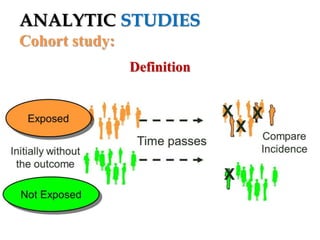
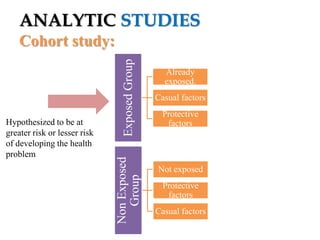
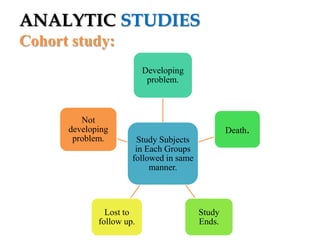
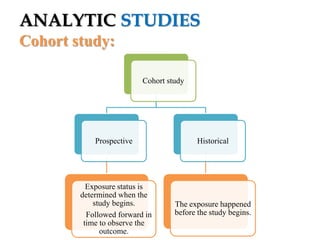
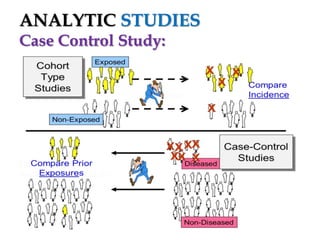
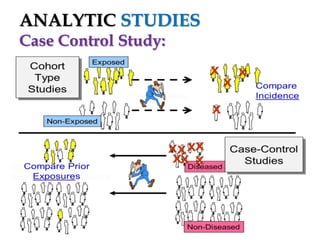
The document provides an overview of analytic studies in epidemiology, focusing on cohort and case-control study designs. Cohort studies follow two groups (exposed and non-exposed) over time to assess health outcomes, while case-control studies compare groups with and without outcomes to analyze past exposures. Each study design has its advantages and disadvantages related to data collection, cost, time, and potential biases.