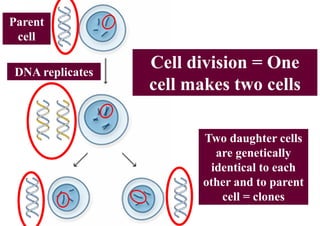
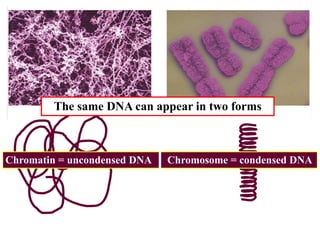
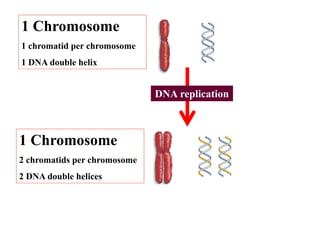
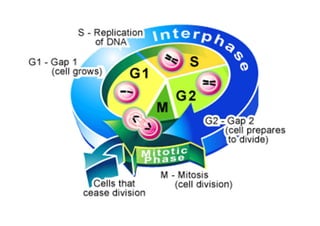
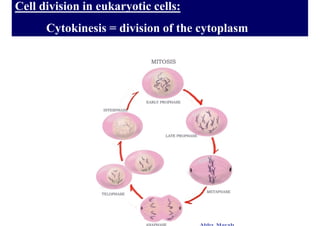
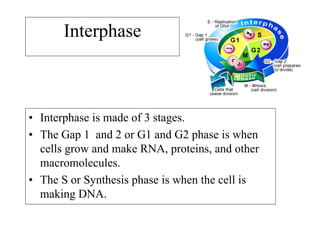
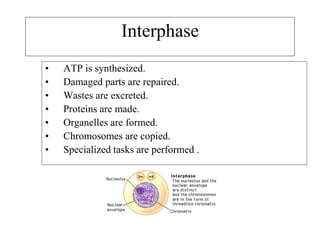
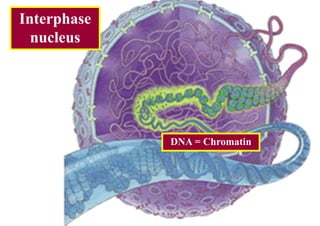
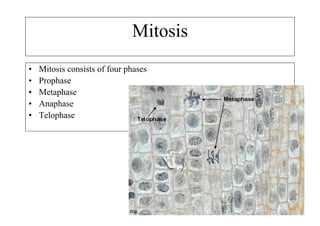
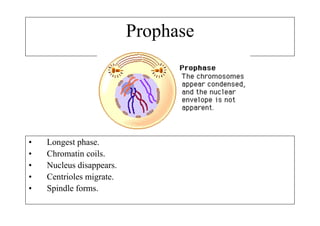
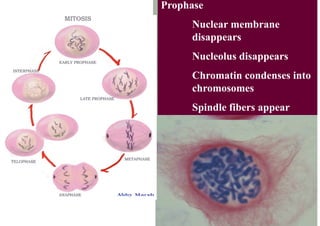
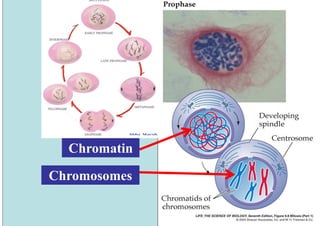
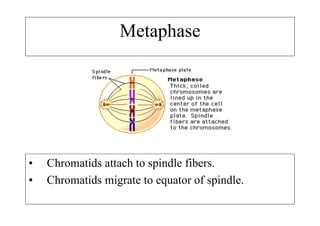
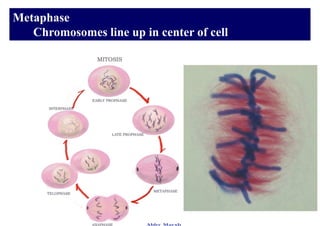
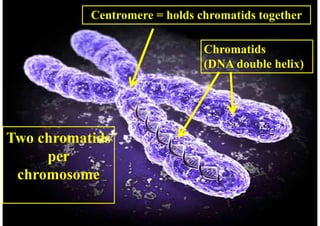
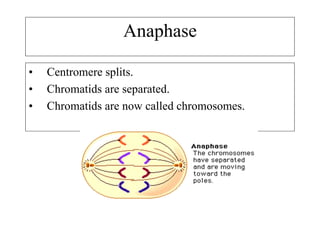
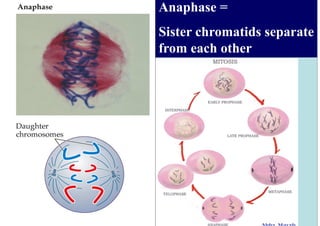
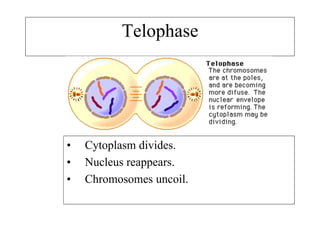
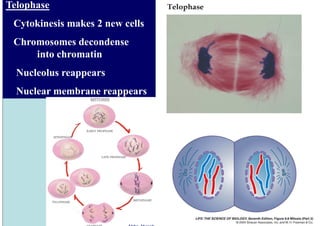
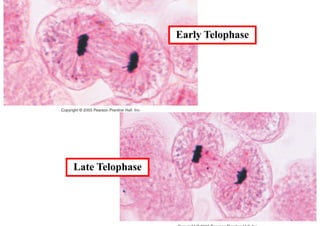
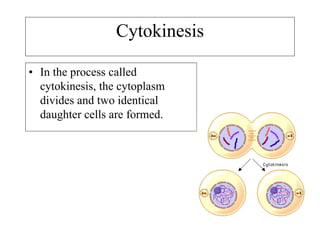
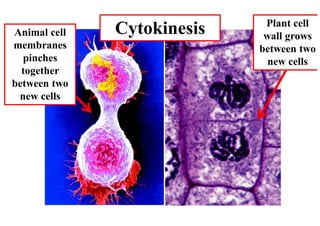
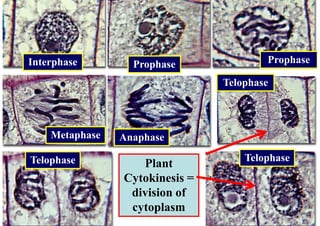
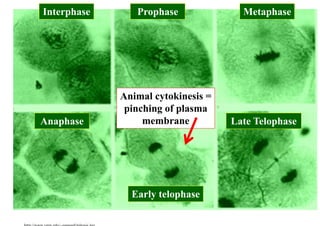
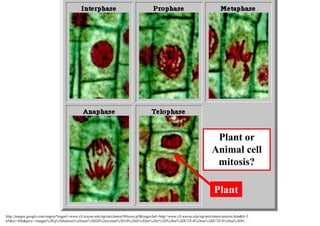
The cell cycle consists of interphase and mitosis. During interphase, the cell grows and duplicates its DNA. Mitosis is divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase where the duplicated chromosomes separate and two identical daughter cells form through cytokinesis. In plant cells, cytokinesis involves cell plate formation while in animal cells it involves cleavage furrow invagination.