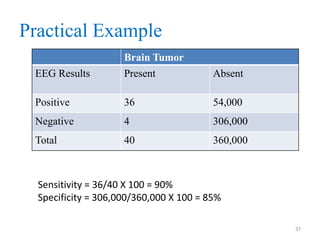
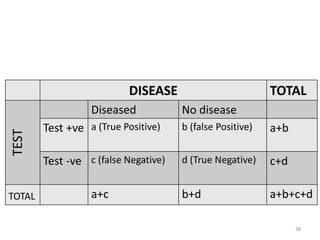
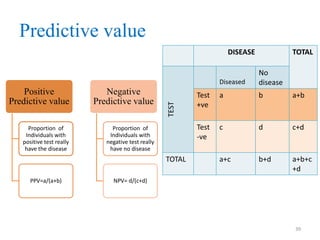
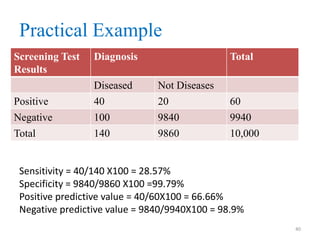
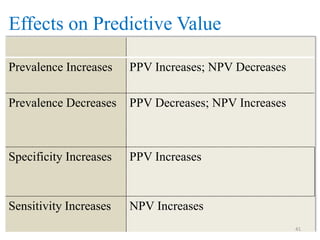
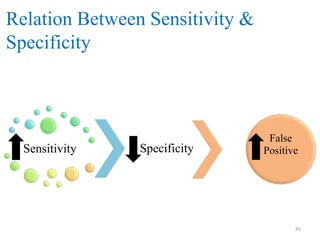
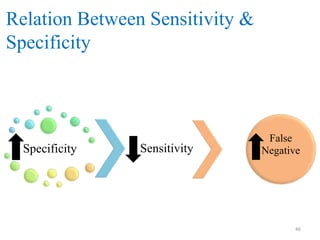
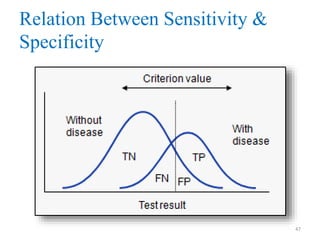
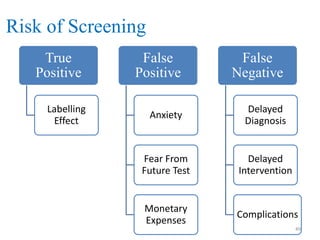
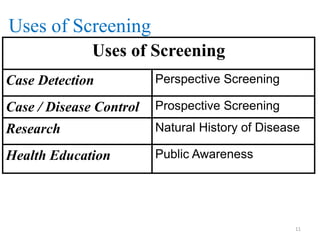
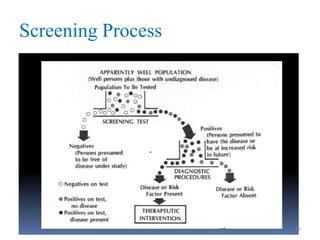
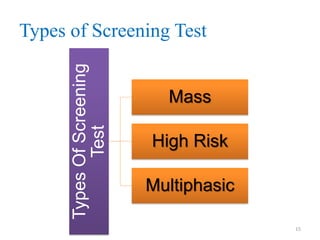
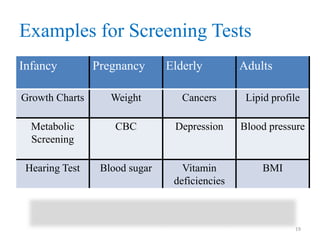
Screening tests are used to detect disease or risk of disease in asymptomatic individuals. They differ from diagnostic tests in that they are used on large populations rather than single individuals, are less accurate, and are not conclusive. The main purposes of screening are to reduce disease burden and identify high-risk groups. Successful screening programs require diseases that are a high public health concern, reliable and acceptable tests, and availability of appropriate treatment. Sensitivity measures the test's ability to correctly identify those with disease, while specificity measures its ability to correctly identify those without disease. Risks of screening include false positives which can cause anxiety, and false negatives which can delay diagnosis and treatment.



















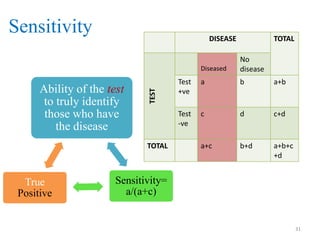
![Sensitivity
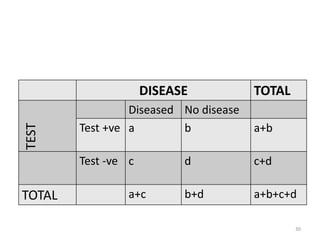
[[A 90% Sensitivity means that 90% of the diseased
people screened by the test will give a “true
positive” and the remaining 10% a “false negative
results”]]
Positive test
and have the
disease.
Negative test
and have the
disease.
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/screening-140217071714-phpapp02/85/Screening-32-320.jpg)
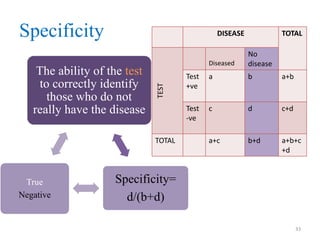
![Specificity
[[A 90% Specificity means that 90% of the non
diseased people screened by the test will give a “true
negative” result, and the remaining 10% a “false
negative results”]]
Negative test and do
not have the disease.
Negative test and have the
disease.
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/screening-140217071714-phpapp02/85/Screening-34-320.jpg)