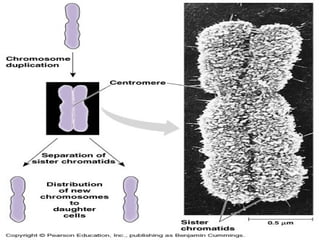
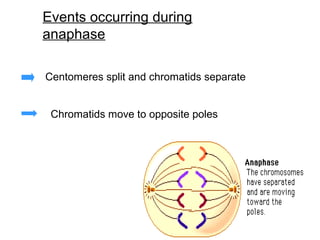
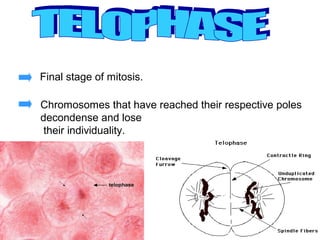
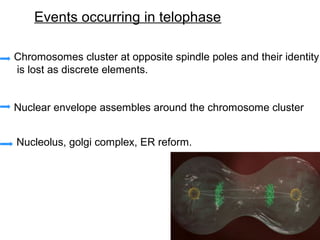
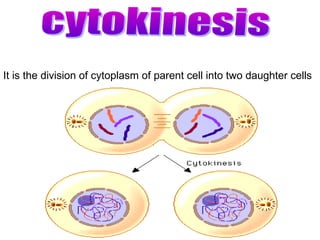
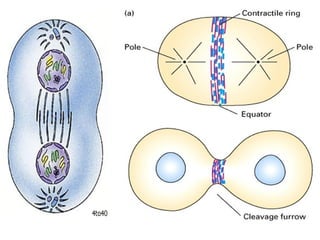
The document summarizes the key events of mitosis and cytokinesis. It describes how sister chromatids separate during anaphase and move towards opposite poles. During telophase, chromosomes decondense and nuclear envelopes reform. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm, with animal cells forming a cleavage furrow and plant cells forming a cell plate. Mitosis and cytokinesis are important for growth, repair, and development in multicellular organisms.