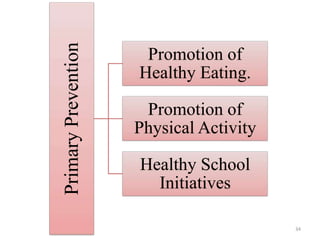
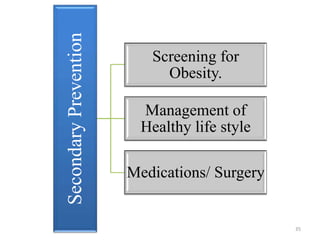
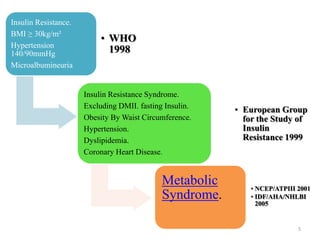
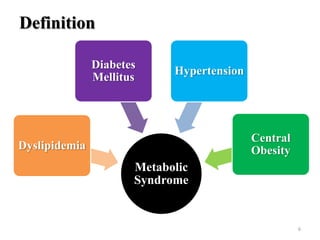
This document discusses metabolic syndrome, including its history, criteria for diagnosis, epidemiology, risk factors, complications, etiology, and prevention. Metabolic syndrome is defined as a cluster of conditions that occur together, including increased blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome is high worldwide and increasing, with risk factors including older age, female gender, obesity, physical inactivity, and genetic factors. Complications of metabolic syndrome include increased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and mortality. Prevention focuses on lifestyle changes like healthy diet, exercise, and weight management.






![Epidemiology
International Burden
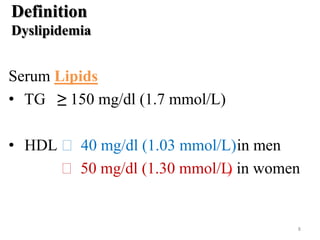
• U.S. prevalence adults (22% - 34.6%) [IDF 2006]
• Sweden prevalence (24% m &19% f)[IDF 2007]
• India prevalence of (19.52%) [ATPIII 2010]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicsyndrome-131214133156-phpapp01/85/Metabolic-syndrome-in-Community-Medicine-12-320.jpg)
![Epidemiology
Regional Burden
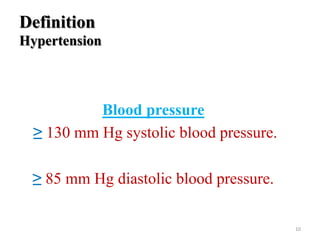
• Turkey 33.9% (28% m & 39.6% f) [ATP III/ 2007]
• Iranian (34.7%m &37.4%f) [ ATPII, IDF/ 2007]
• Tunisia (24.3%m, 45.5%f) [ ATPIII, IDF/2007]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicsyndrome-131214133156-phpapp01/85/Metabolic-syndrome-in-Community-Medicine-13-320.jpg)
![Epidemiology
Regional Burden
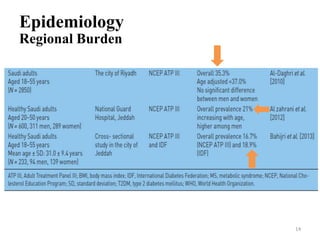
• Jordan 37.4% (31.7% m & 41.0% f)[ATPIII/ 2007]
• Oman 21.0% [ATPIII/ 2003]
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicsyndrome-131214133156-phpapp01/85/Metabolic-syndrome-in-Community-Medicine-15-320.jpg)

![Epidemiology
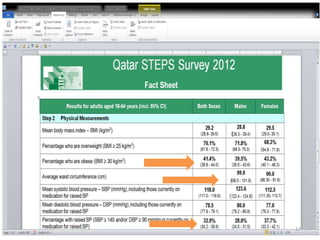
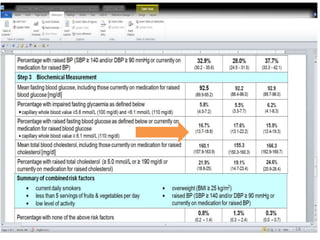
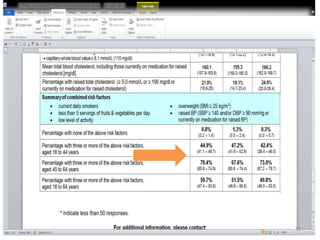
Situation in Qatar
• Overall prevalence of
among obese patients was
46.3%.
• [IDF/ 2010]
• The prevalence was higher
in females (50%) than in
males (42.4%).
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicsyndrome-131214133156-phpapp01/85/Metabolic-syndrome-in-Community-Medicine-20-320.jpg)