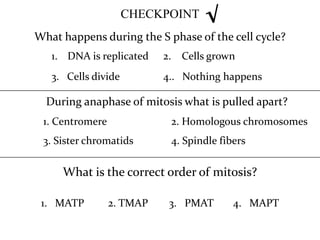
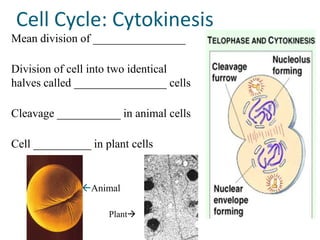
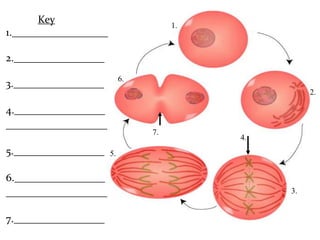
The document discusses the cell cycle and mitosis. It explains that the cell cycle includes interphase, where DNA replicates, and mitosis, where cells divide into two identical daughter cells through the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells with the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent cell through nuclear division and cytokinesis.