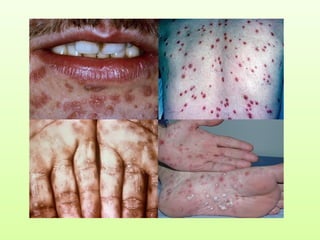
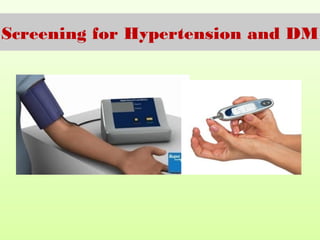
This document discusses different types of screening. It defines screening as searching for unrecognized disease through tests on apparently healthy people. The main types discussed are:
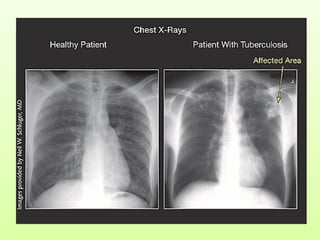
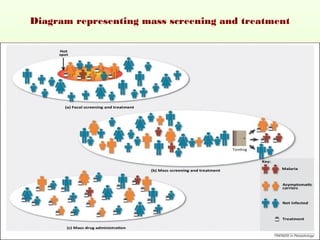
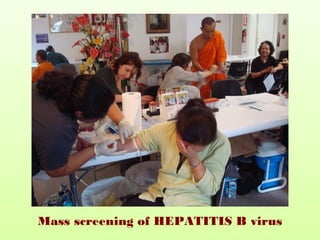
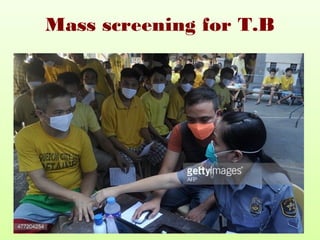
1. Mass screening tests entire populations, like tuberculosis screening, regardless of risk. It finds hidden diseases for treatment but not prevention.
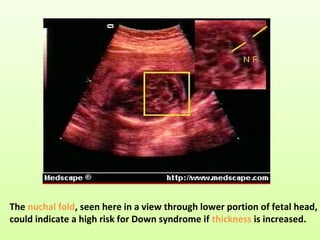
2. High-risk screening selectively tests groups at higher risk, like screening babies if a family has Down's syndrome.
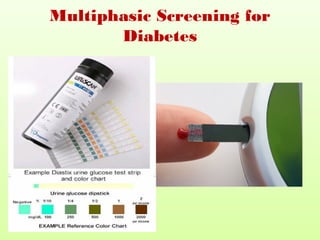
3. Multiphasic screening uses multiple tests on many people at once, combining tests, exams, and measurements to screen for several diseases simultaneously.
4. Multipurpose screening screens populations for more than one disease using multiple tests at the same time, like screening pregnant women for several